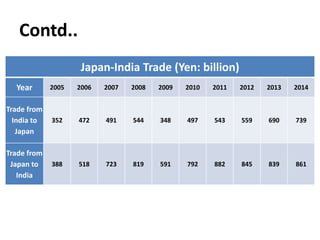
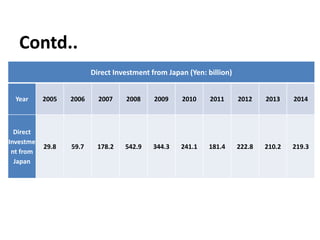
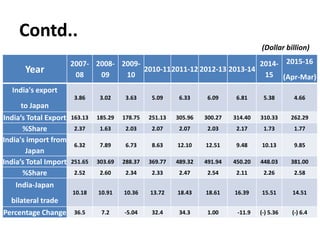
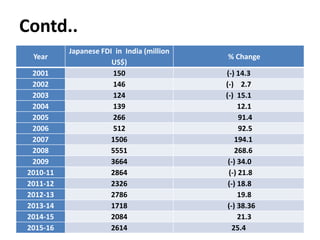
The document summarizes the trade relationship between India and Japan. It outlines that trade began in the 6th century with the introduction of Buddhism to Japan, and diplomatic relations were established in 1952. Trade has increased significantly since then, with Japan becoming India's largest aid donor. Key exports to Japan include agricultural products, iron ore, and seafood; while imports from Japan include machinery, electronics, and transport equipment. Bilateral trade reached $18.51 billion in 2014. Japan is also a major foreign investor in India.