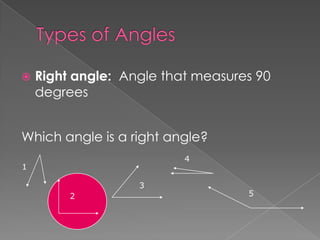
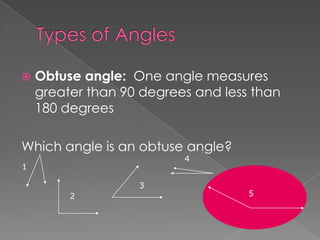
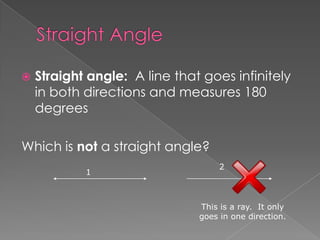
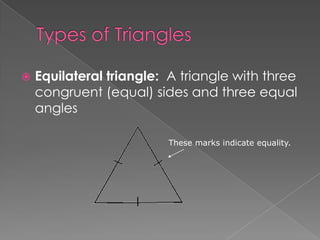
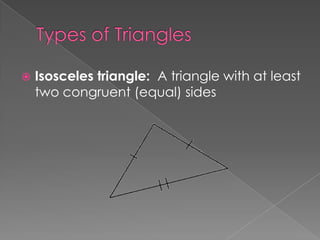
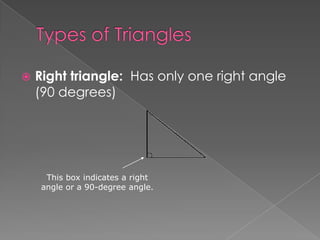
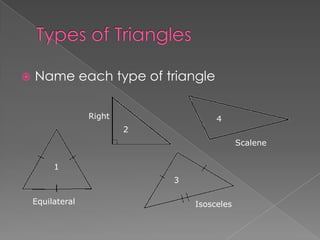
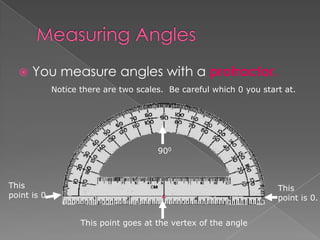
The document defines and provides examples of different types of angles (acute, right, obtuse, straight) and triangles (equilateral, isosceles, right, scalene). It explains that an angle is formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, and the interior angles of any triangle always sum to 180 degrees. Examples are given of how to identify, measure, and name different angles and triangles.