Embed presentation
Downloaded 57 times






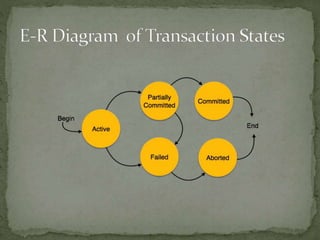


Transactions can be in one of several states to handle failures and ensure consistency. The states are active while executing, partially committed once enough information is written to disk for recovery, committed if fully completed, and aborted if rolled back with the database restored to its prior state. States can transition from active to either committed or aborted, with partially committed as an intermediate step, to ensure transactions can be recovered or undone following a failure.







