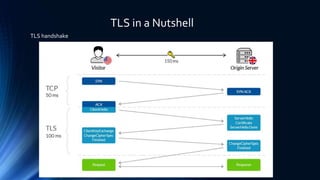
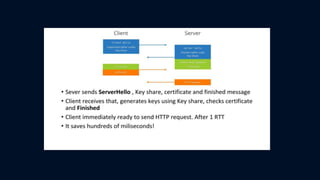
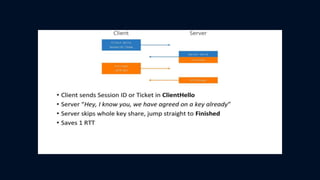
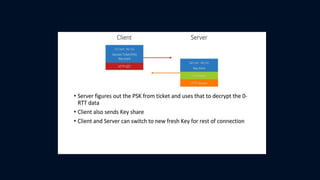
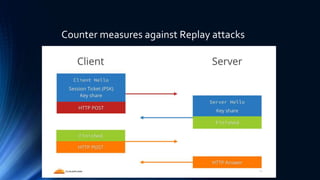
The document discusses Transport Layer Security (TLS) version 1.3, including what SSL is, the evolution from SSL to TLS, a comparison of TLS 1.2 and 1.3, and two caveats in TLS 1.3. SSL was a method to secure and encrypt sensitive information over HTTPS and had vulnerabilities like BEAST and POODLE that impacted browser security. TLS was developed as an updated standard by IETF in 1999 and revised in 2006 and 2008, addressing issues with earlier SSL versions. TLS 1.3 focuses on authentication, confidentiality, integrity and includes improvements like 0-RTT resumption and forward secrecy.