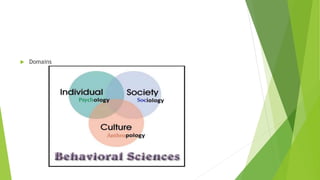
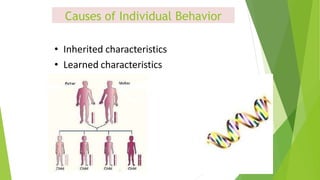
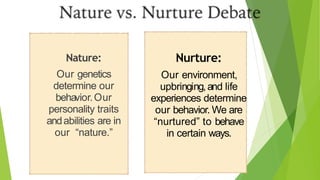
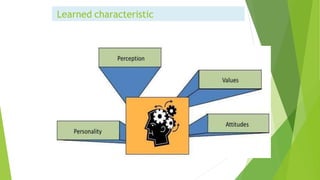
Behavioral science, encompassing psychology, sociology, and anthropology, studies human behavior as a response to various stimuli. It explores the nature versus nurture debate, examining how genetics and environment influence personality traits and behaviors. Attitudes and values, shaped by upbringing and cultural context, also play a crucial role in determining individual behaviors.