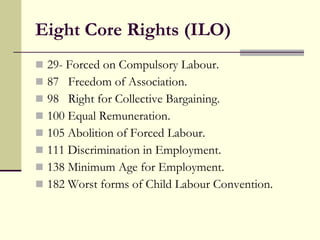
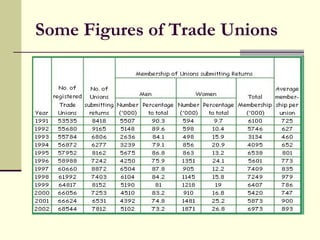
Trade unions in India were formed to protect and promote the interests of workers by representing them, negotiating on their behalf, and giving them a voice in important decisions. Their key functions include collective bargaining for better wages and working conditions, and providing various services to members. While multiple unions can exist in one industry, having too many unions can cause issues, so a single union per industry is often suggested as the ideal solution. Some of the major national trade union organizations in India are AITUC, CITU, HMS, and INTUC.