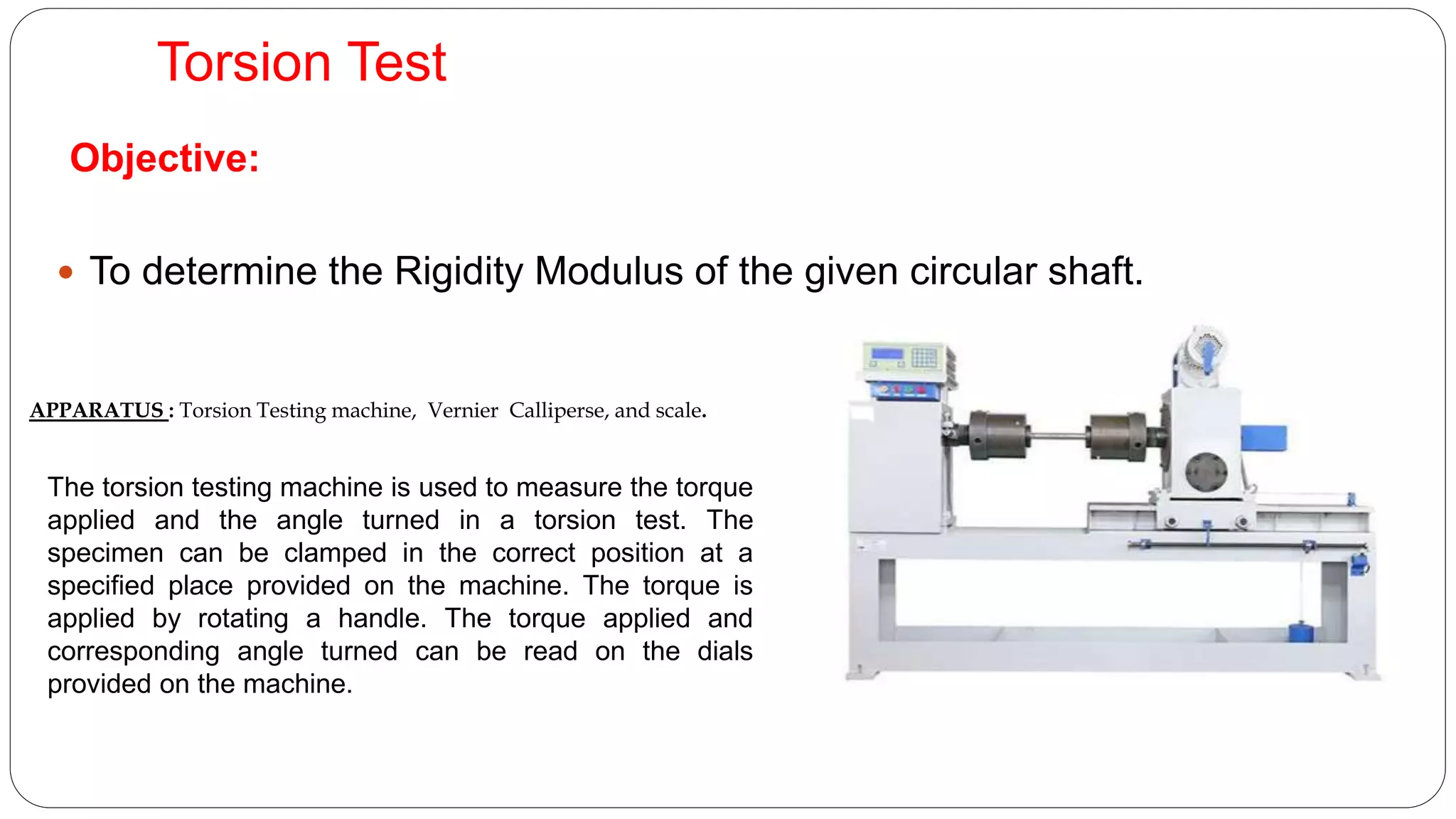
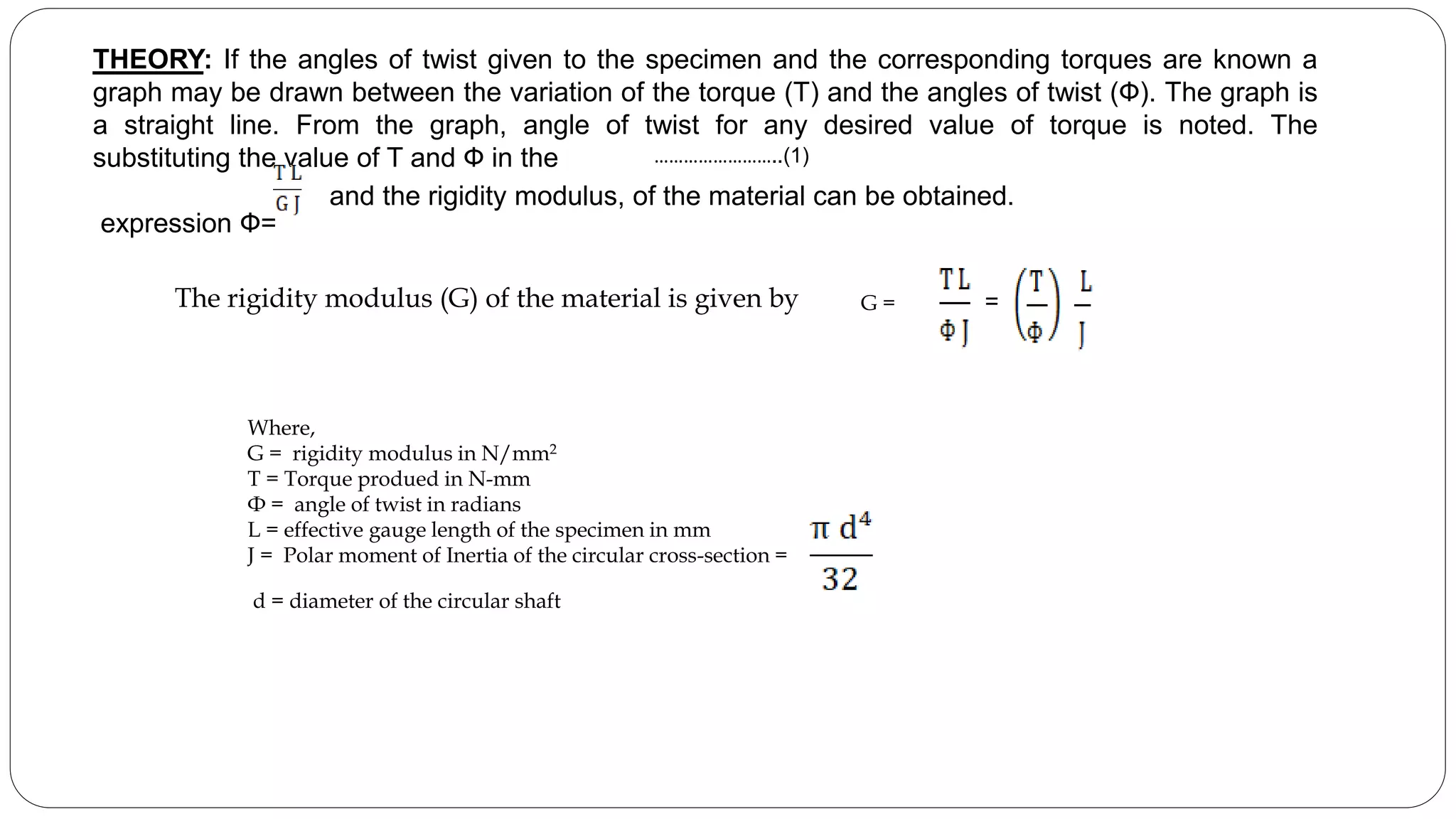
The document describes conducting a torsion test to determine the rigidity modulus of a circular shaft specimen. It details the process which includes: clamping the specimen in a torsion testing machine, applying increasing torque to induce twist, measuring the corresponding torque and angle of twist values, plotting a graph of torque versus twist angle, and using the slope to calculate the rigidity modulus formula. The objectives, apparatus used, theory, procedure, observations recorded during testing, calculations, and final result are provided.