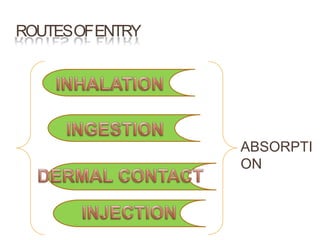
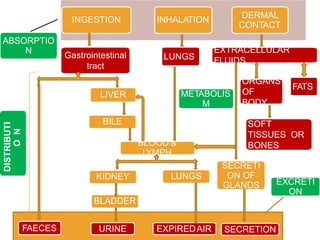
Toxicology is the study of the harmful effects of chemicals on living organisms. All substances can be toxic depending on dose, with even something essential like vitamin A becoming poisonous at high enough levels. Common routes chemicals enter the body include ingestion, inhalation, and dermal contact. Factors like dose, formulation, and individual susceptibility determine a substance's toxicity. Pesticides aim to control pests but can also harm nontarget species like humans if exposed, so their use requires minimizing risks to human and environmental health.