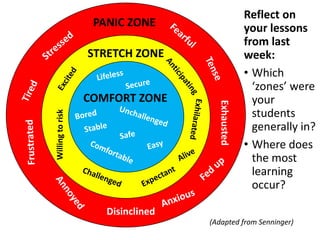
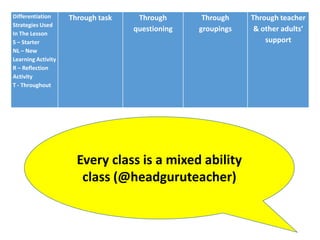
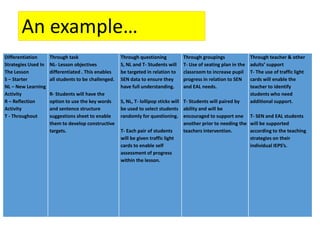
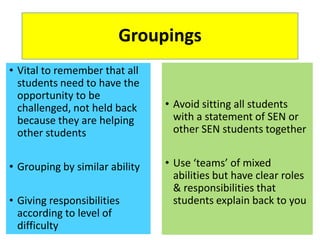
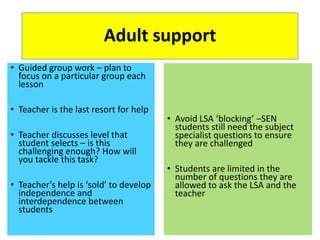
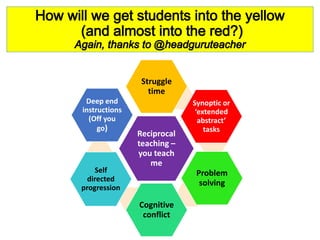
This document discusses strategies for embedding stretch and challenge for all students. It emphasizes that the most learning occurs when students are in their "stretch zone", at the edge of their competence where they feel a temporary loss of security. The document then provides examples of differentiation strategies teachers can use in their lessons through tasks, grouping, questioning, and adult support to ensure all students, including those with special educational needs, are appropriately challenged.