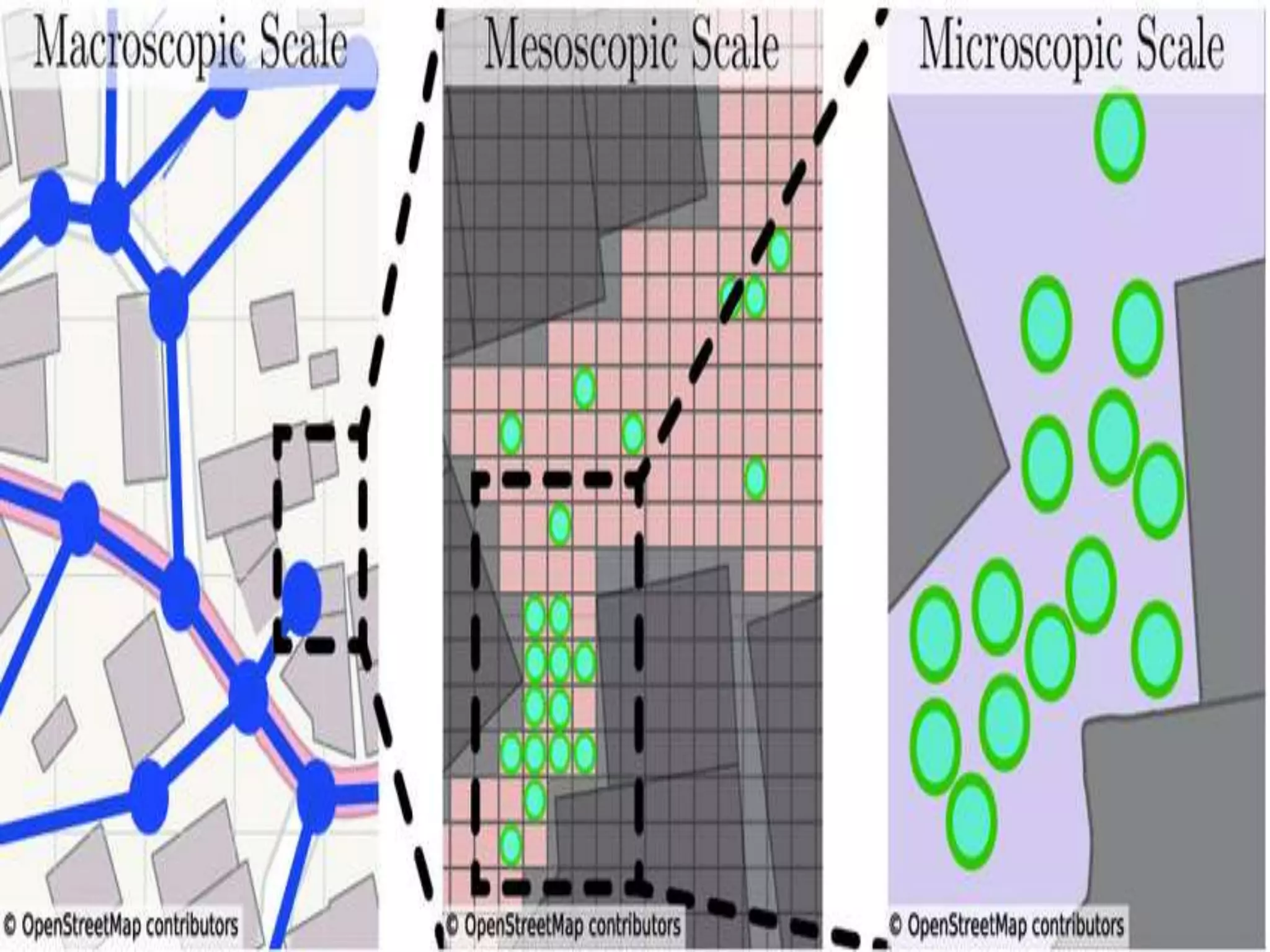
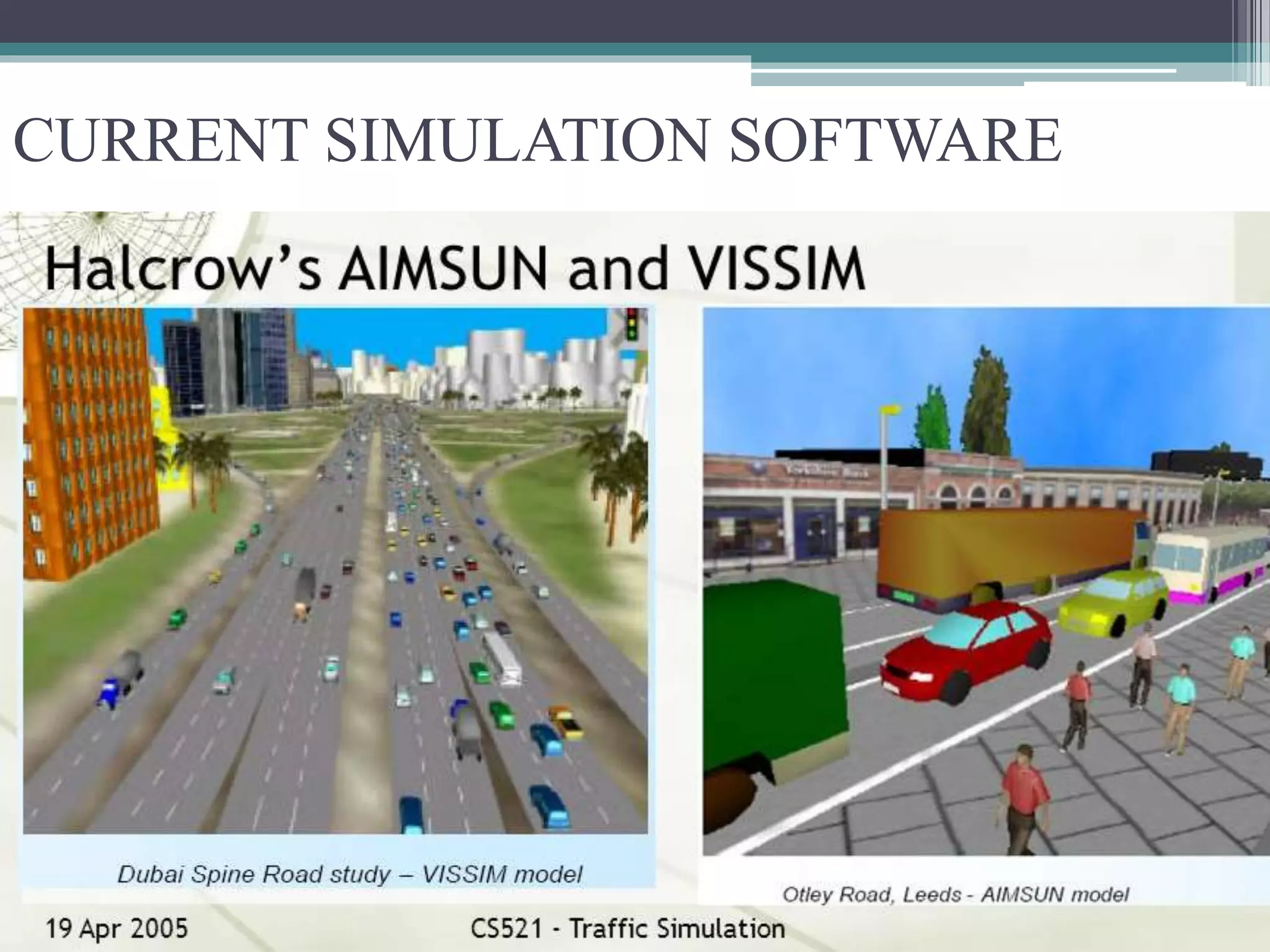
This document discusses traffic simulation and modelling. It covers different types of traffic models including microscopic, mesoscopic, and macroscopic models. Microscopic models track individual vehicles, macroscopic models aggregate traffic flow data, and mesoscopic models have aspects of both. Simulation models are presented as an alternative to analytical models which require extensive field data collection. The advantages of simulation include being cheaper than field studies and allowing testing of alternative strategies. Current traffic simulation software can model traffic flow at different scales.