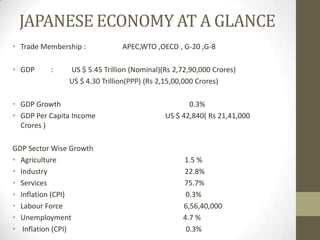
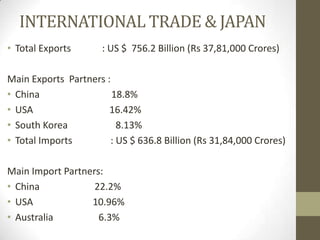
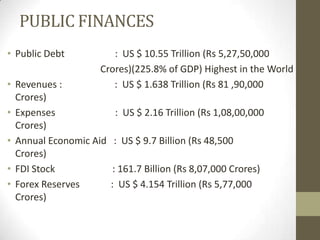
The document provides an overview of the Japanese economy. It notes that Japan has a GDP of $5.45 trillion nominal and $4.3 trillion PPP, with GDP growth of 0.3%. Services make up 75.7% of GDP. Exports total $756.2 billion with main partners being China and the US, while imports total $636.8 billion mainly from China and the US. Public debt is 225.8% of GDP, the highest in the world. Major industries are dominated by a few large conglomerates. The government plays an active role in the economy through various ministries and policies.