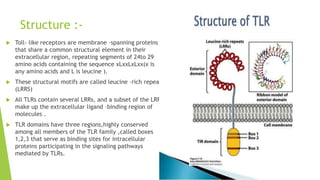
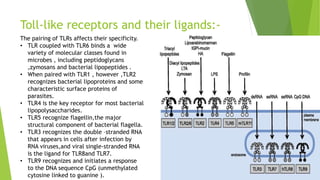
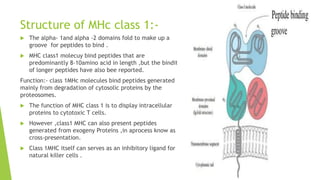
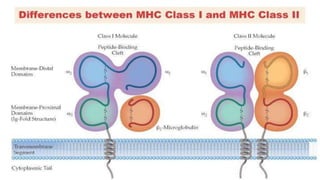
Toll-like receptors are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system by recognizing structurally conserved molecules from microbes. There are multiple Toll-like receptors that recognize different microbial components. Upon activation, Toll-like receptors recruit adaptor proteins to initiate signaling pathways that result in immune responses. The major histocompatibility complex is a set of genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. Major histocompatibility complex molecules are involved in antigen presentation and discriminating between self and non-self.