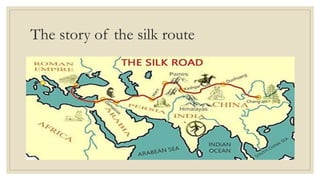
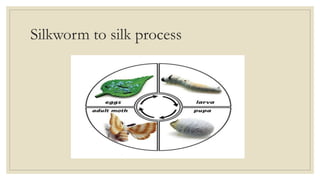
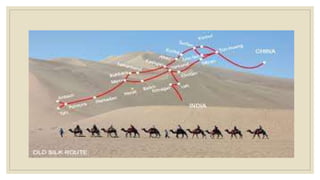
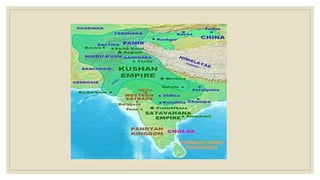
The document discusses trade and kingdoms in South India during ancient times. Three main kingdoms - the Cholas, Cheras, and Pandyas - controlled coastal areas to facilitate international trade. Each kingdom had two centers of power, one inland and one on the coast. Kings received gifts rather than taxes and funded their rule through military expeditions and tribute. Sangam poets composed poems that honored these kings in exchange for rewards. The document also briefly discusses the Satavahanas dynasty in western India and the Silk Route connecting China to West Asia and Europe.