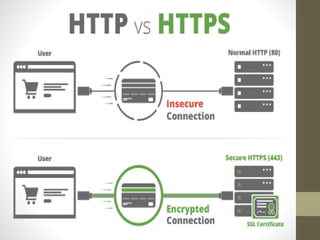
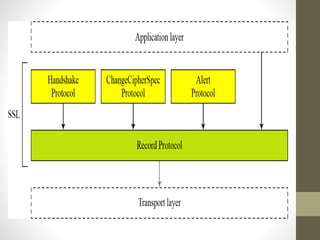
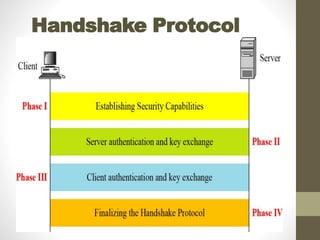
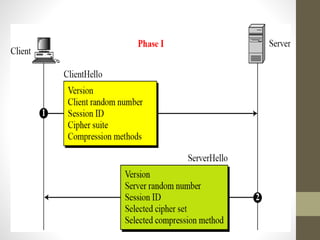
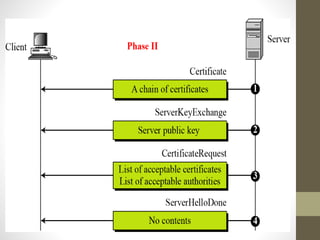
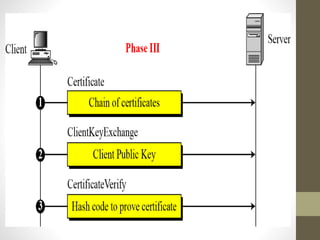
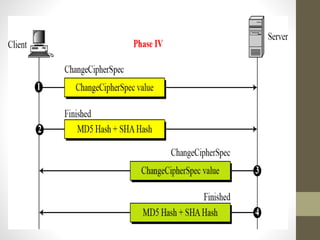
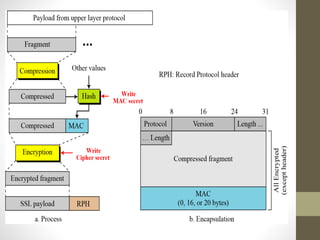
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) encrypt communication between web browsers and servers to provide privacy and security. SSL/TLS aims to provide confidentiality, integrity protection, and authentication. The SSL/TLS handshake protocol establishes a secure connection in four phases: negotiating algorithms, authenticating the server, authenticating the client, and establishing encryption keys. Subsequent data transfer uses the SSL record protocol to encrypt, compress, and authenticate messages securely.