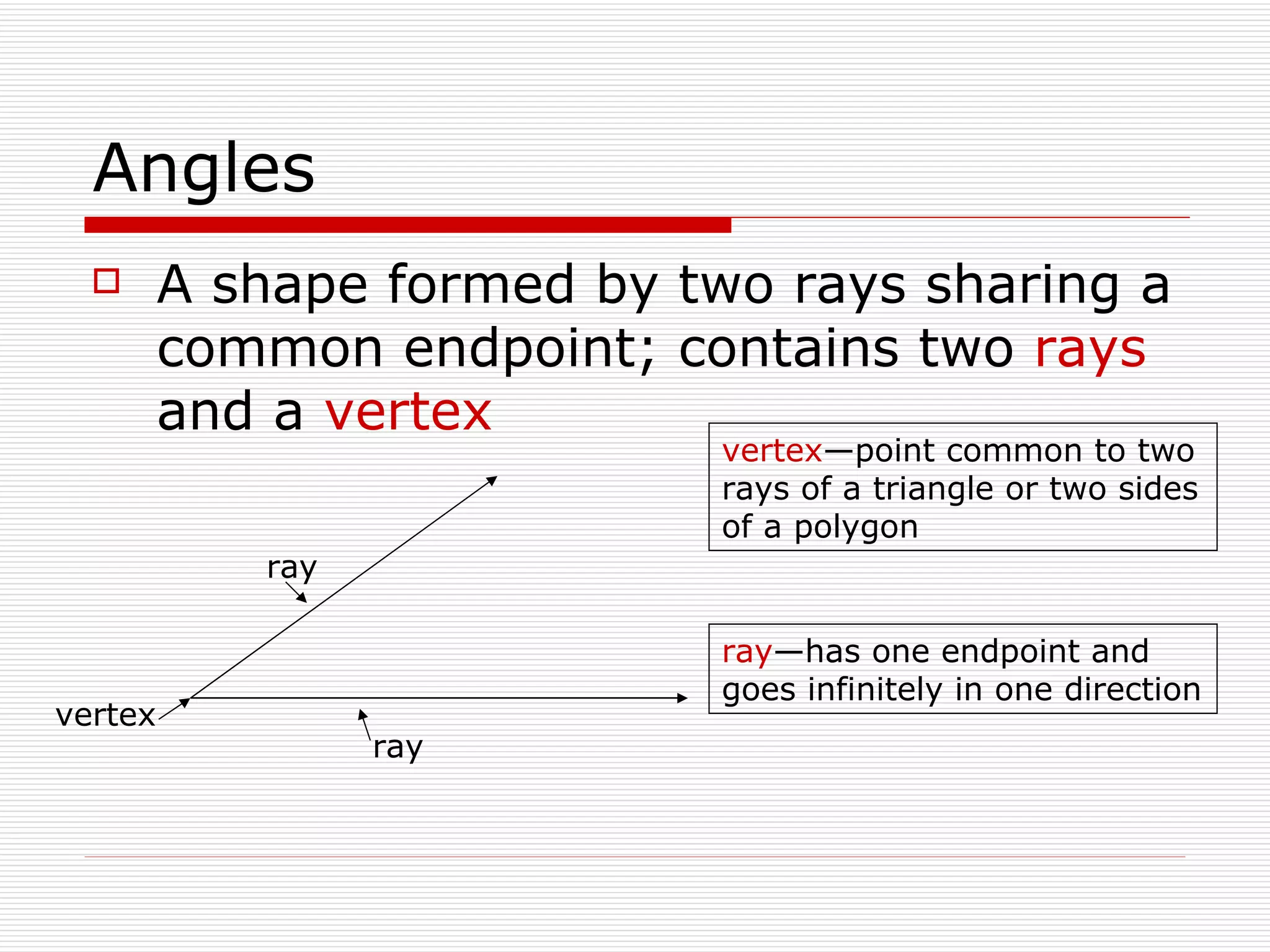
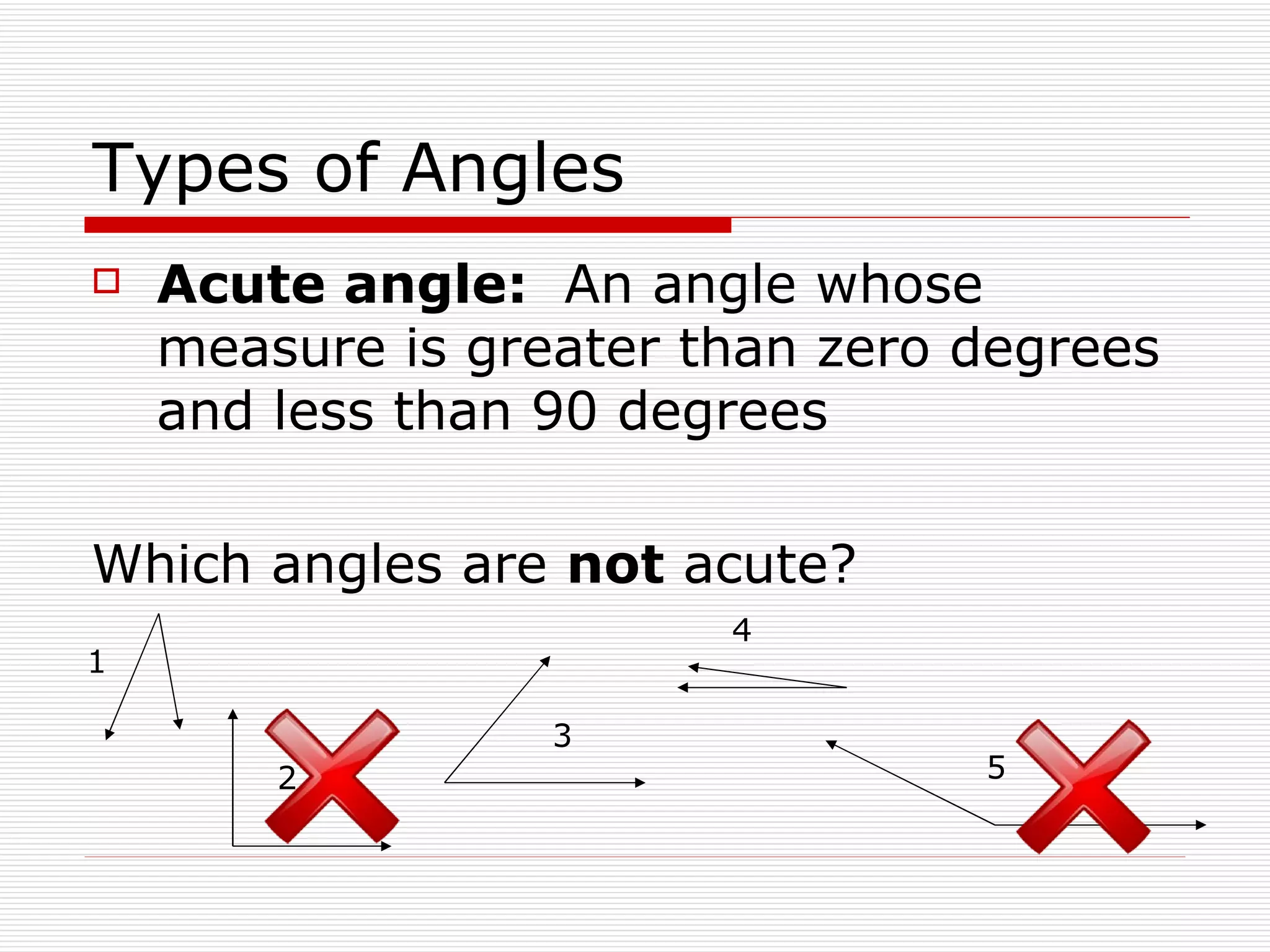
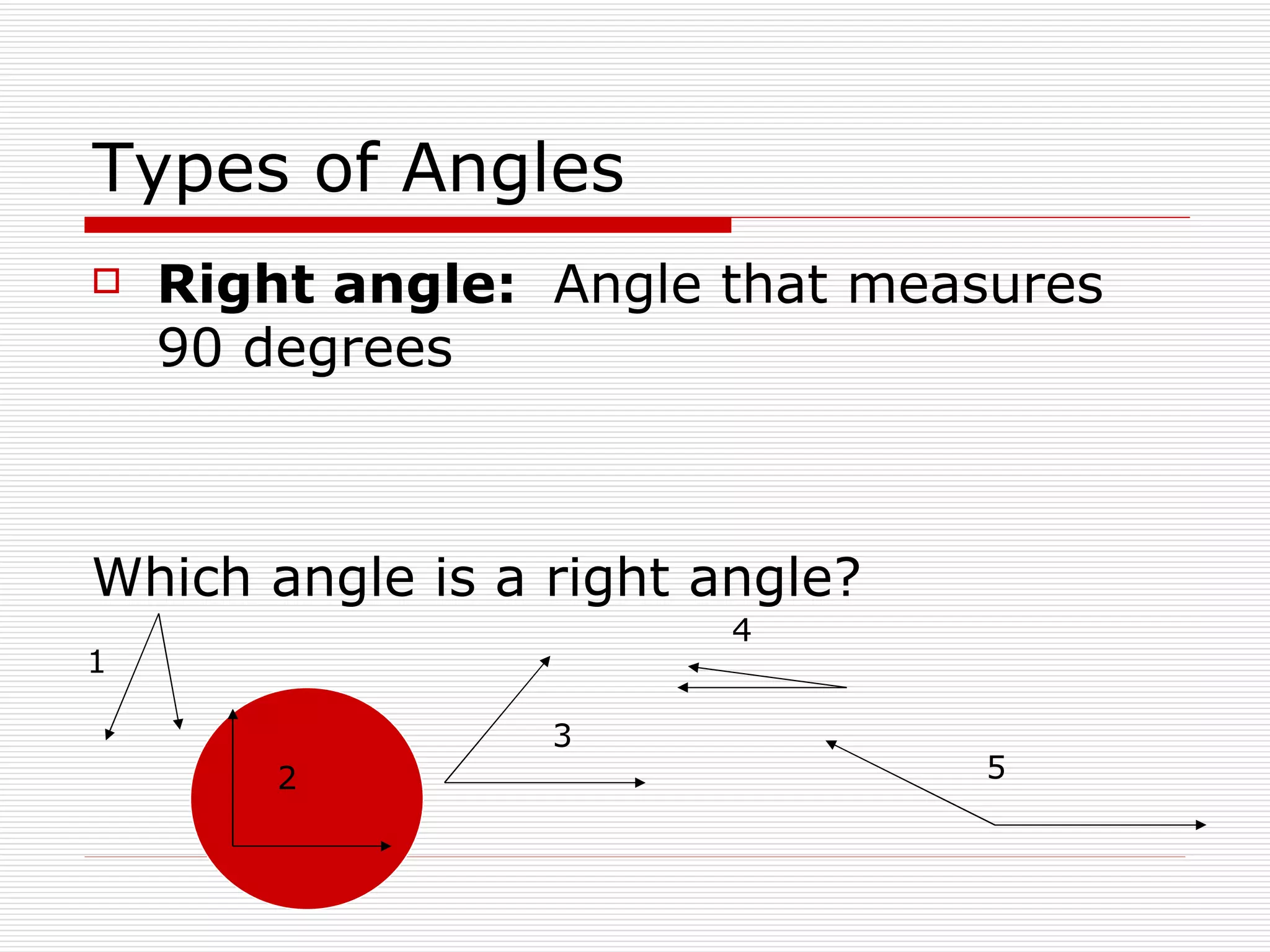
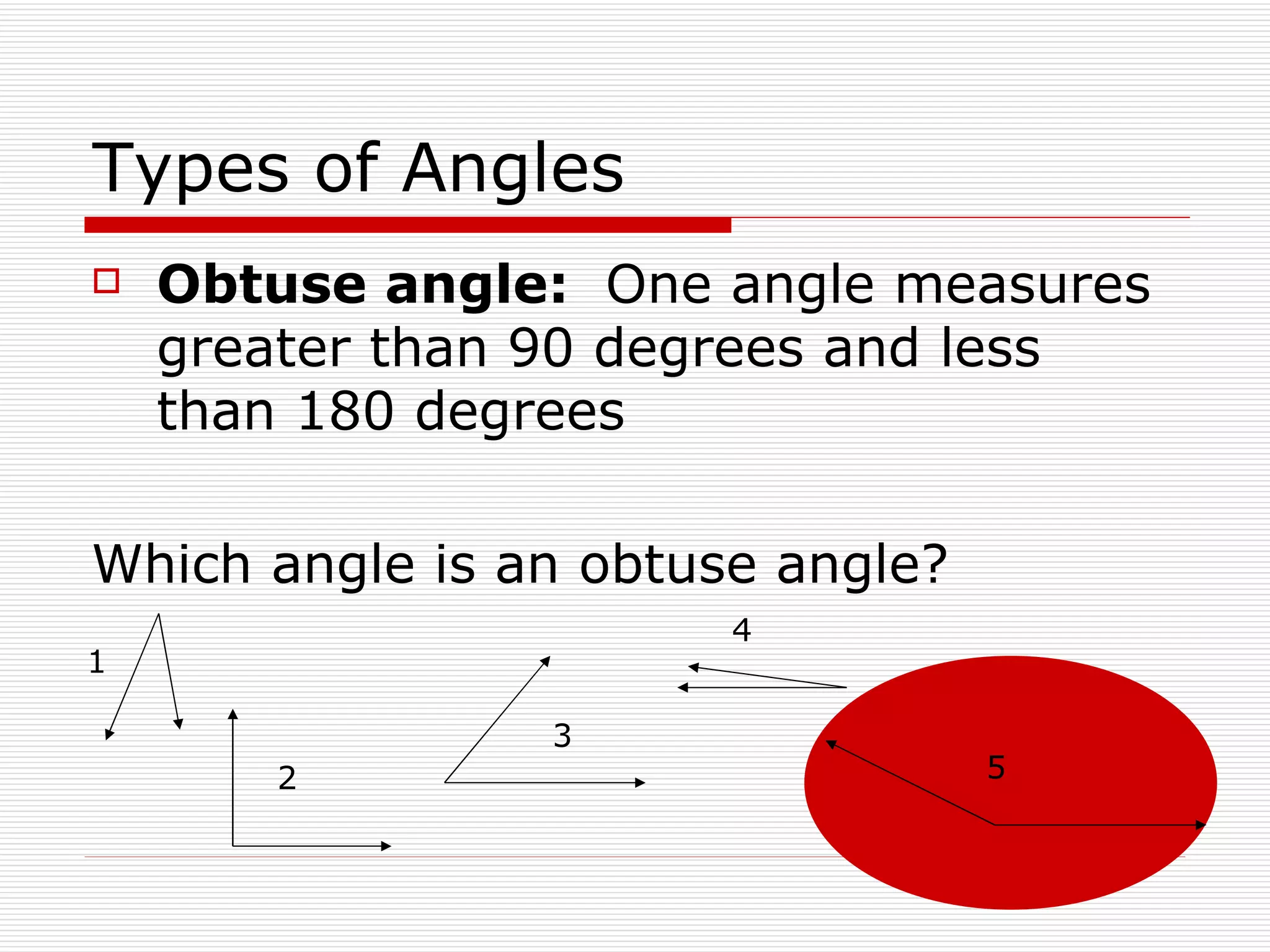
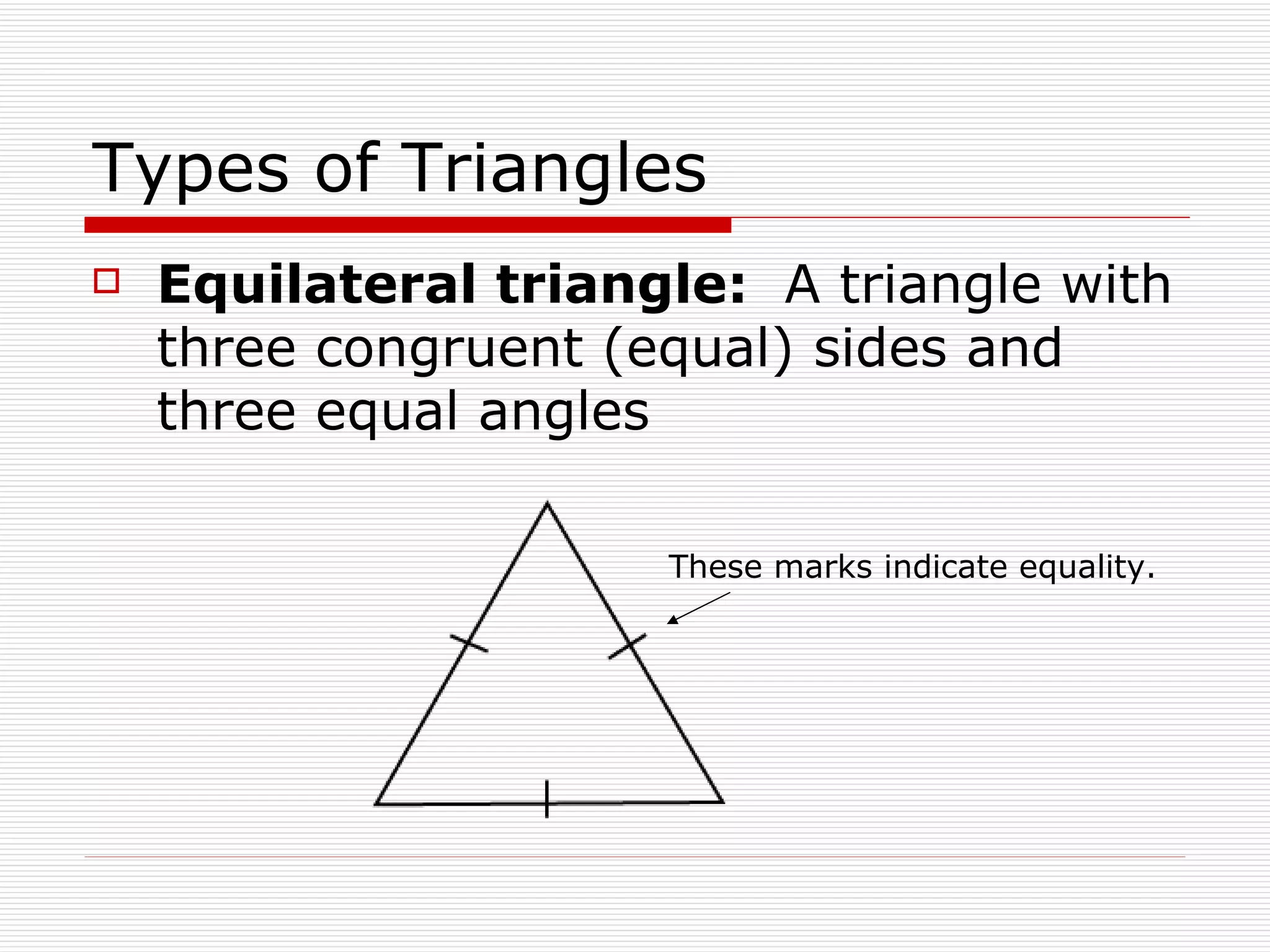
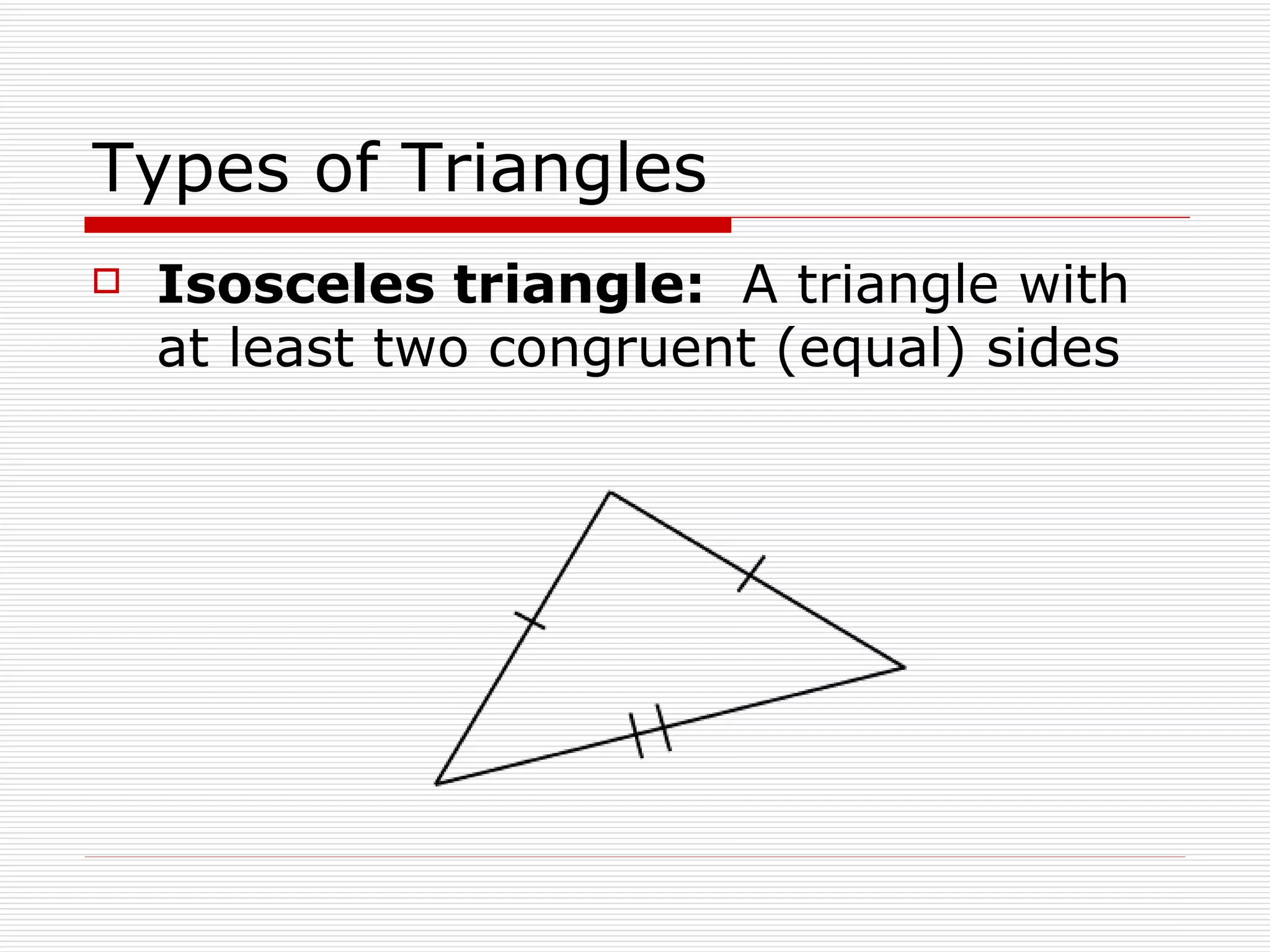
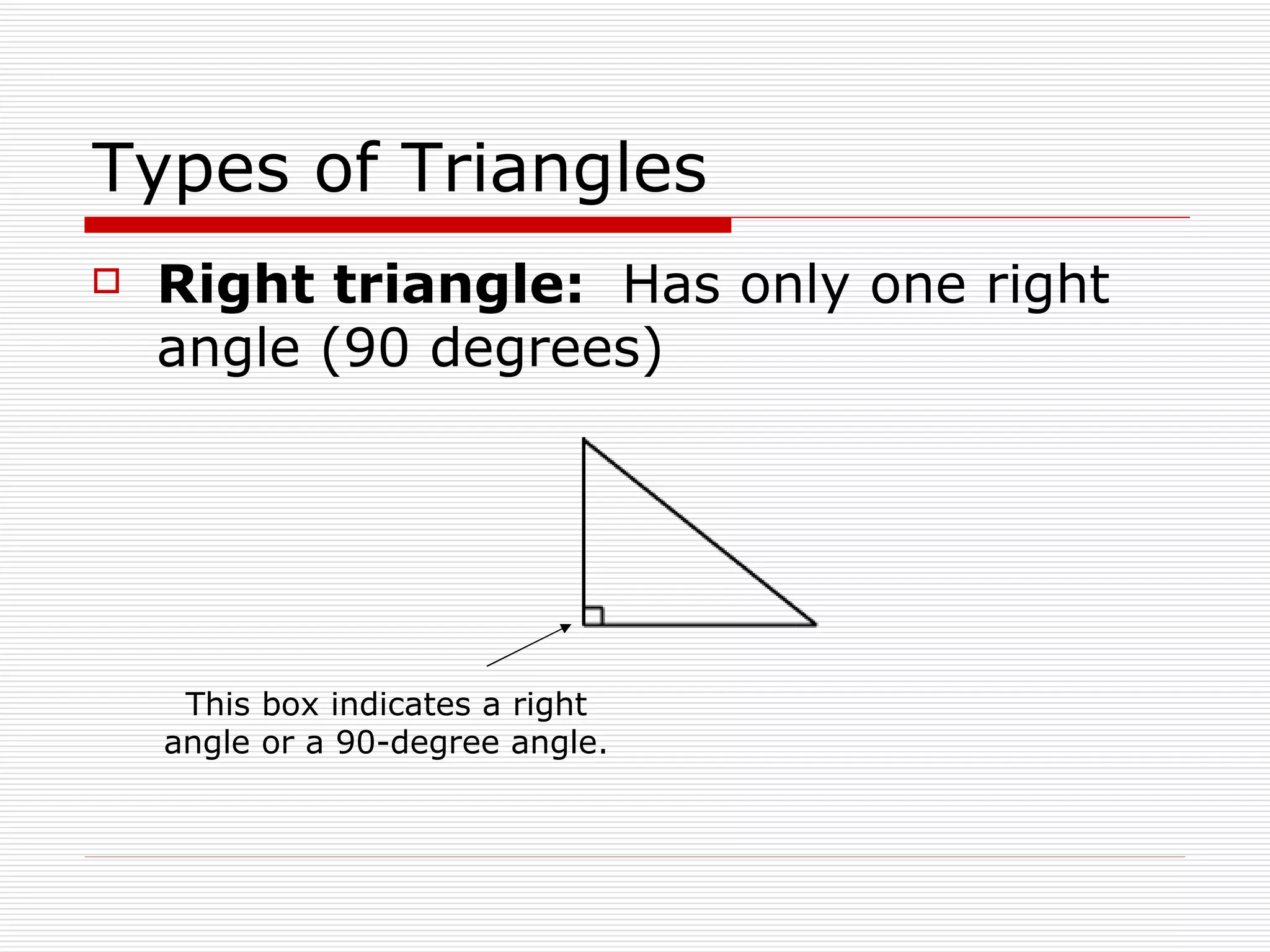
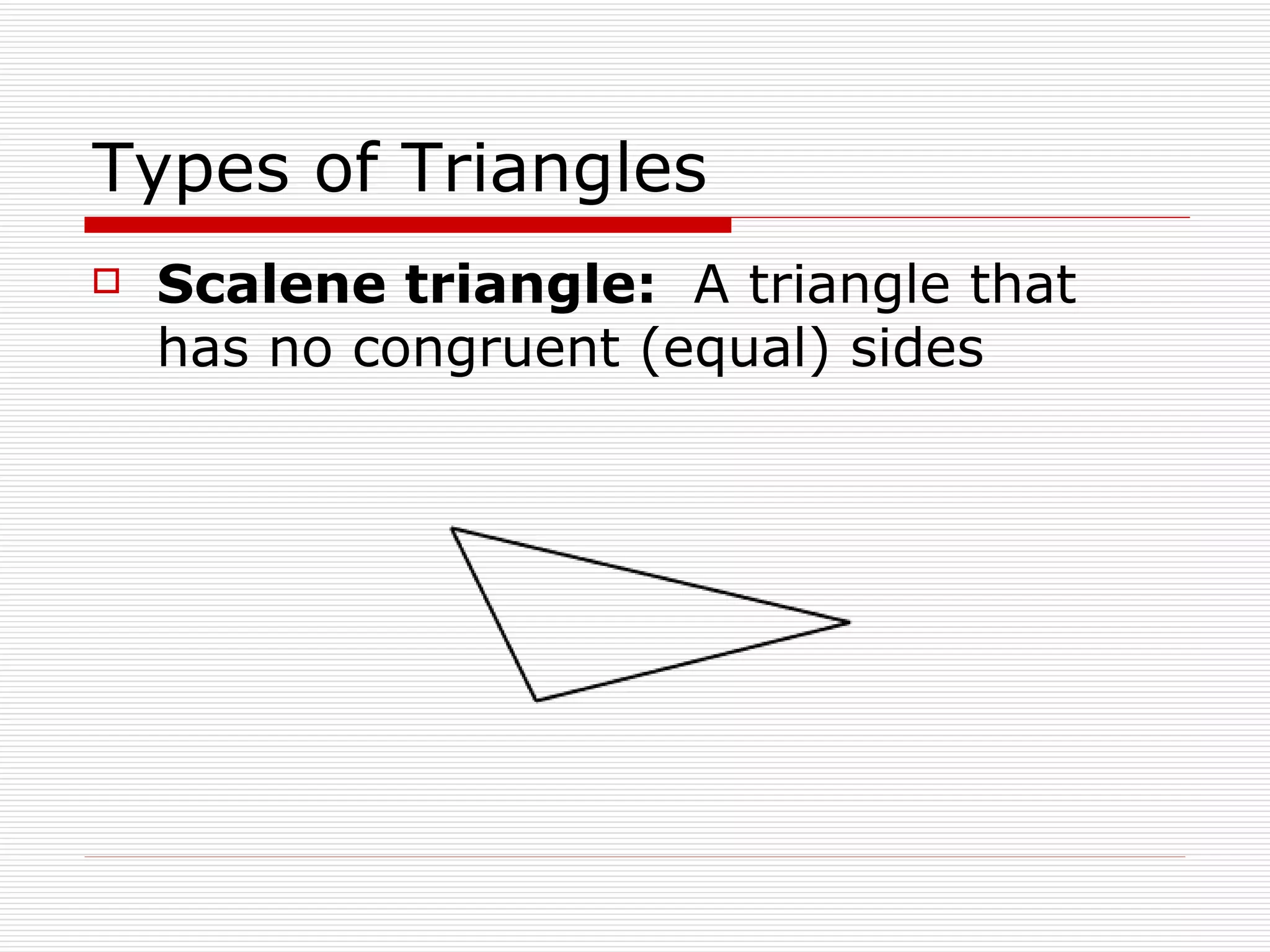
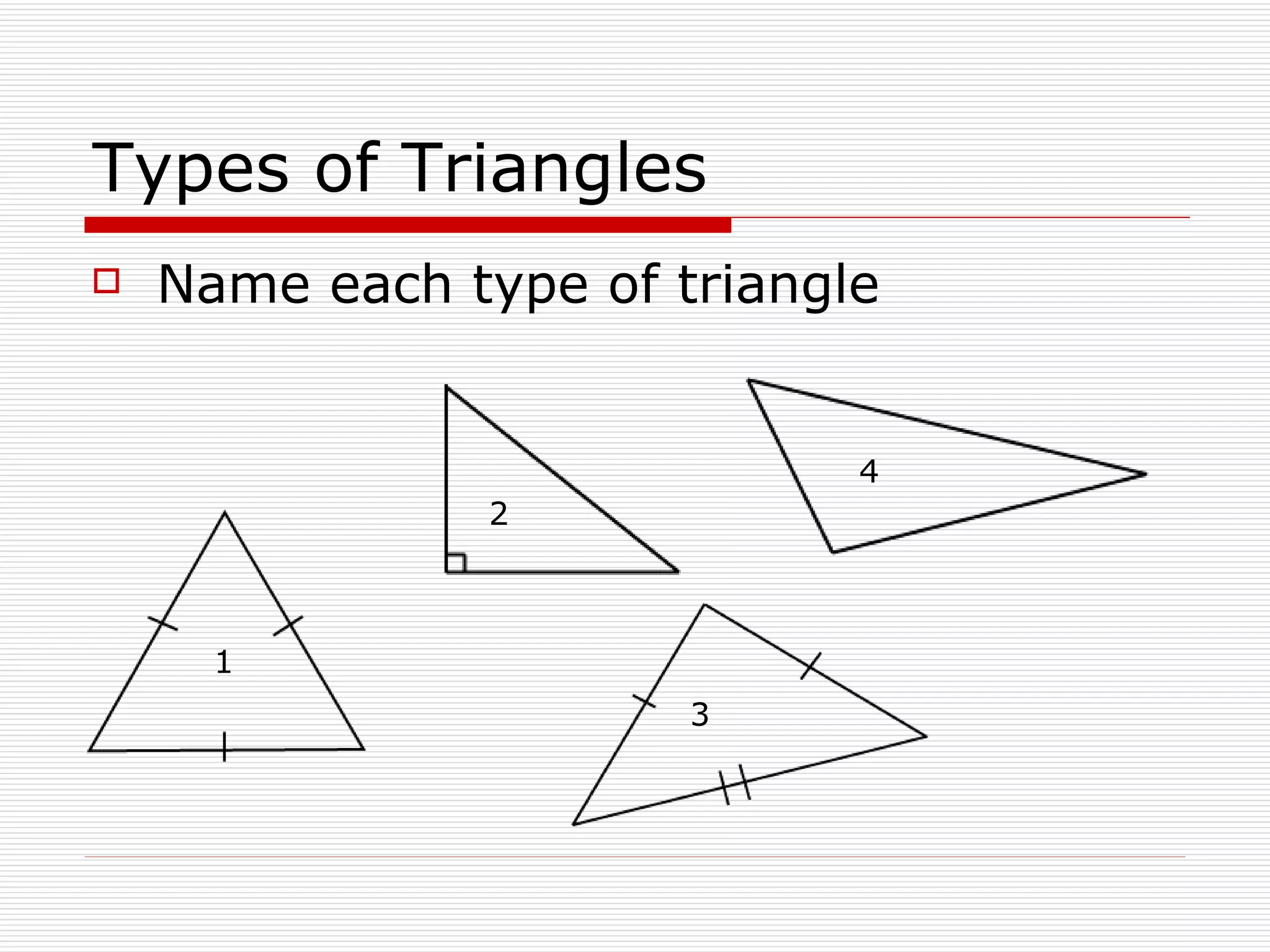
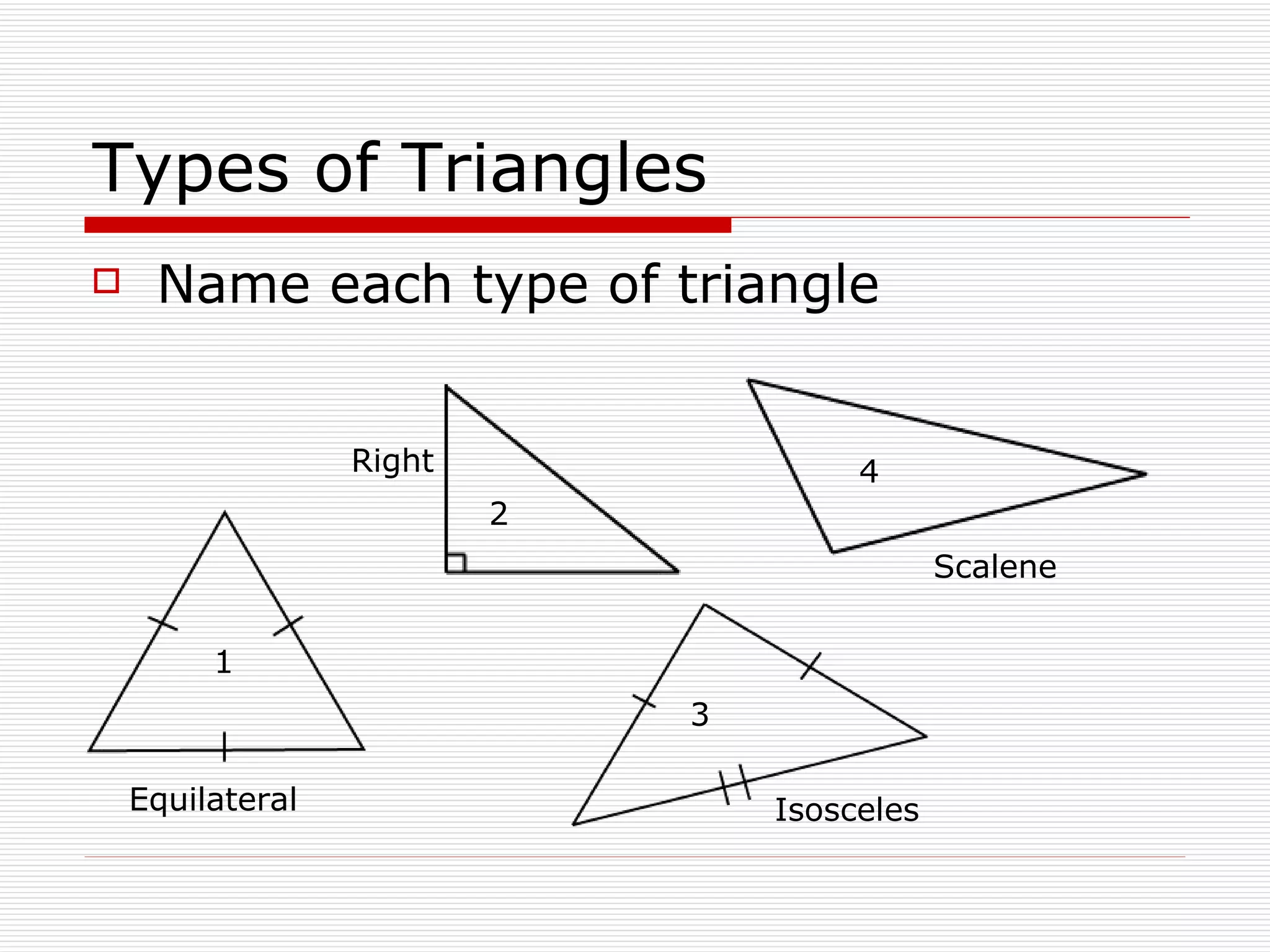
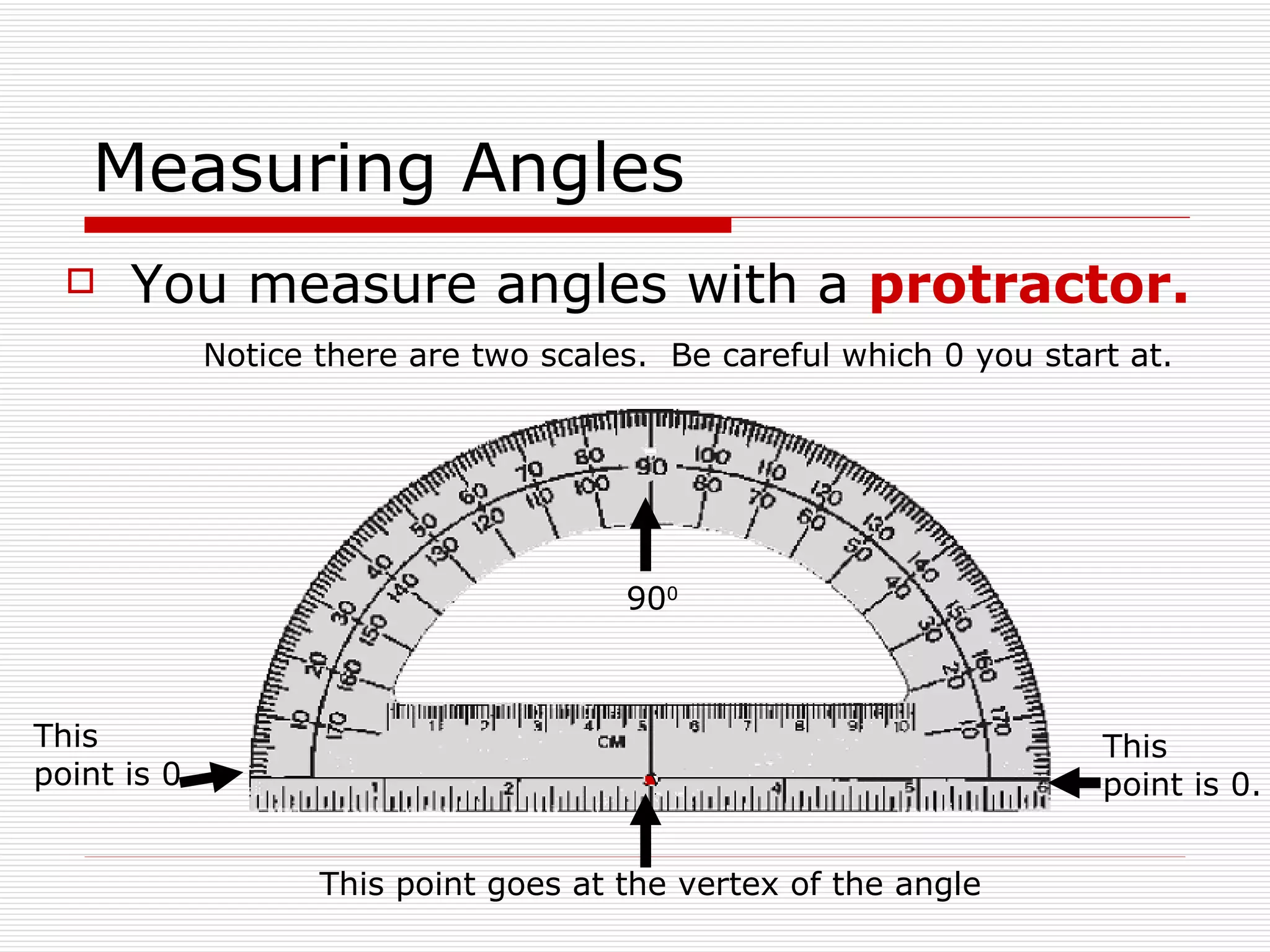
This document defines and describes different types of angles and triangles. It discusses acute, right, and obtuse angles. It also defines equilateral, isosceles, right, and scalene triangles. The document notes that the interior angles of a triangle always sum to 180 degrees and that angles are measured using a protractor.