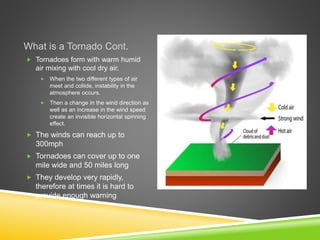
Tornadoes form when warm, humid air collides with cool, dry air, causing instability in the atmosphere and a spinning wind. They appear as a funnel-shaped cloud that can be over a mile wide and 50 miles long, with winds reaching 300 mph. Tornadoes most commonly occur in the central US between March and May. While they can cause significant damage and an average of 80 deaths per year in the US, building giant walls may help reduce but not eliminate tornadoes in high-risk areas, though the project would be very costly.