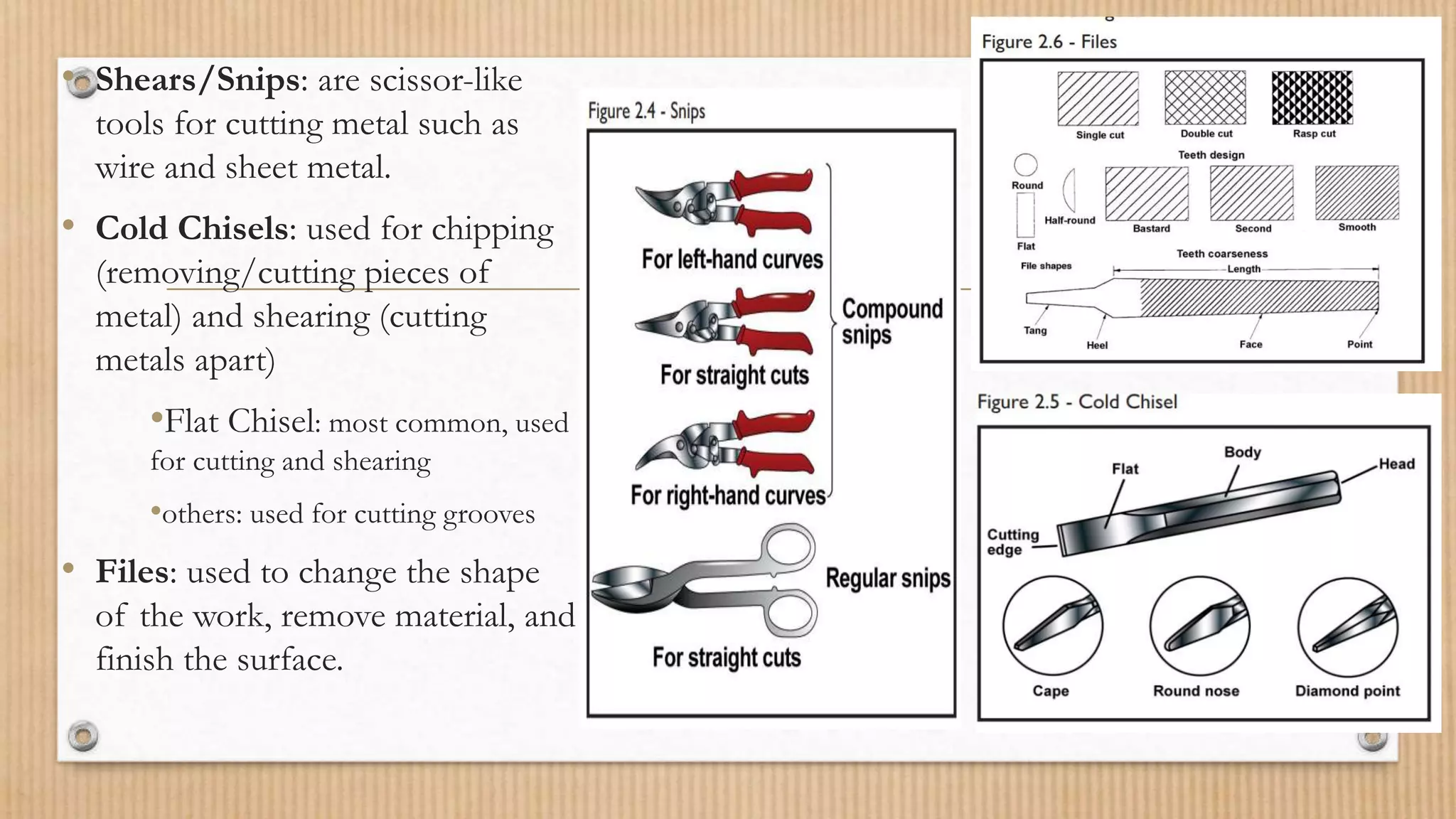
This document provides an overview of common hand tools used for woodworking, metalworking, and crafts involving wood, metal, and bamboo materials. It describes various measurement, marking, cutting, smoothing, shaping, drilling, fastening, and power tools. Measurement tools include combinations squares, framing squares, speed squares, tape measures, and levels. Cutting tools include saws, chisels, and files. Smoothing tools include planes. Drilling tools include hand drills and braces. Fastening tools include clamps, nails, screws, and hammers.