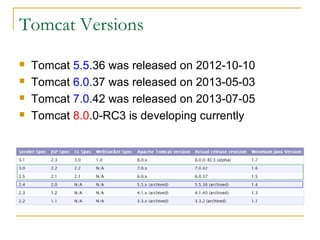
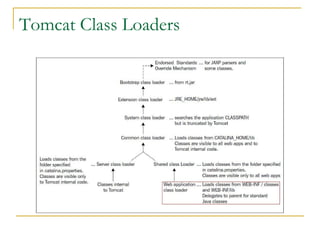
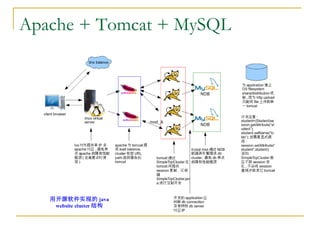
Tomcat New Evolution discusses the new features introduced in Tomcat 6 and 7. Some key highlights include:
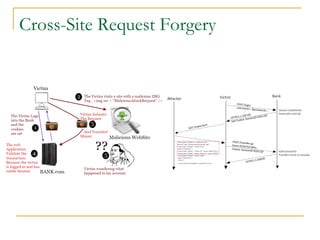
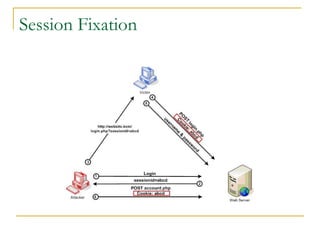
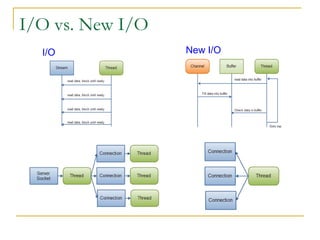
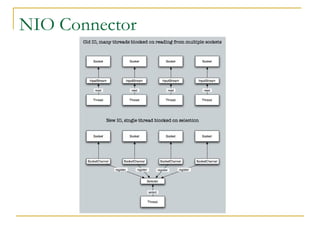
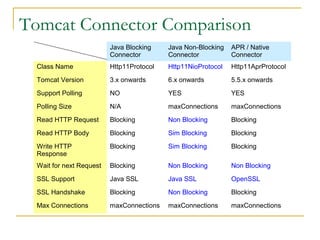
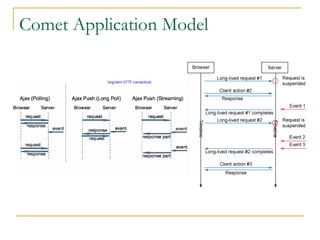
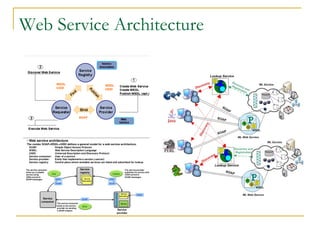
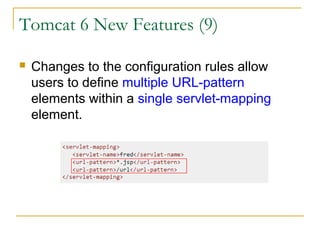
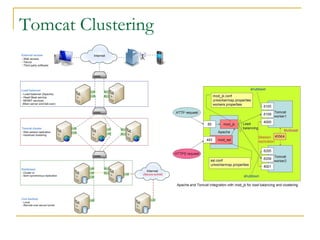
- Tomcat 6 introduced features like memory leak prevention, CSRF protection, session fixation protection, NIO connector, Comet support, logging improvements, web services support, and clustering.
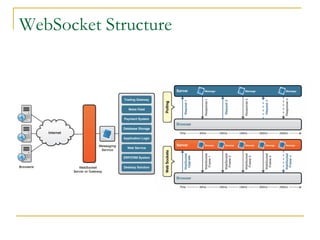
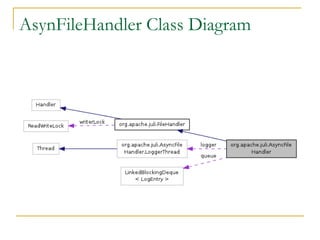
- Tomcat 7 features included externalizing static resources, WebSocket support, easier embedded usage, and asynchronous logging.
- Both versions aimed to improve performance, security, and scalability through these new capabilities. Tomcat continues evolving to support newer standards and address common issues.