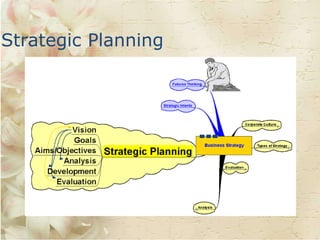
The document discusses corporate culture and strategic planning. It defines corporate culture as the beliefs and values shared by employees of an organization, which is reflected in how people behave and interact, both internally and externally. Corporate culture can be driven by an organization's vision, mission statement, and leadership. Strategic planning involves analyzing an organization's position using tools like SWOT and PEST, developing a strategy based on the vision and objectives, and constantly evaluating results to improve. Different types of strategies discussed include those focused on competitive advantage, market dominance, new product development, and global expansion.