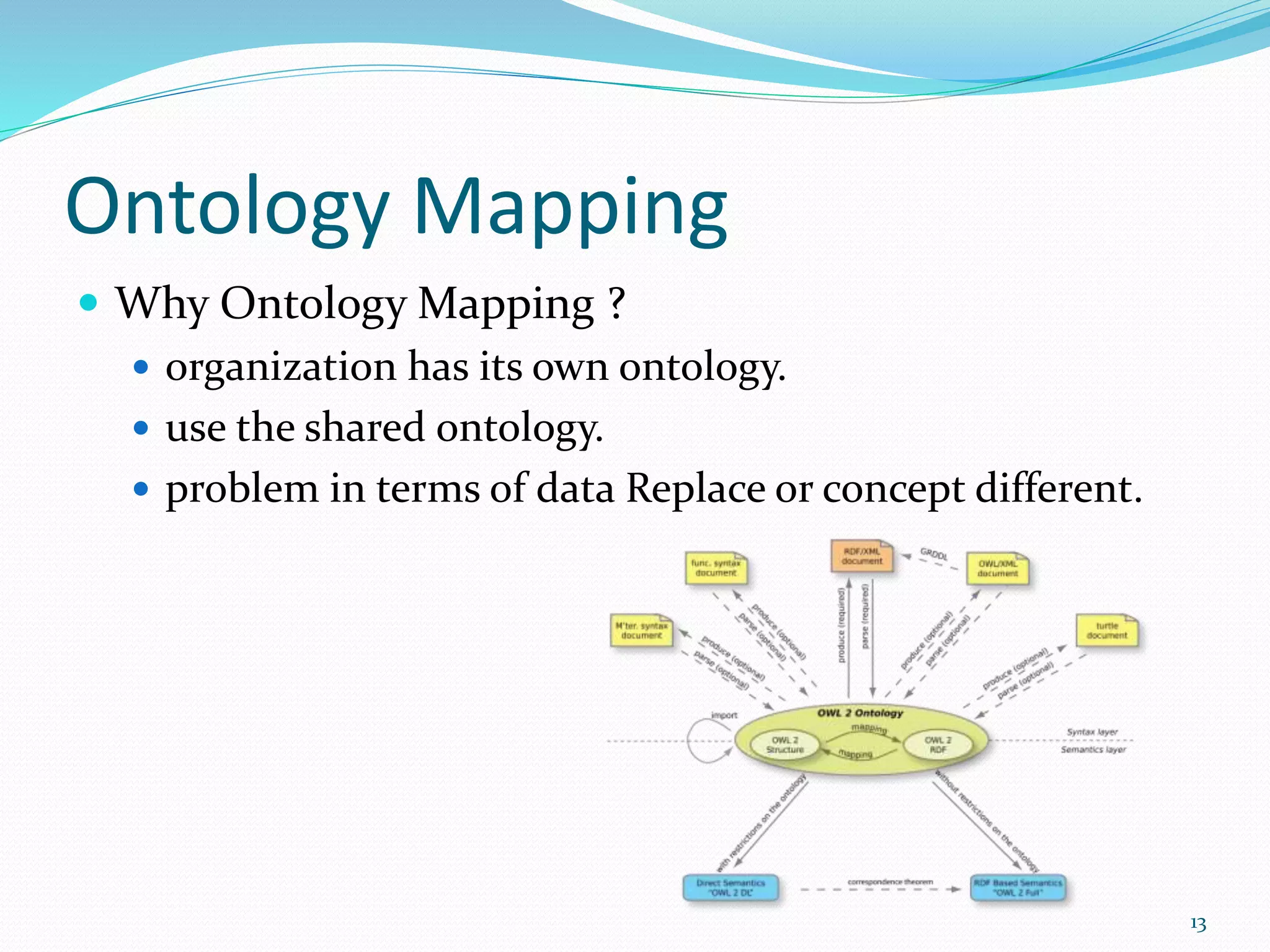
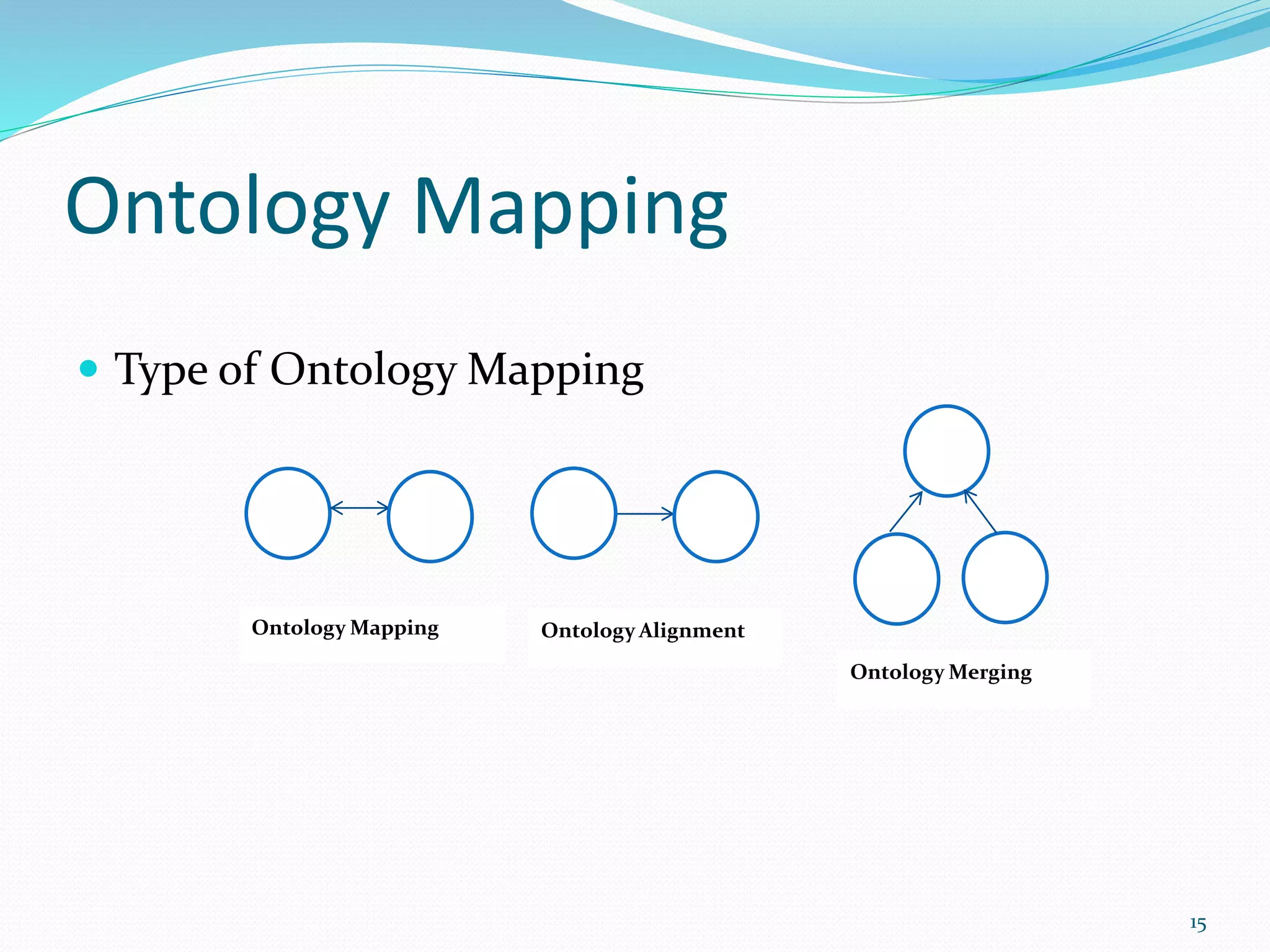
This document discusses ontology mapping. It begins with an introduction to the semantic web and ontologies. Ontology mapping is important for allowing different ontologies to be aligned and related. There are different types of ontology mapping including alignment, merging, and mapping. The document then surveys some popular ontology mapping techniques including GLUE, PROMPT, and QOM. It evaluates these techniques and discusses their inputs, outputs, and approaches. The document concludes that semantic web research is important for advancing web technologies and realizing the goals of web 3.0. Future work could involve developing new ontology mapping techniques and publishing research on existing mapping methods.











![Ontology Mapping Research
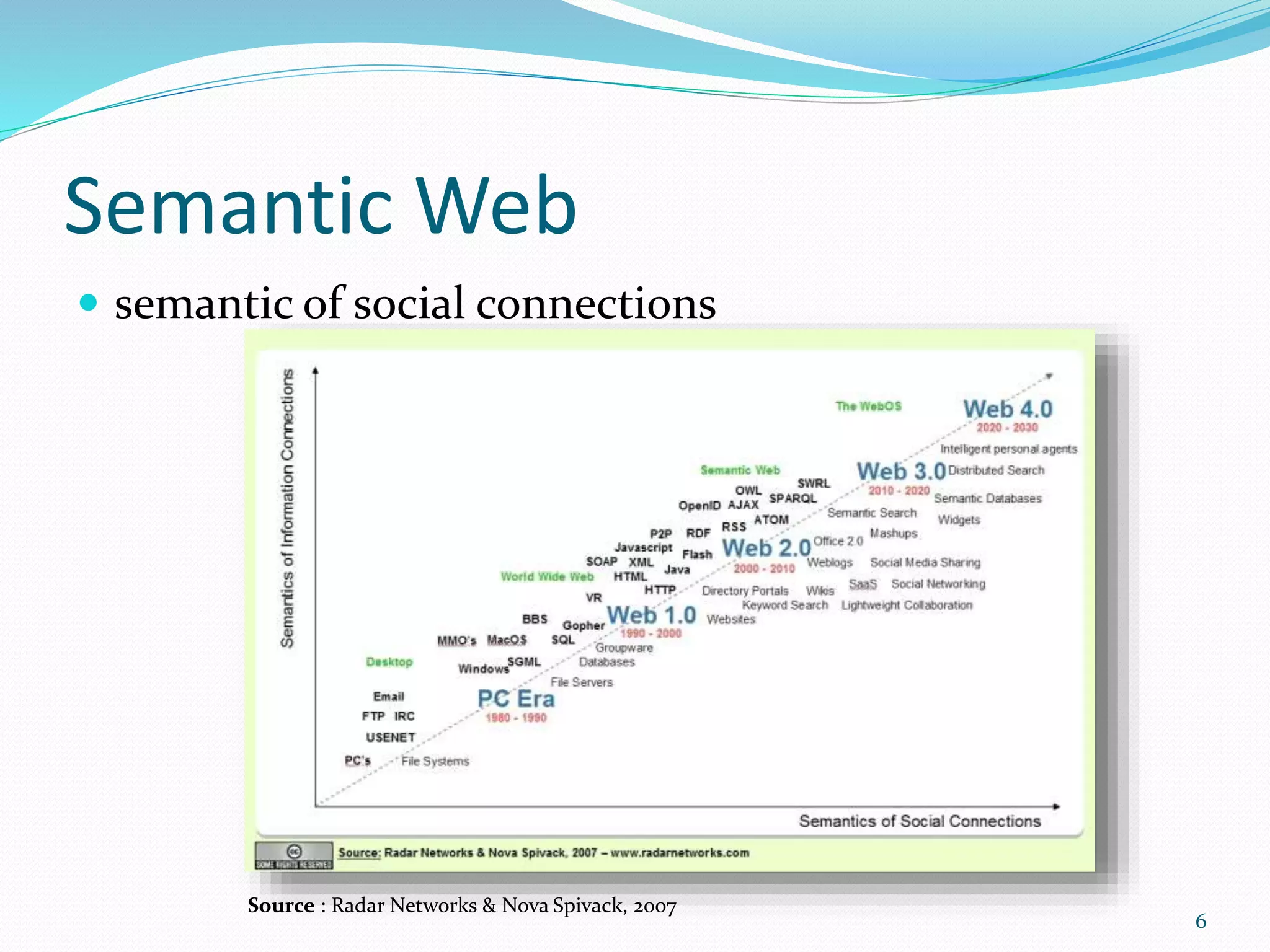
Semantic web Challenges [1]
17
A Classification of the Semantic Web Challenges](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ontologymappingforthesemanticweb-101123163133-phpapp01/75/Ontology-mapping-for-the-semantic-web-17-2048.jpg)
![Ontology Mapping Research
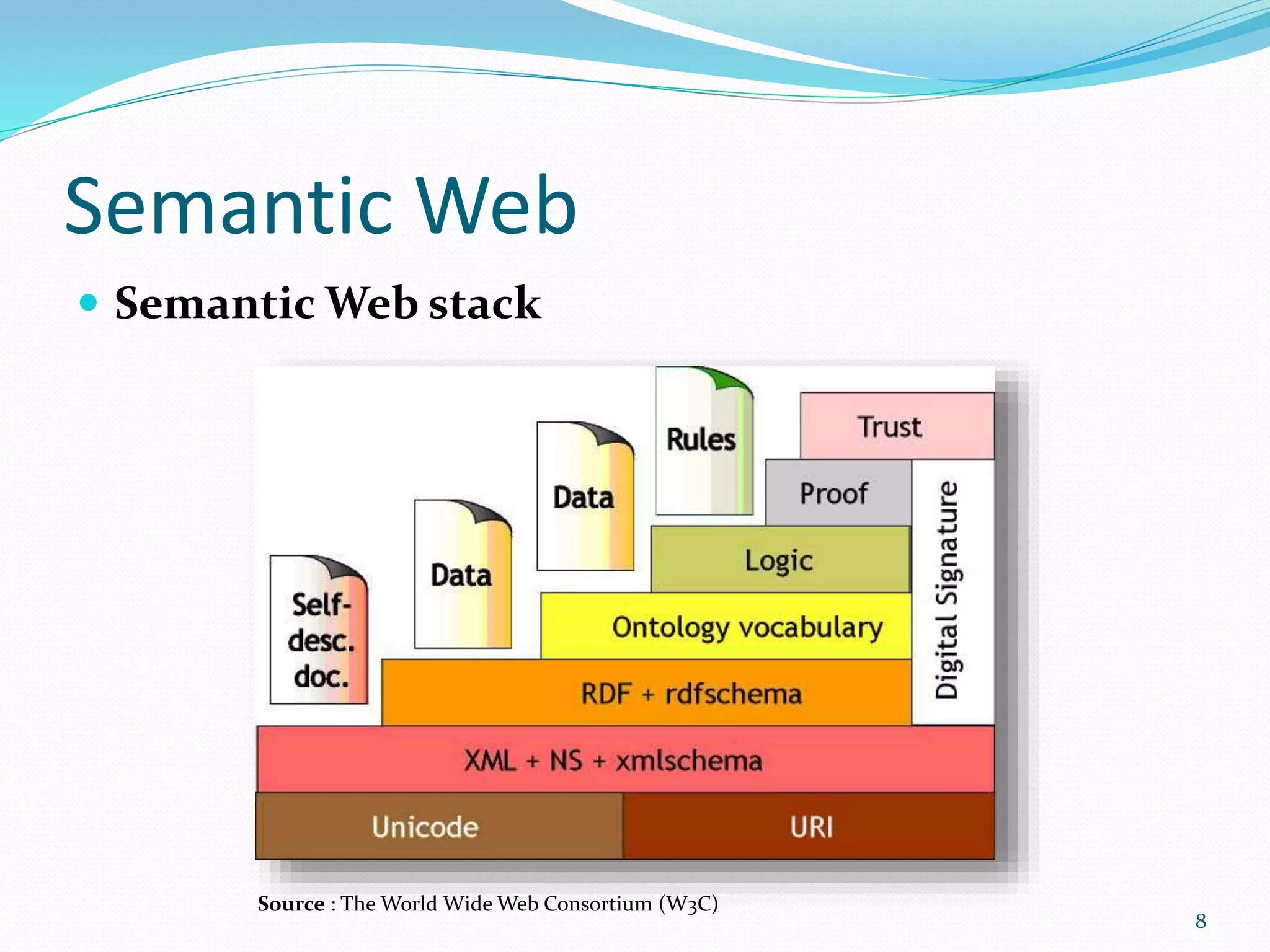
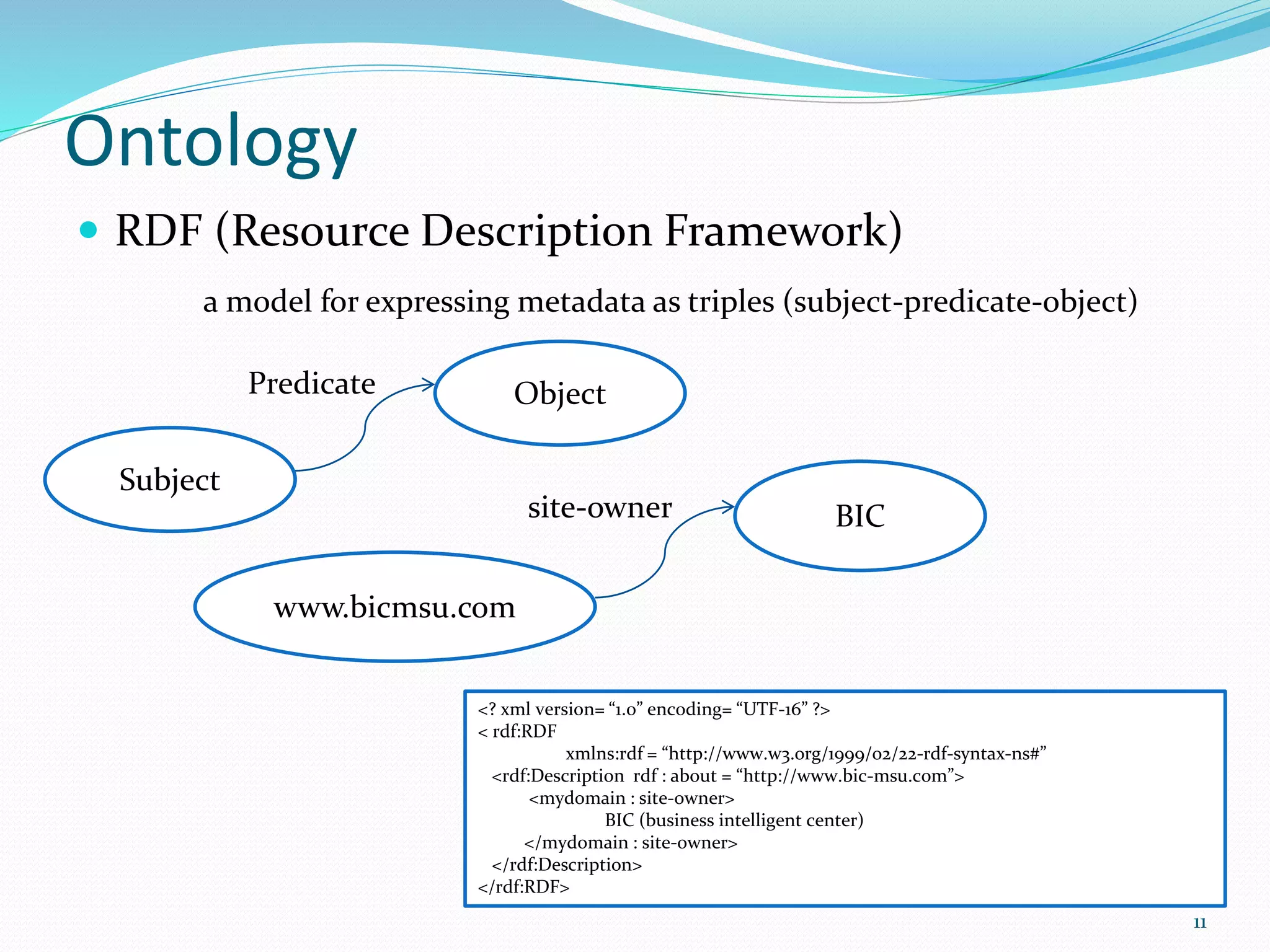
Research Classification of Ontology Mapping [2]
Mapping Discovery
Declarative formal representation of mappings
Reasoning with mappings
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ontologymappingforthesemanticweb-101123163133-phpapp01/75/Ontology-mapping-for-the-semantic-web-18-2048.jpg)

![ GLUE [3] Machine learning techniques to find mappings.
GLUE architecture consists of
Distribution Estimator
Similarity Estimator.
Relaxation Labeler
GLUE output's one to one correspondences between the
taxonomies the ontologies .
String similarity, structure and machine learning strategies.
20
Survey Ontology Mapping Techniques](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ontologymappingforthesemanticweb-101123163133-phpapp01/75/Ontology-mapping-for-the-semantic-web-20-2048.jpg)
![ PROMPT [4]
Input: Two ontology's in OWL/ OKBC
Output: Suggestions of mapping and
a merging ontology based on the choice made by the user.
iPROMPT : Interactive ontology merging tool.
AnchorPROMT : Graph-based mappings to
provide additional information for iPROMPT.
PROMPTDiff : Compares different ontology
versions by combining matchers in a fixed point manner.
PROMPTFactor : Tool for extracting a part of an ontology.
21
Survey Ontology Mapping Techniques](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ontologymappingforthesemanticweb-101123163133-phpapp01/75/Ontology-mapping-for-the-semantic-web-21-2048.jpg)
![ QOM [5]
String similarity, structure and instances.
Input : Two OWL or RDFS ontology's with elements (e.g., classes, properties,
instances) in the ontology's
Output: One-to-one or one-to-none correspondences.
22
Survey Ontology Mapping Techniques](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ontologymappingforthesemanticweb-101123163133-phpapp01/75/Ontology-mapping-for-the-semantic-web-22-2048.jpg)


![References
[1] Keyvanpour M, Hassanzadeh H, Mohammadizadeh B. "Comparative
Classification of Semantic Web Challenges and Data Mining Techniques". Web
Information Systems and Mining, 2009. Shanghai 2009. 200-203.
[2] - N. Noy. Semantic Integration: A Survey of Ontology-based Approaches. Sigmond
Record, Special Issue on Semantic Integration. 2004
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ontologymappingforthesemanticweb-101123163133-phpapp01/75/Ontology-mapping-for-the-semantic-web-25-2048.jpg)
