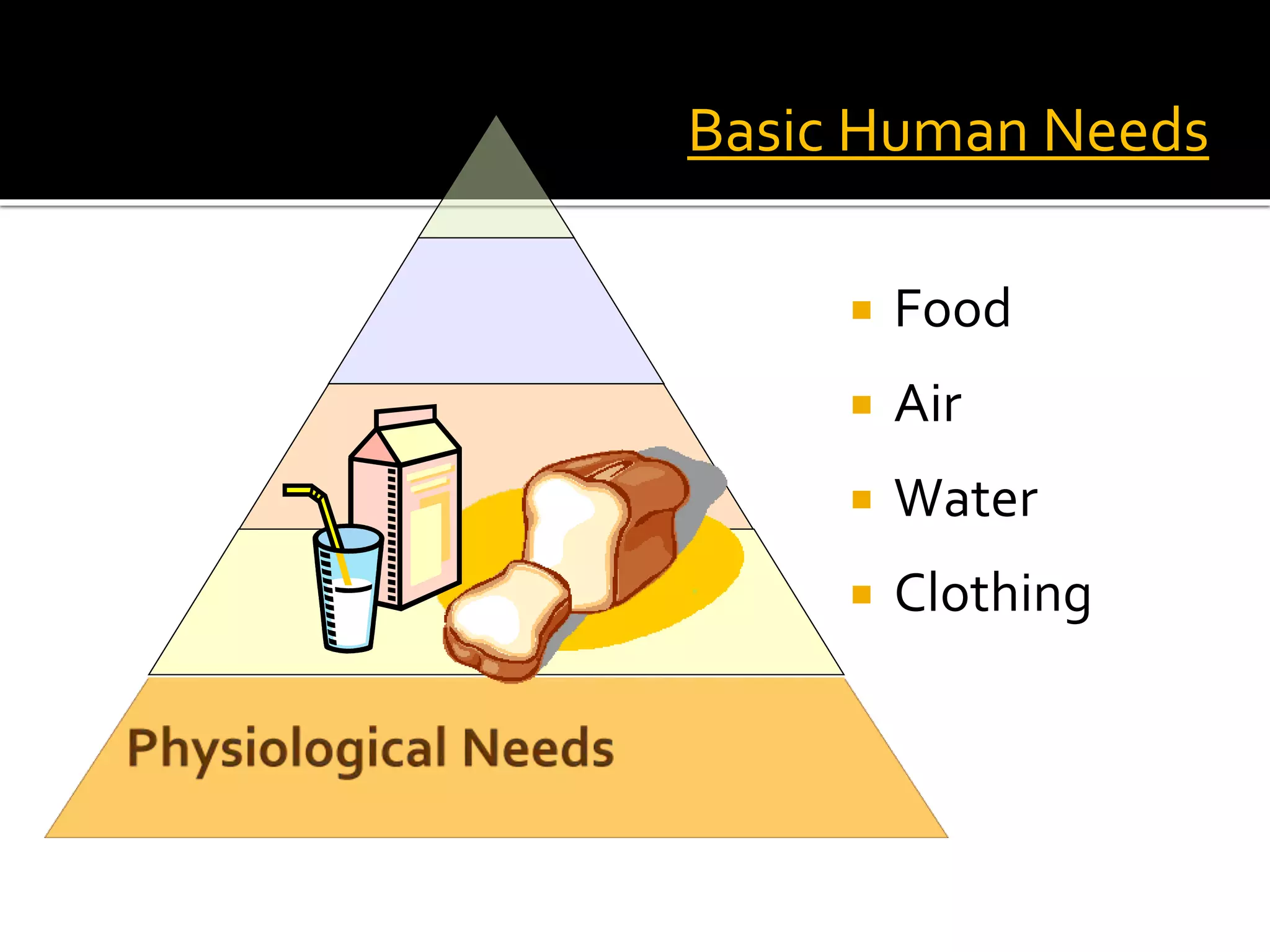
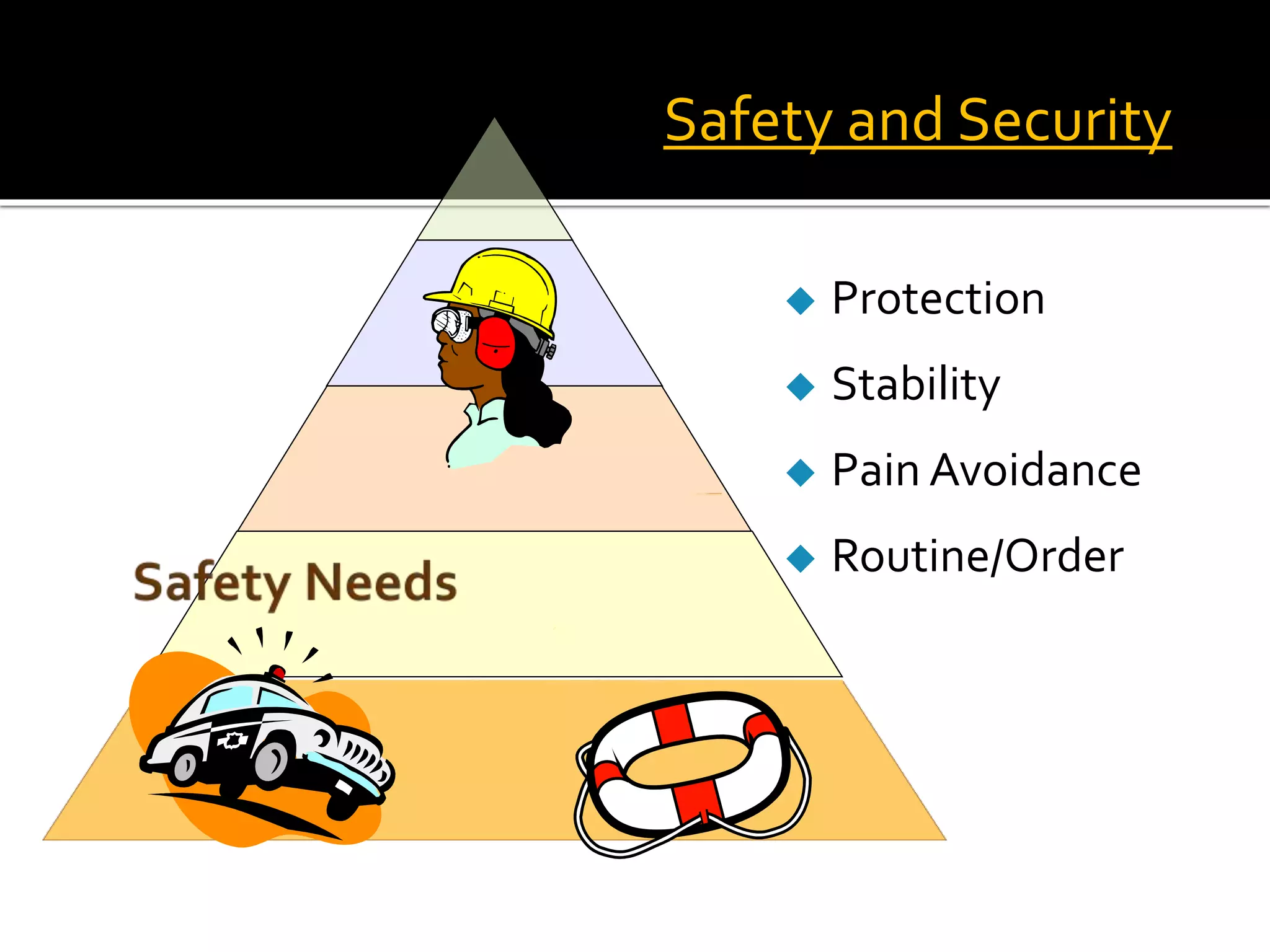
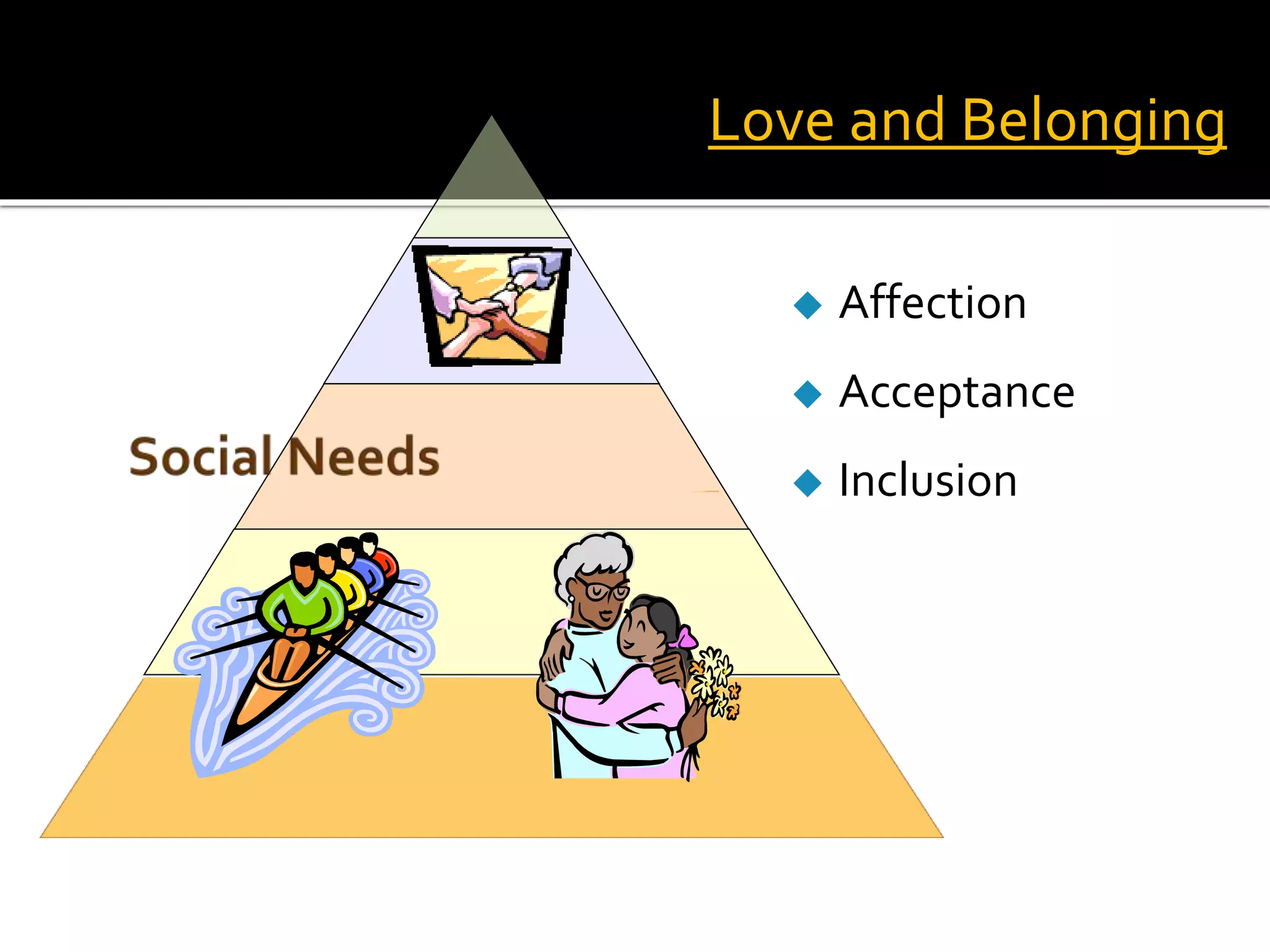
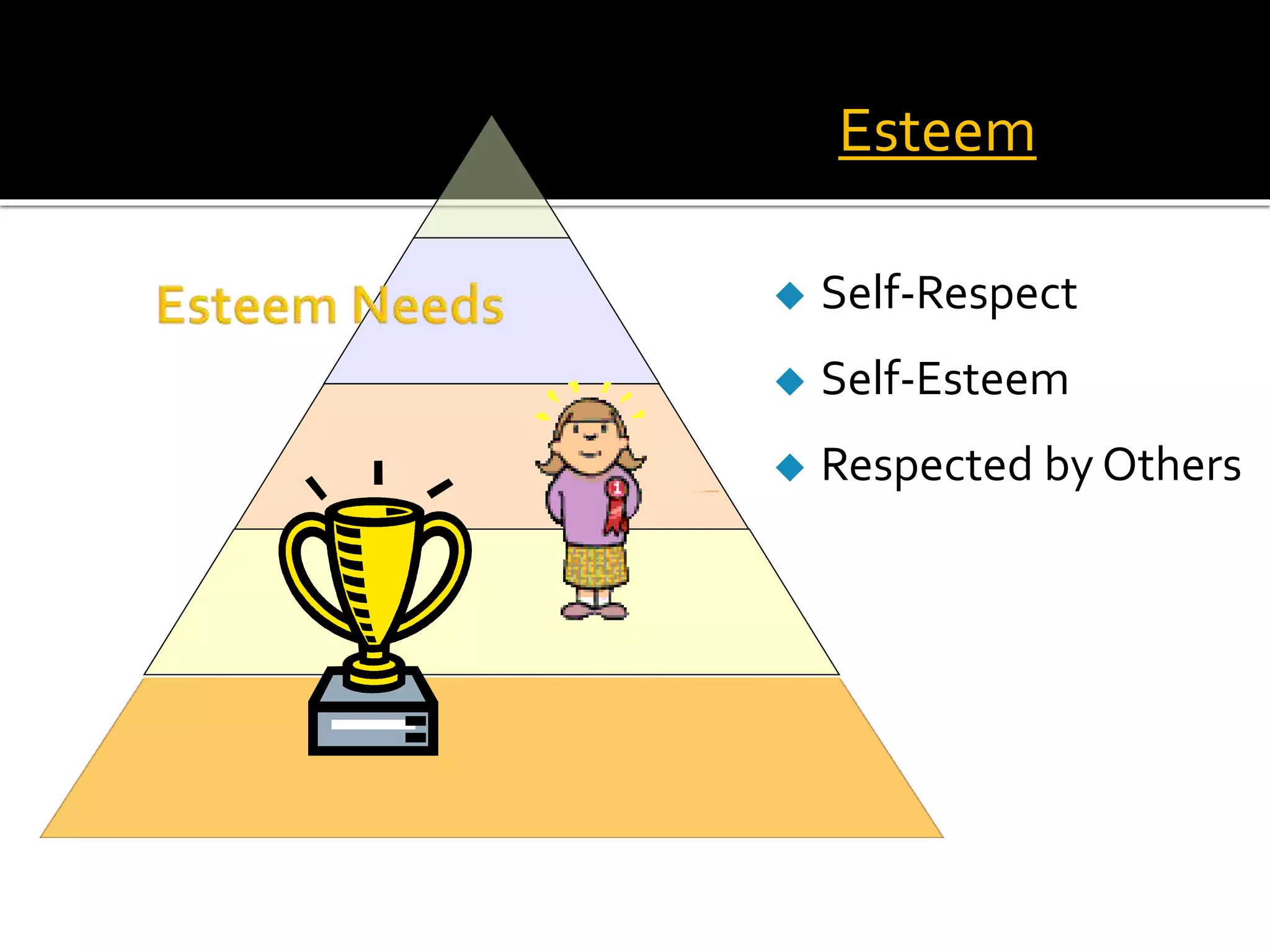
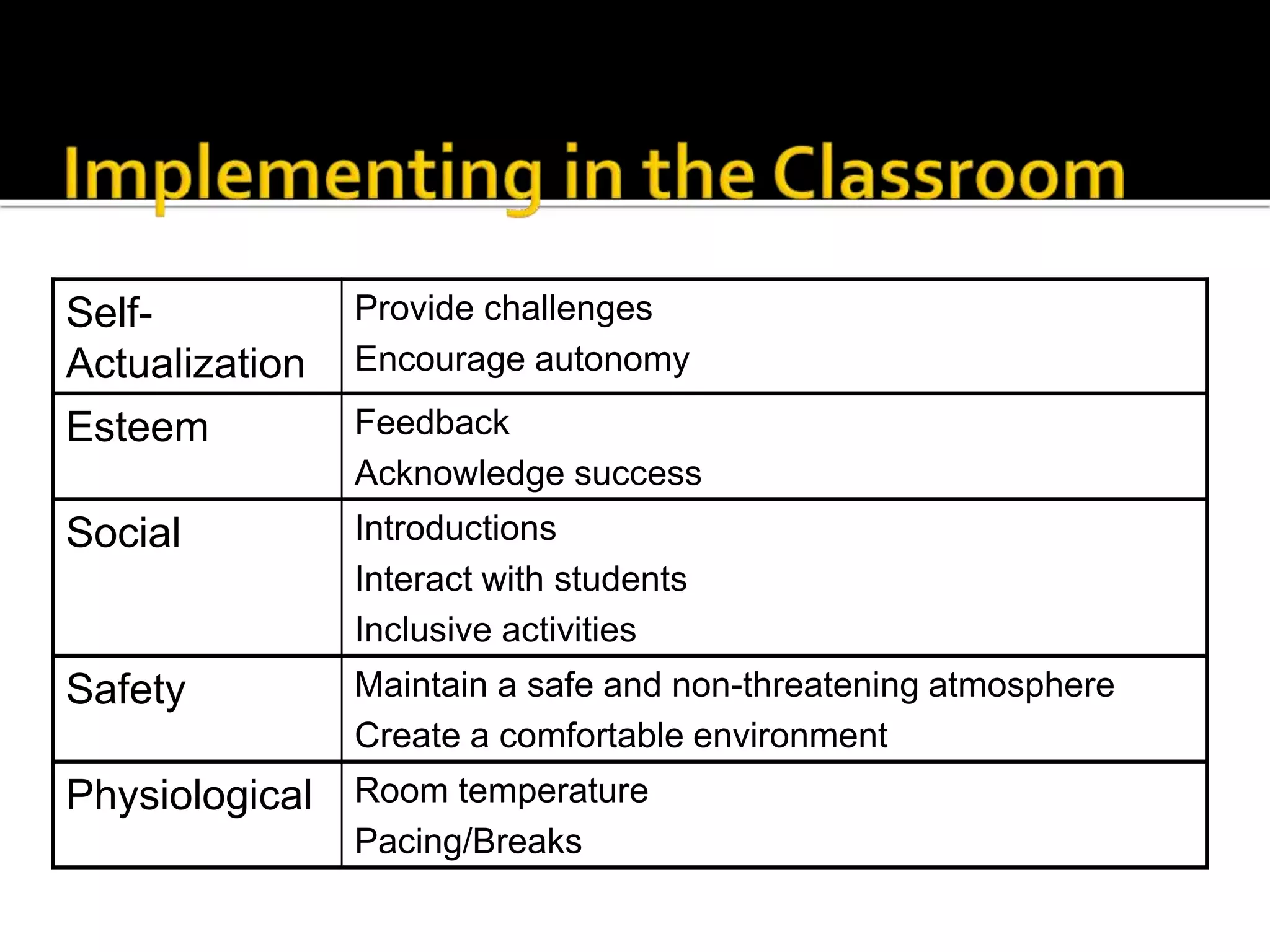
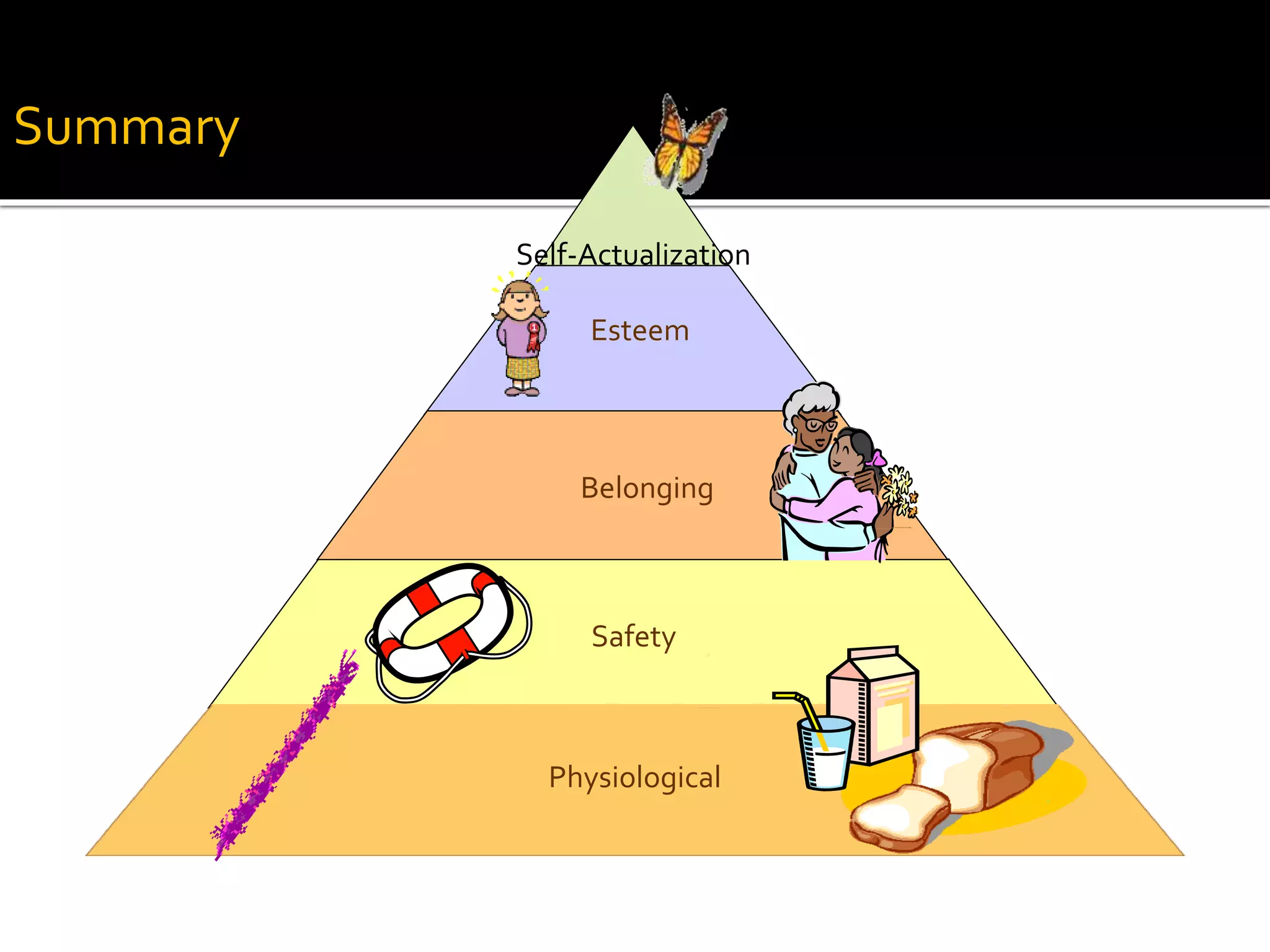
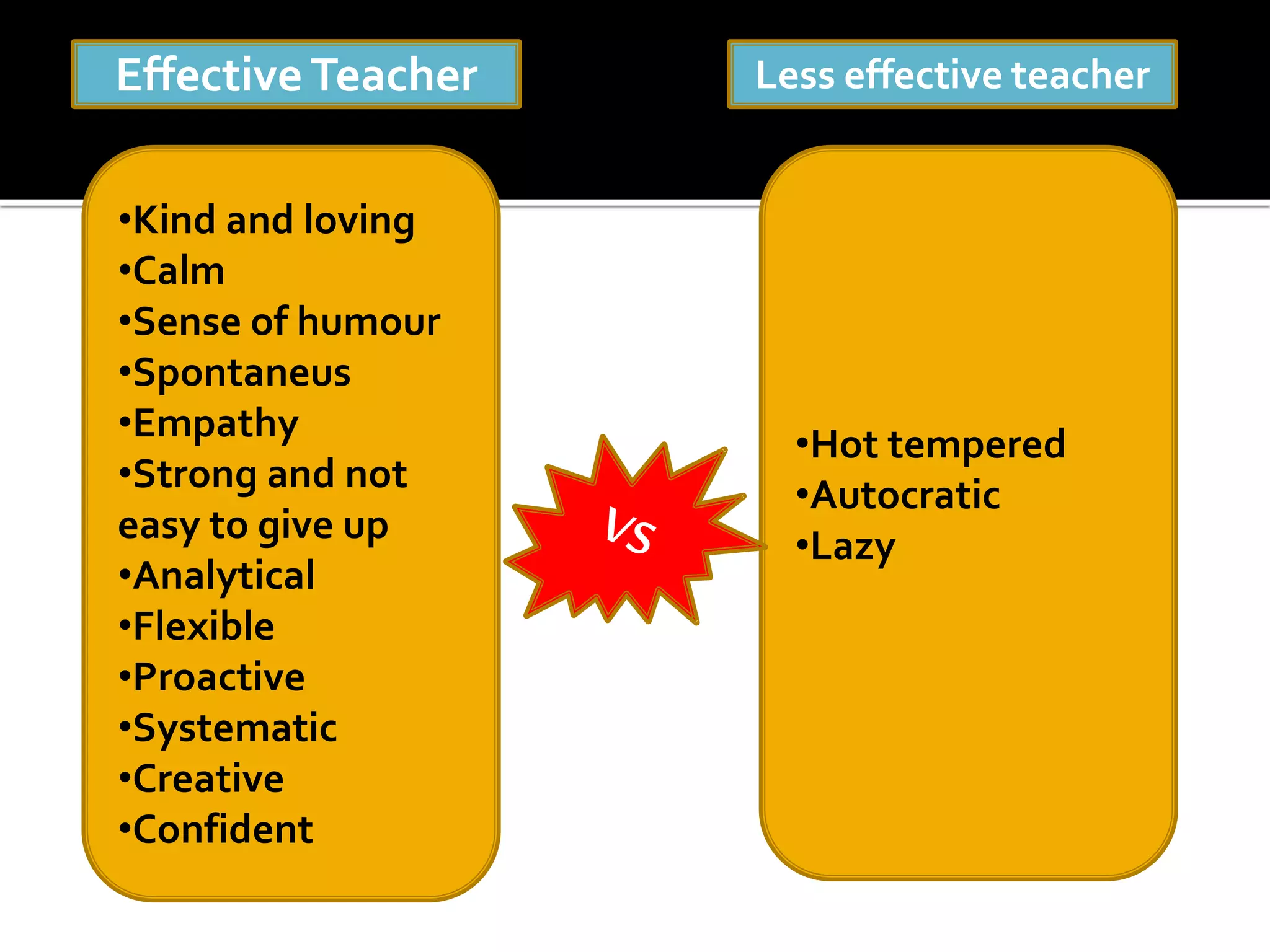
Classroom management involves establishing procedures, rules, and reducing discipline problems. Effective classroom management includes monitoring student behavior, responding appropriately to issues, and maintaining a positive environment. It is the teacher's responsibility to meet students' basic needs for safety, belonging, and self-esteem through inclusive lessons, feedback, and a comfortable classroom. Proactive teaching that addresses problems immediately and models positive behaviors can help motivate students to learn.