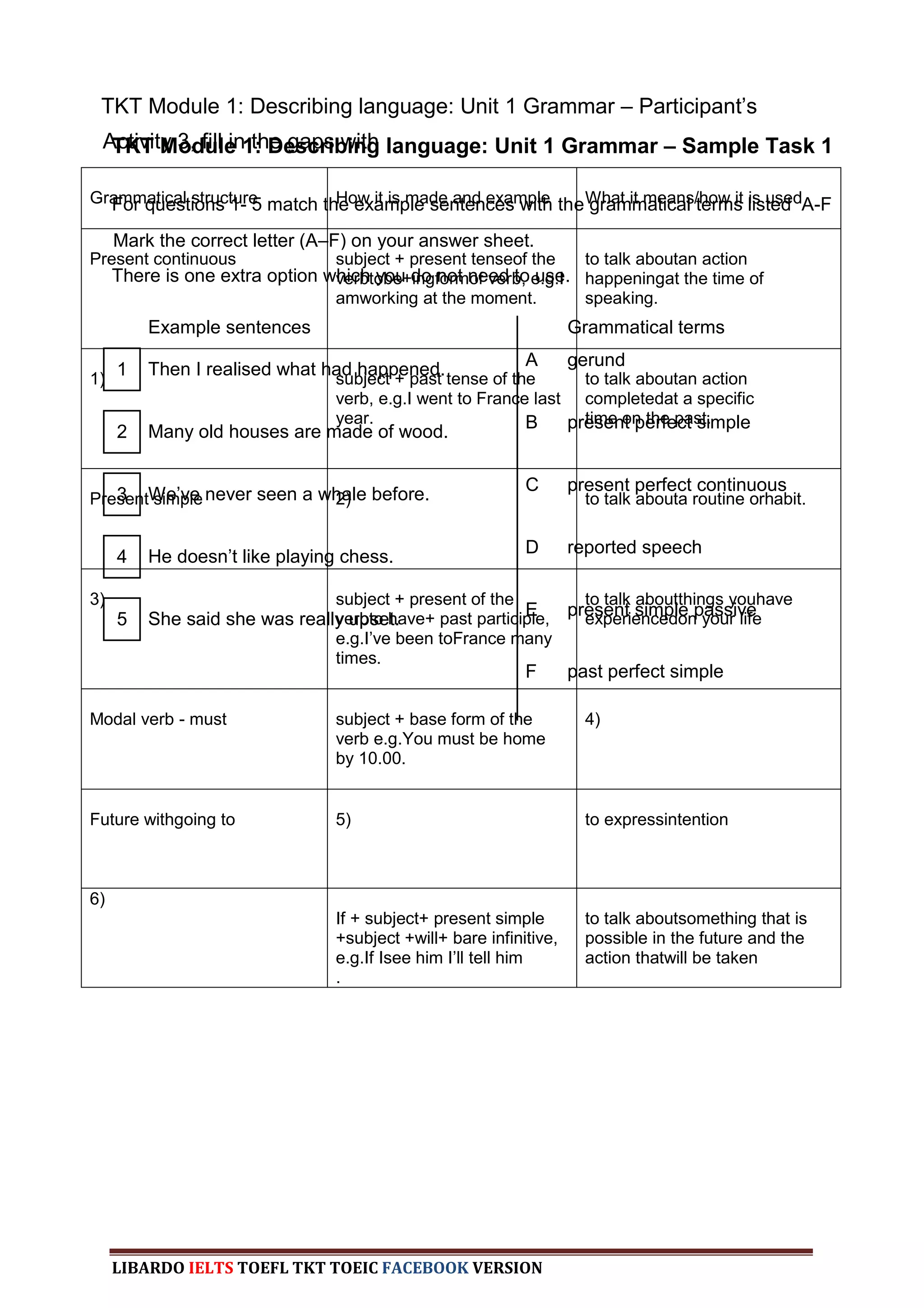
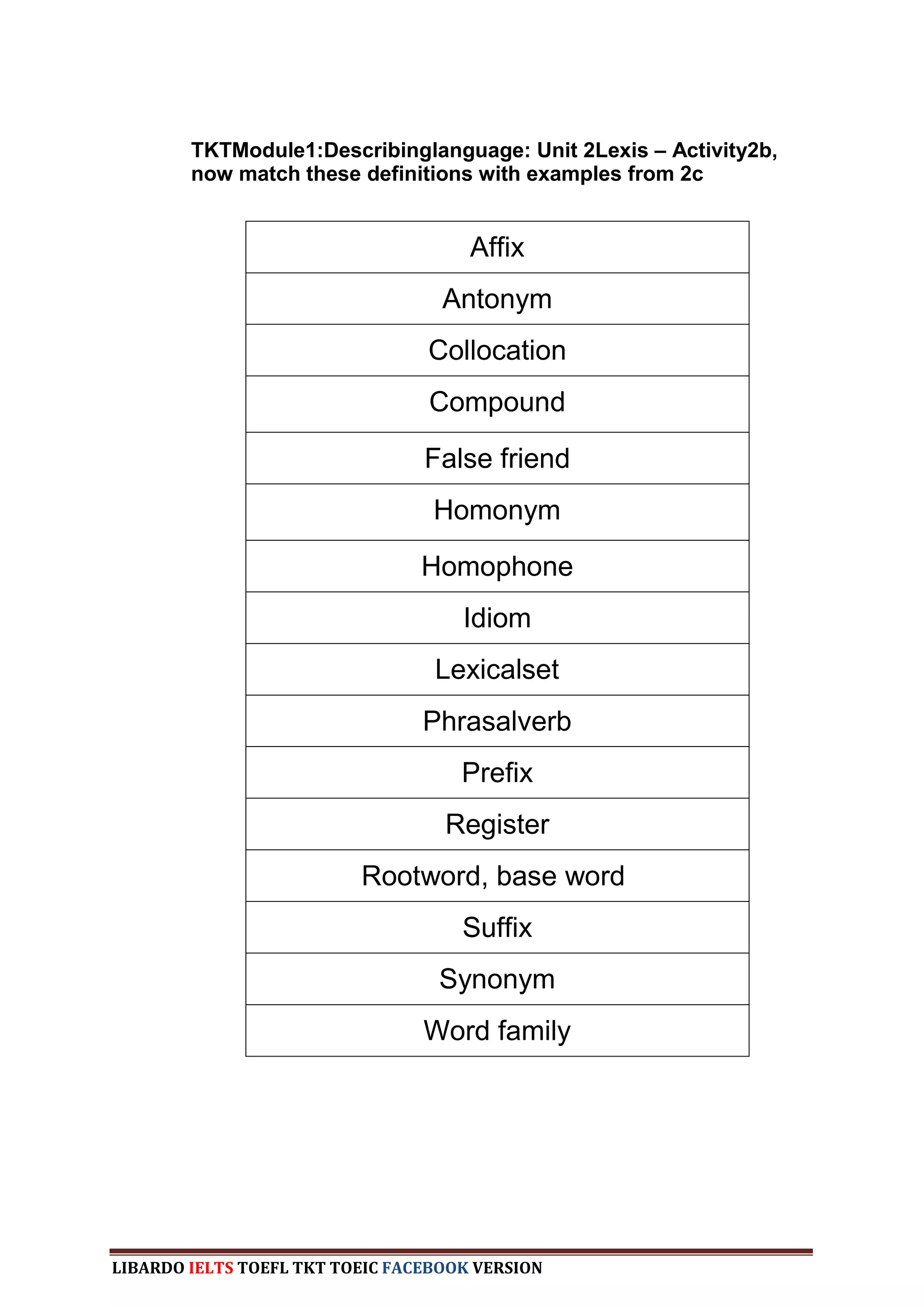
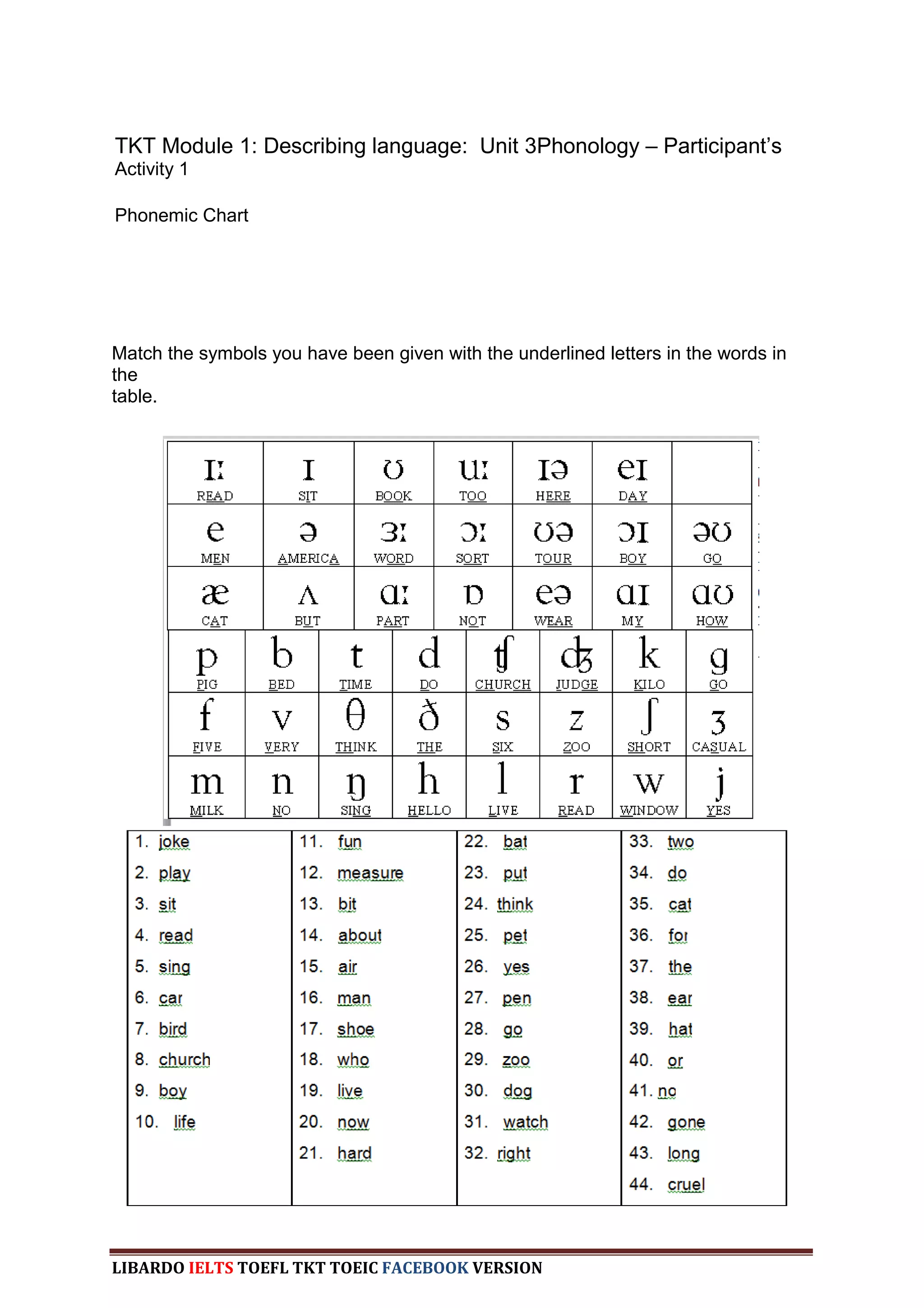
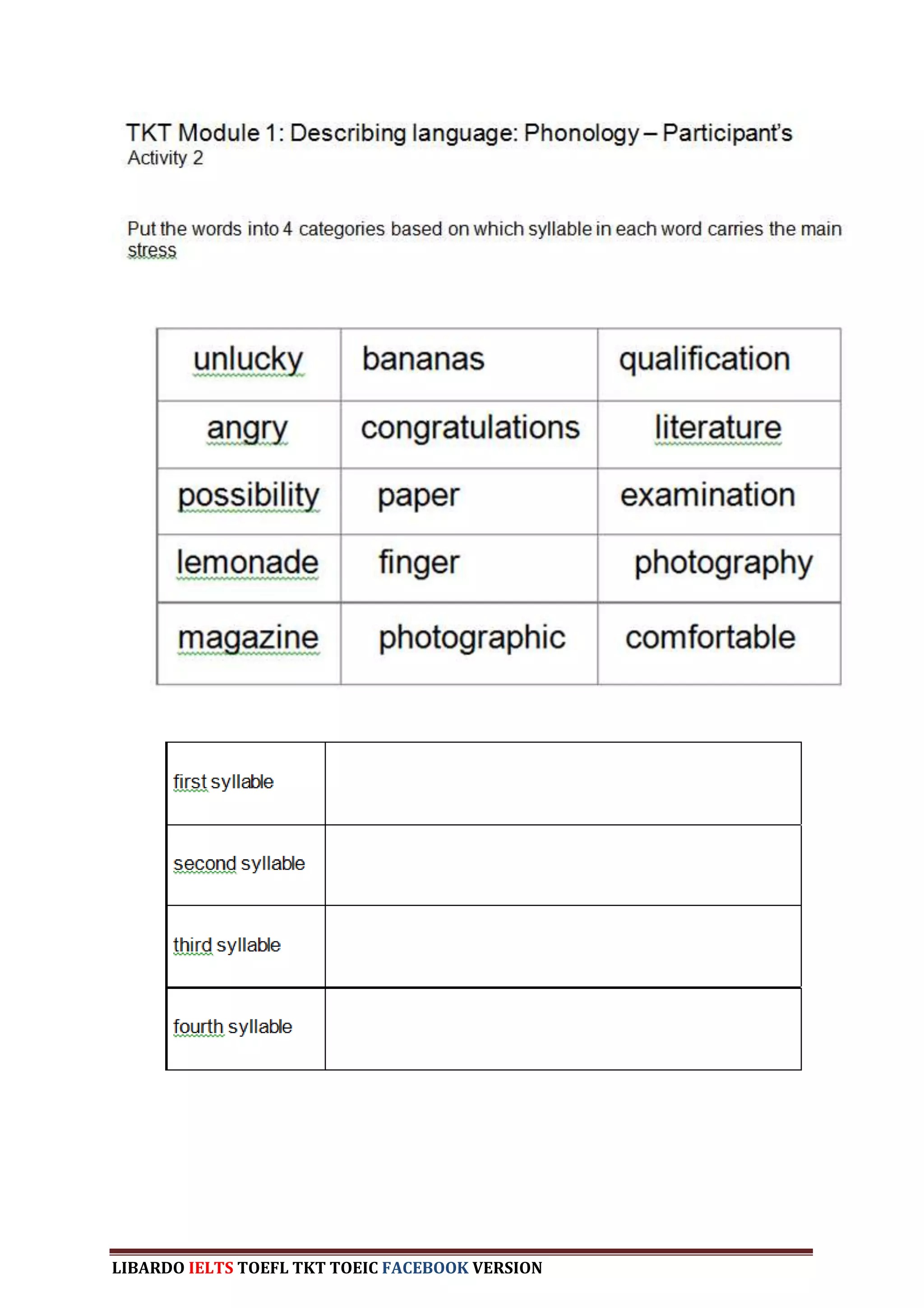
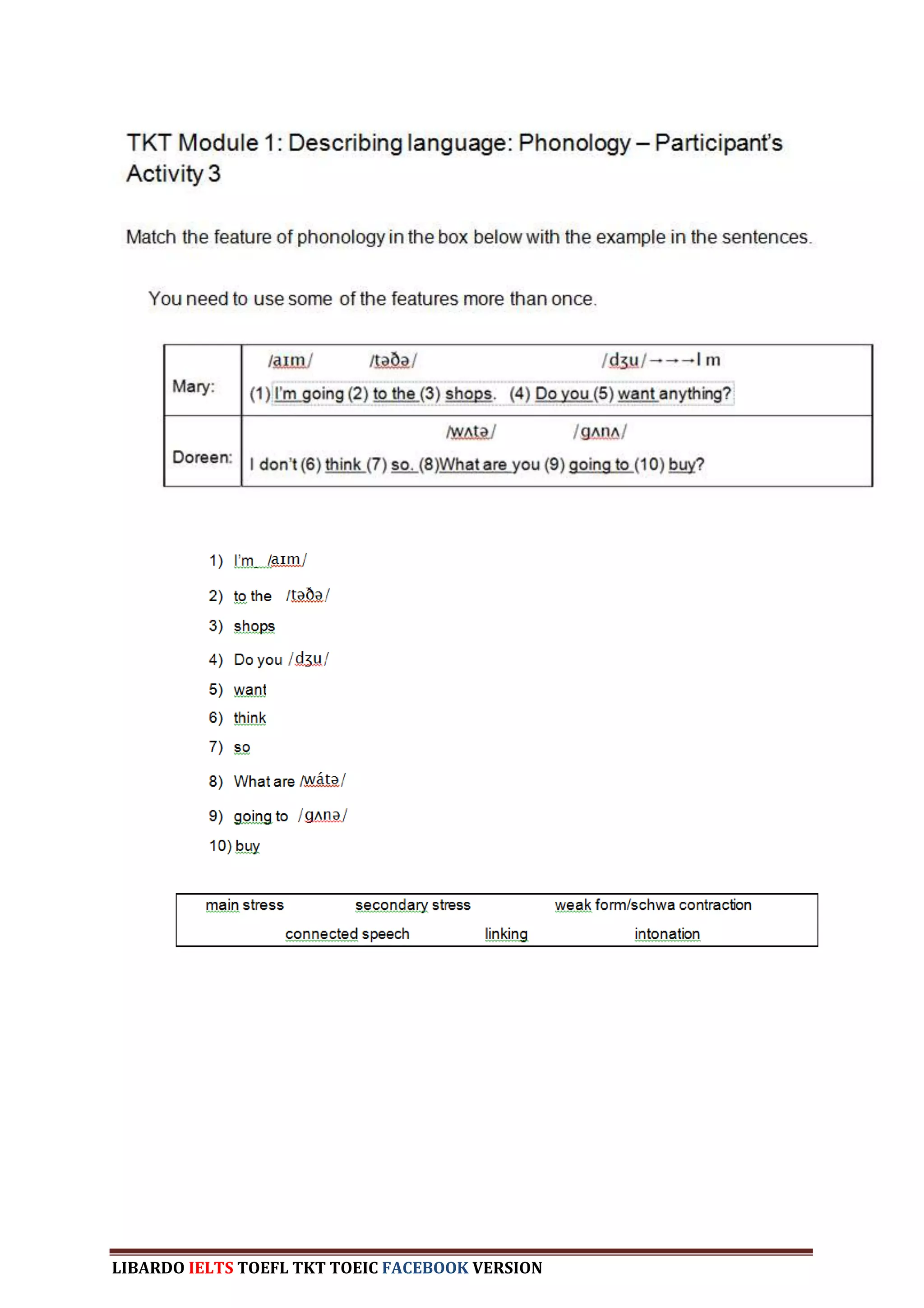
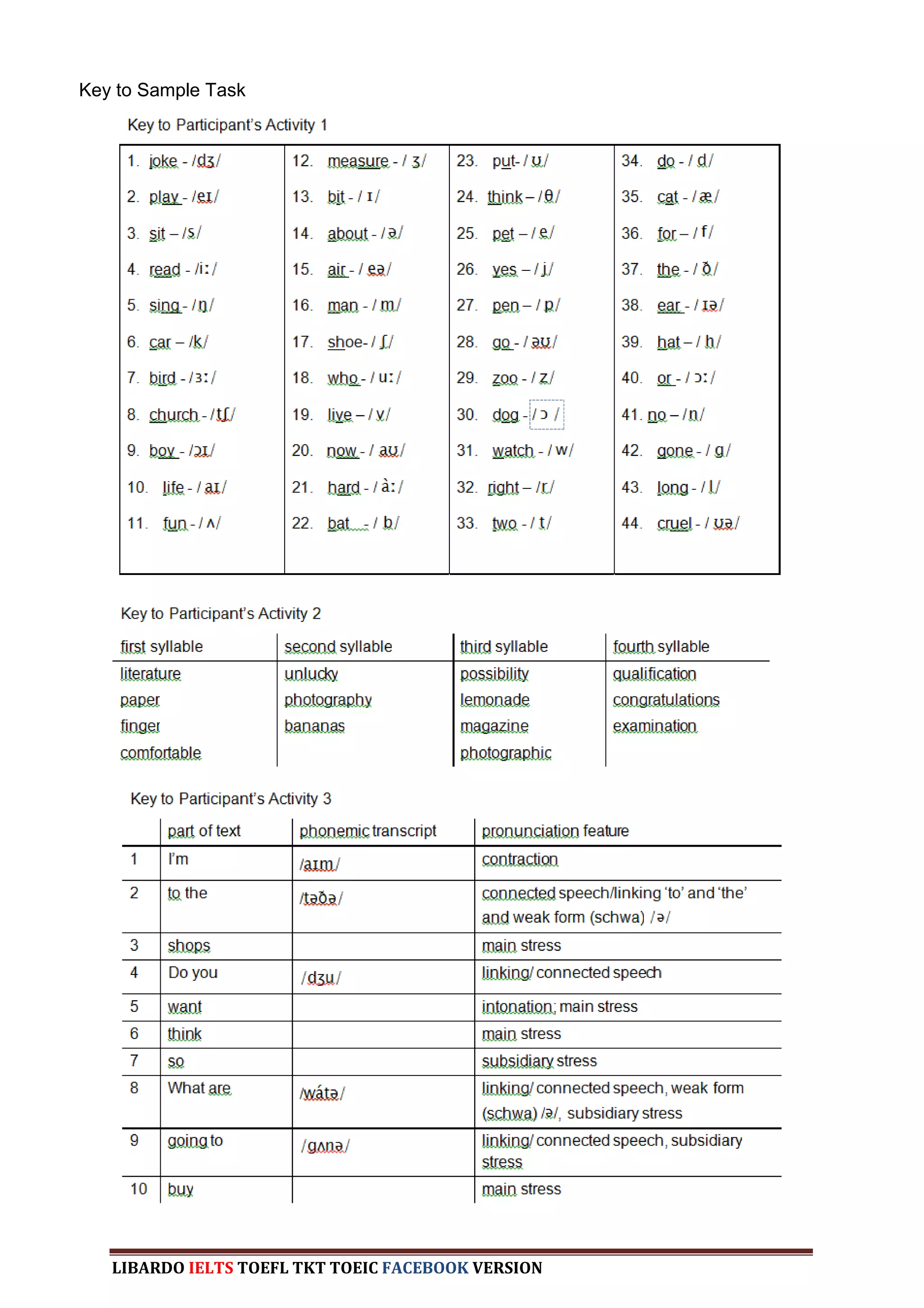
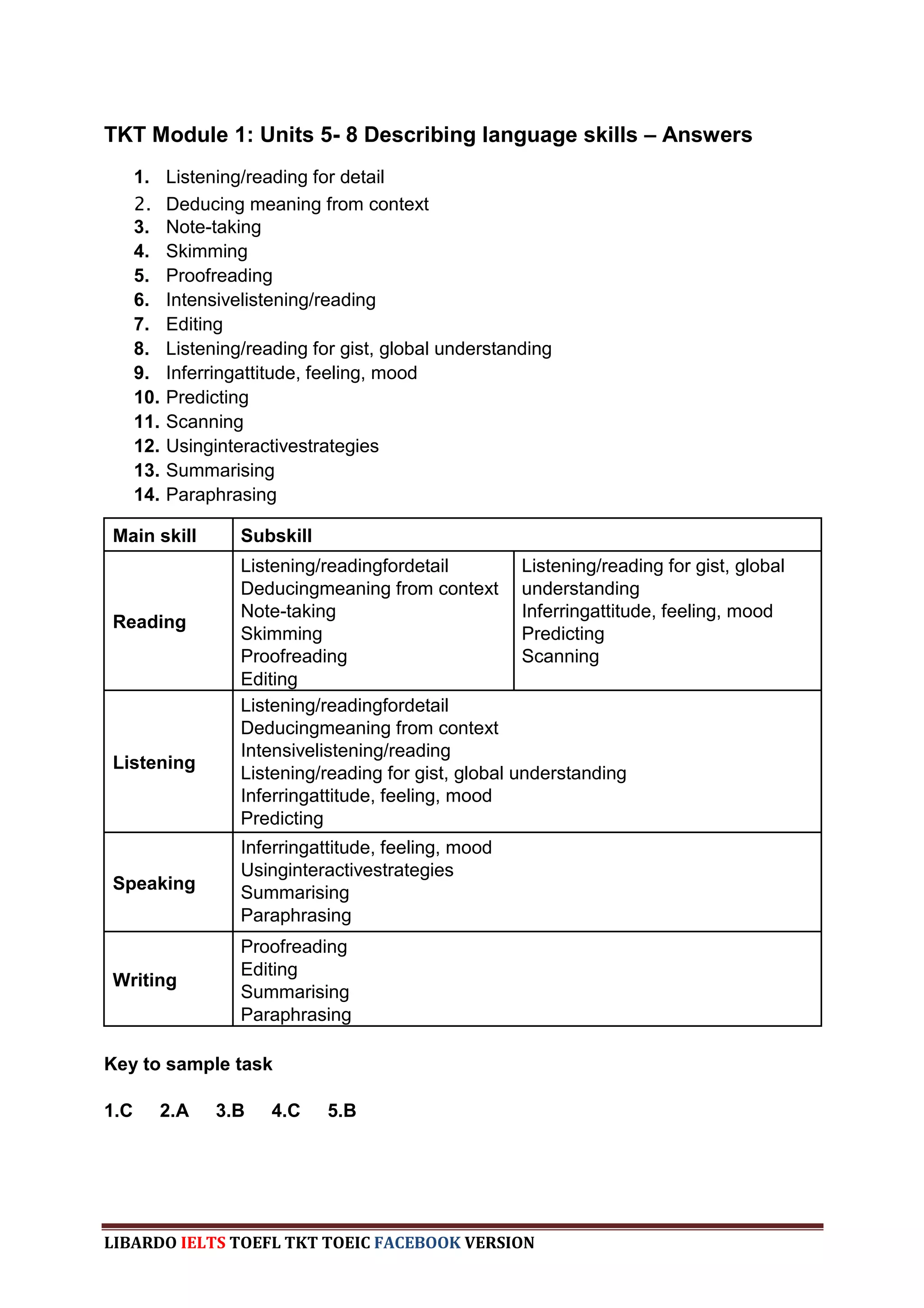
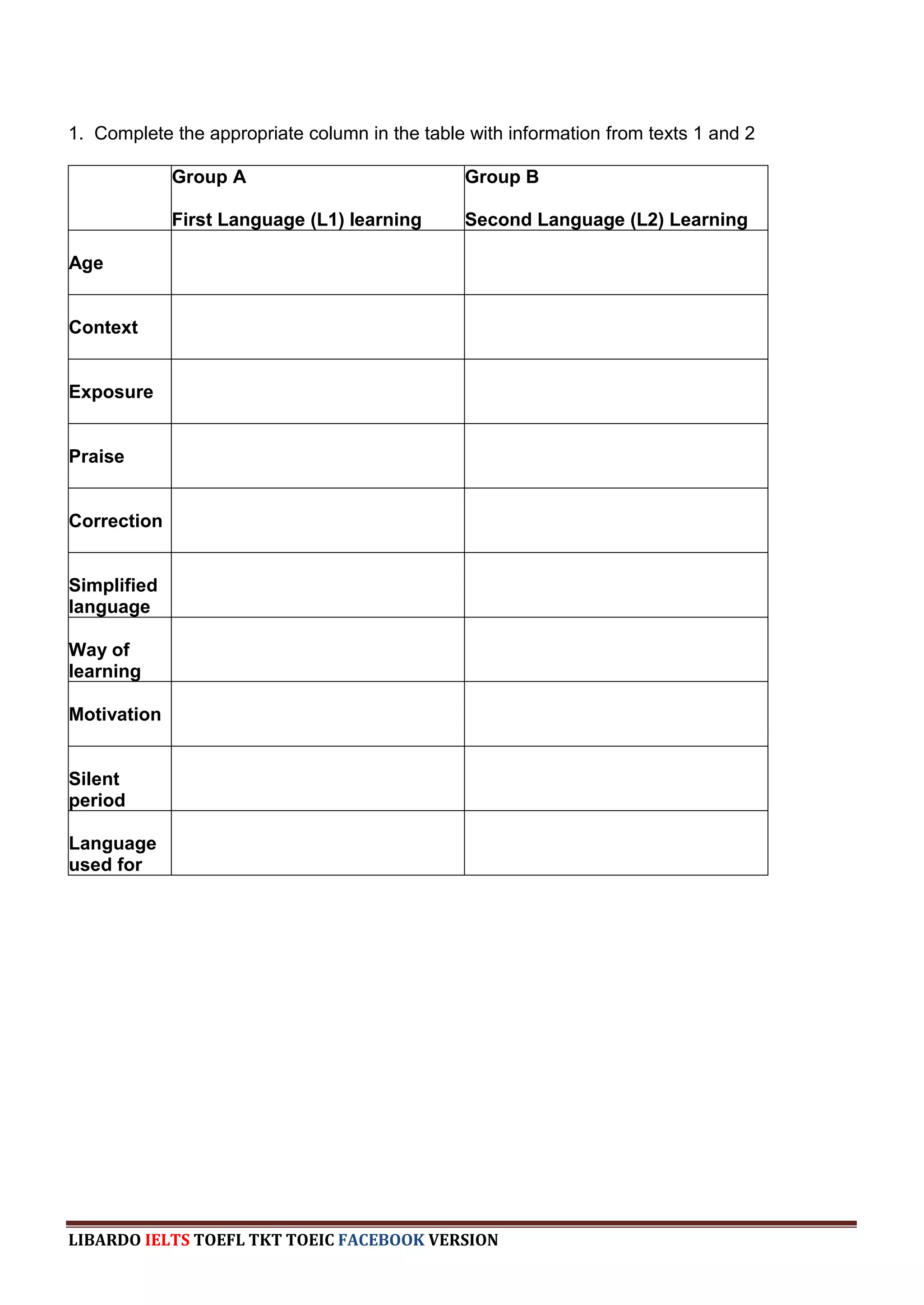
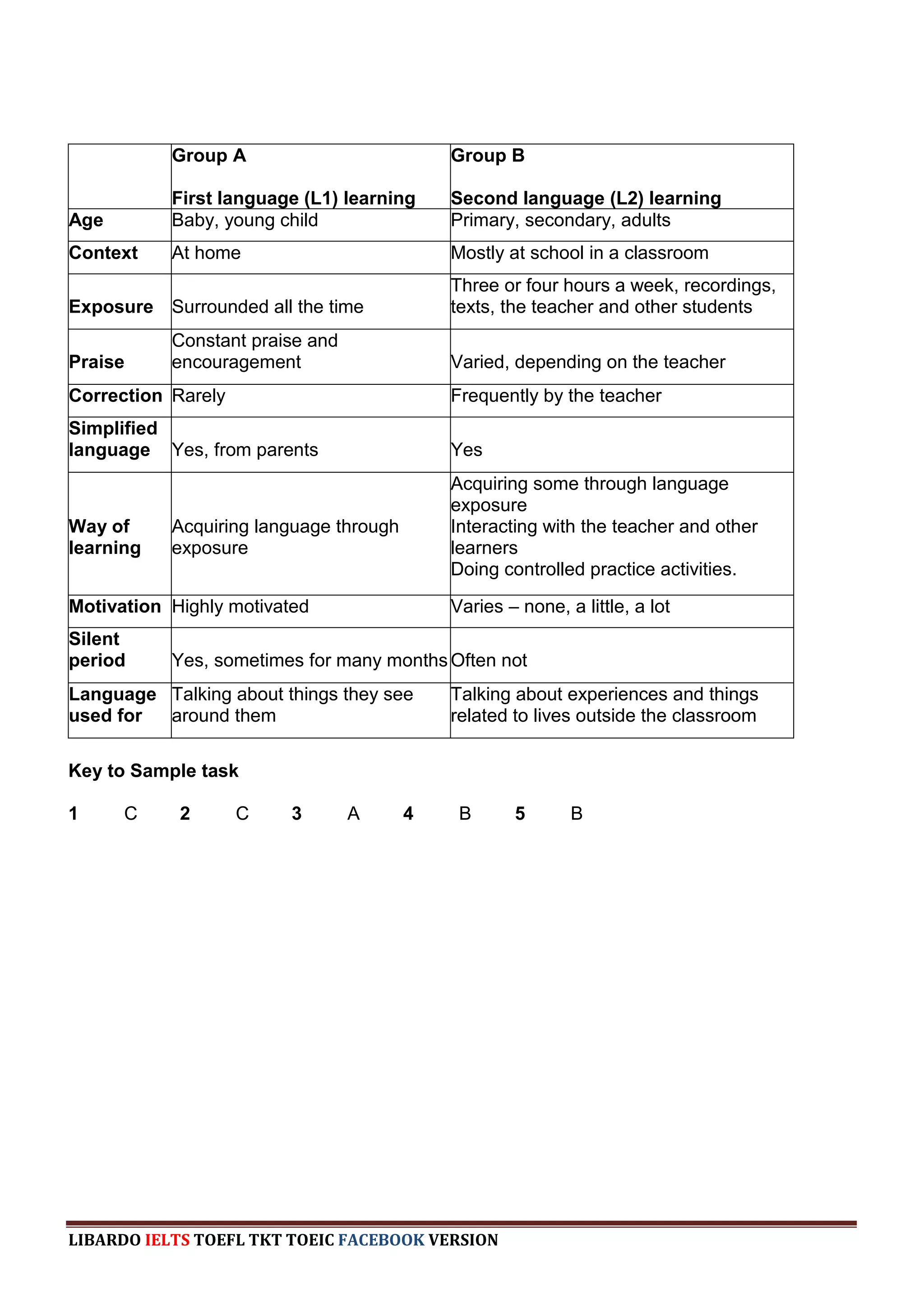
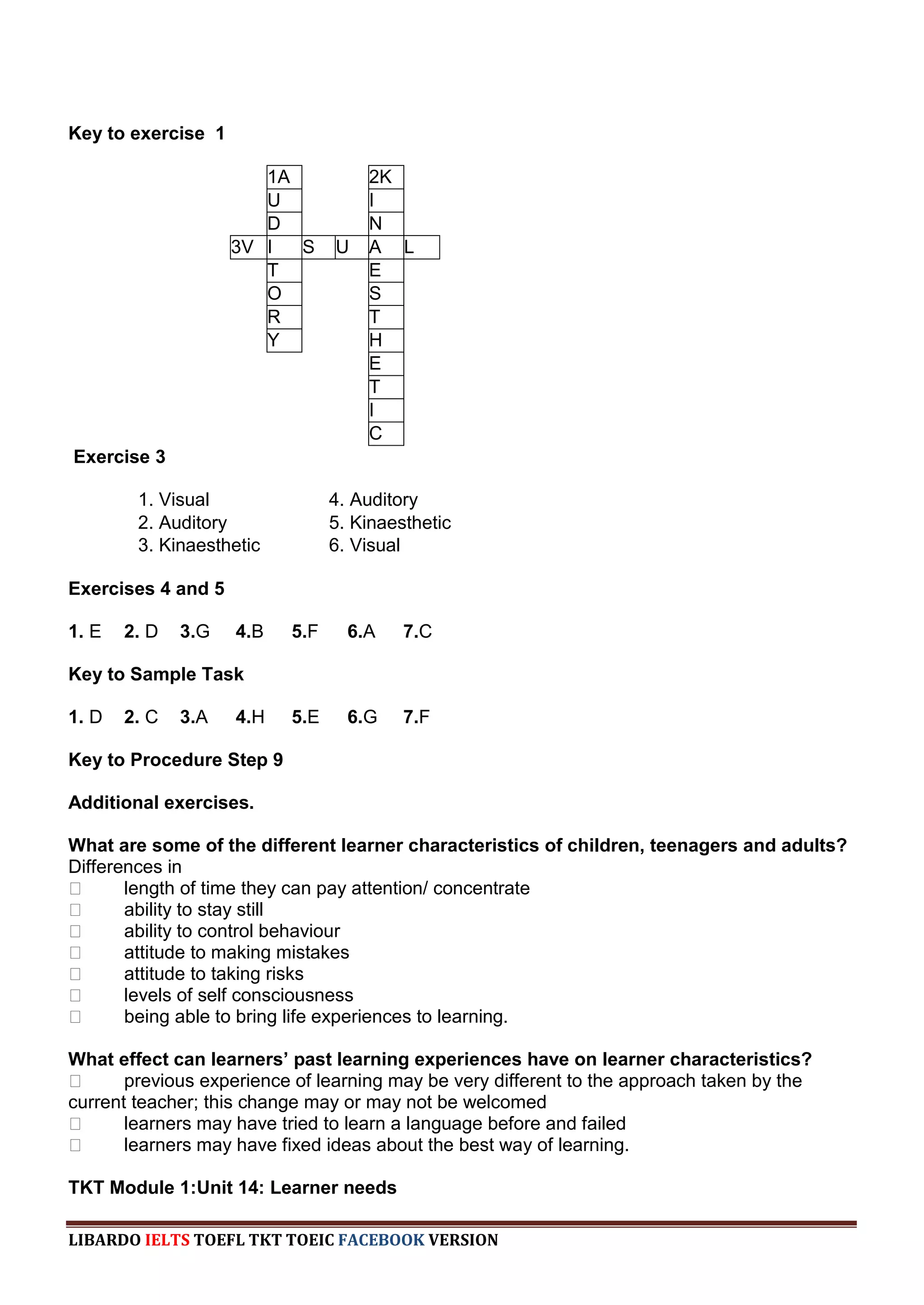
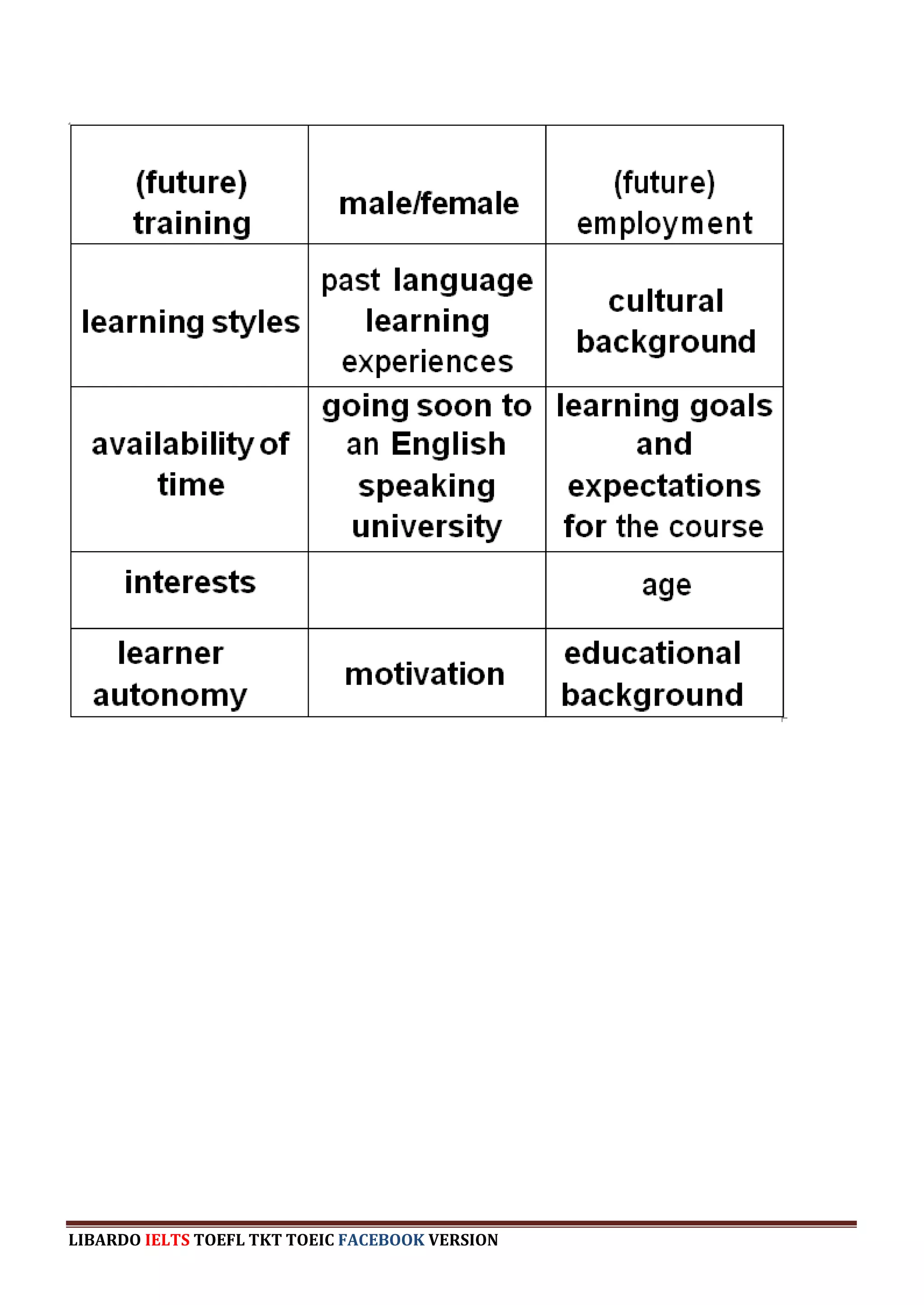
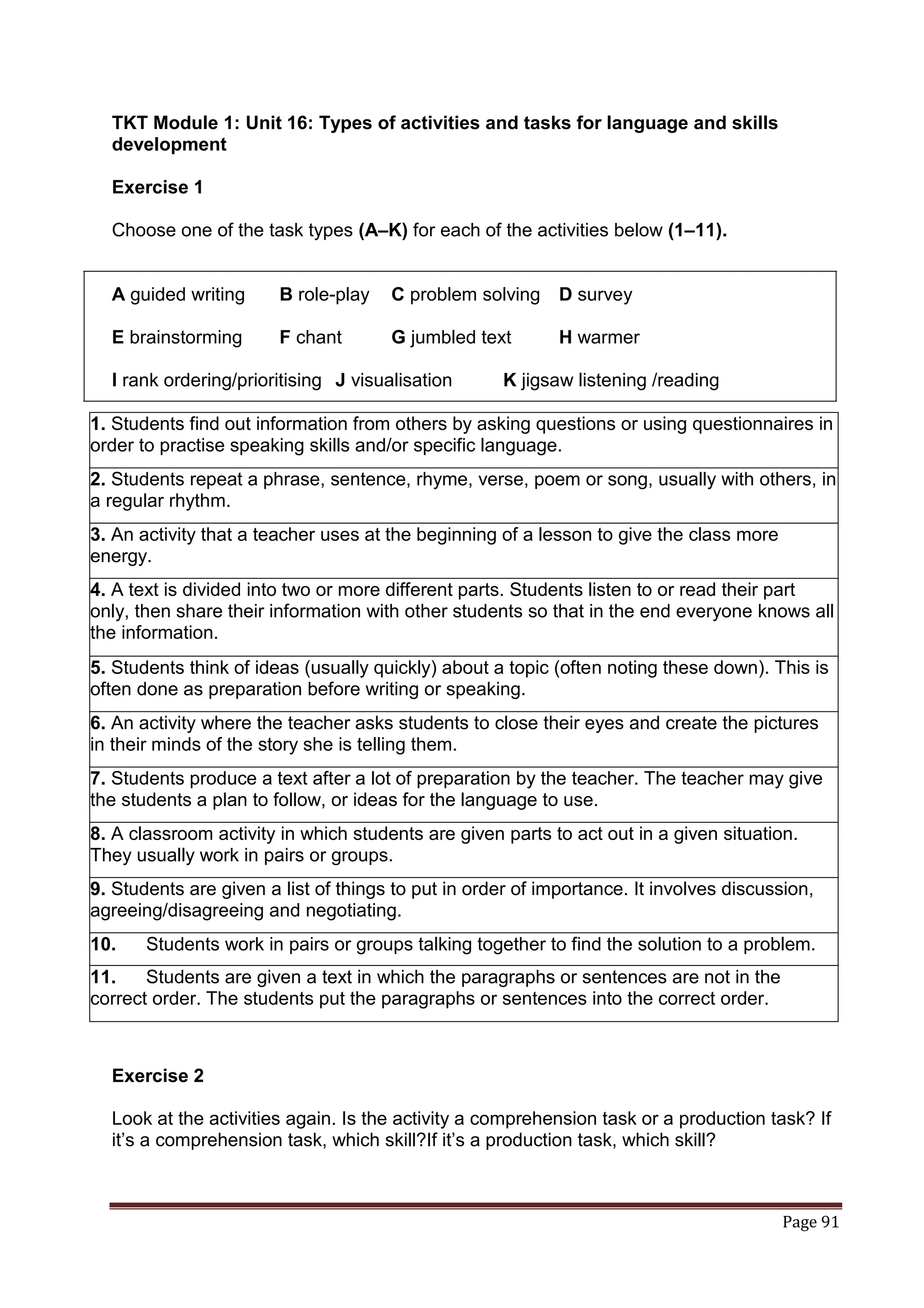
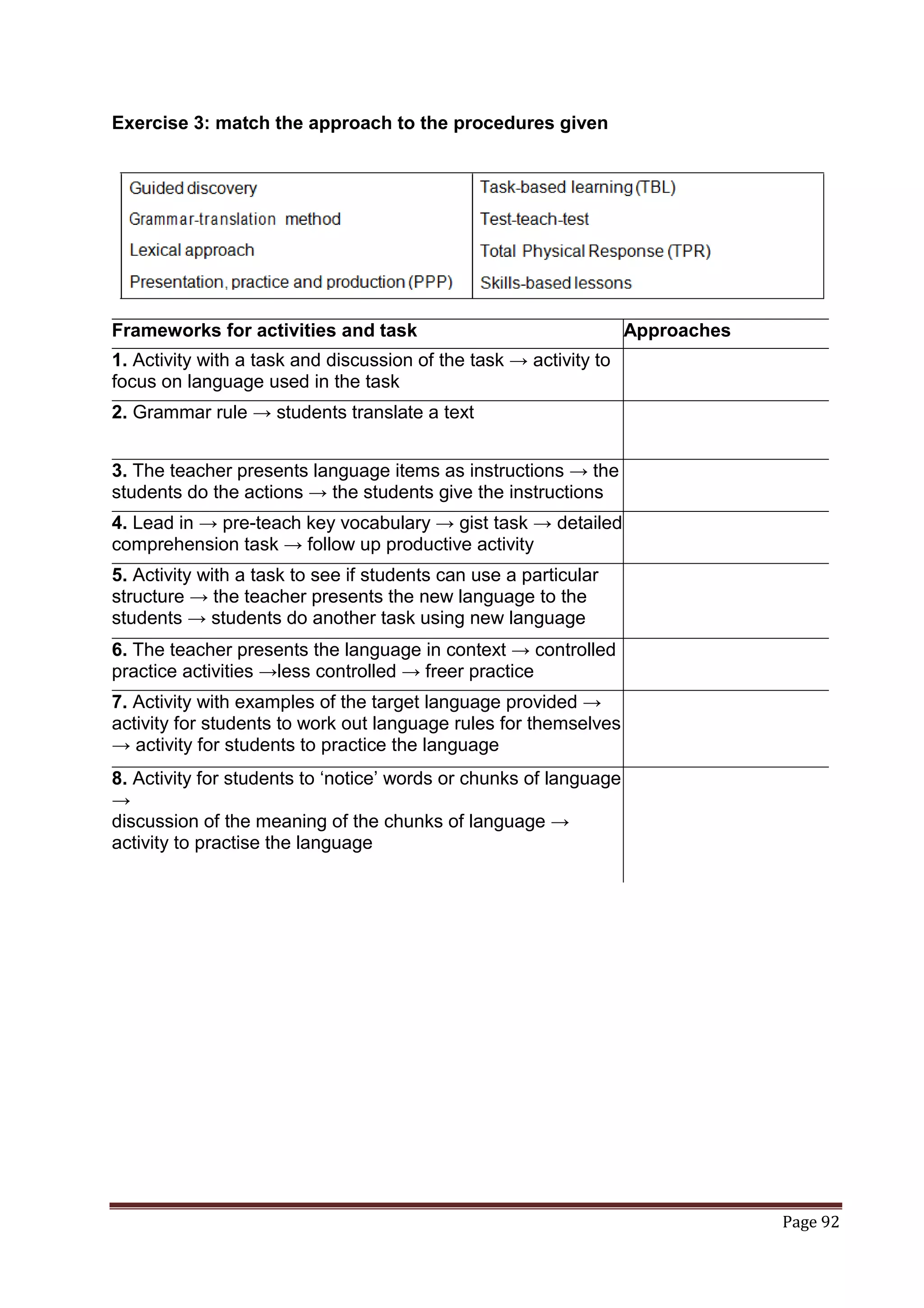
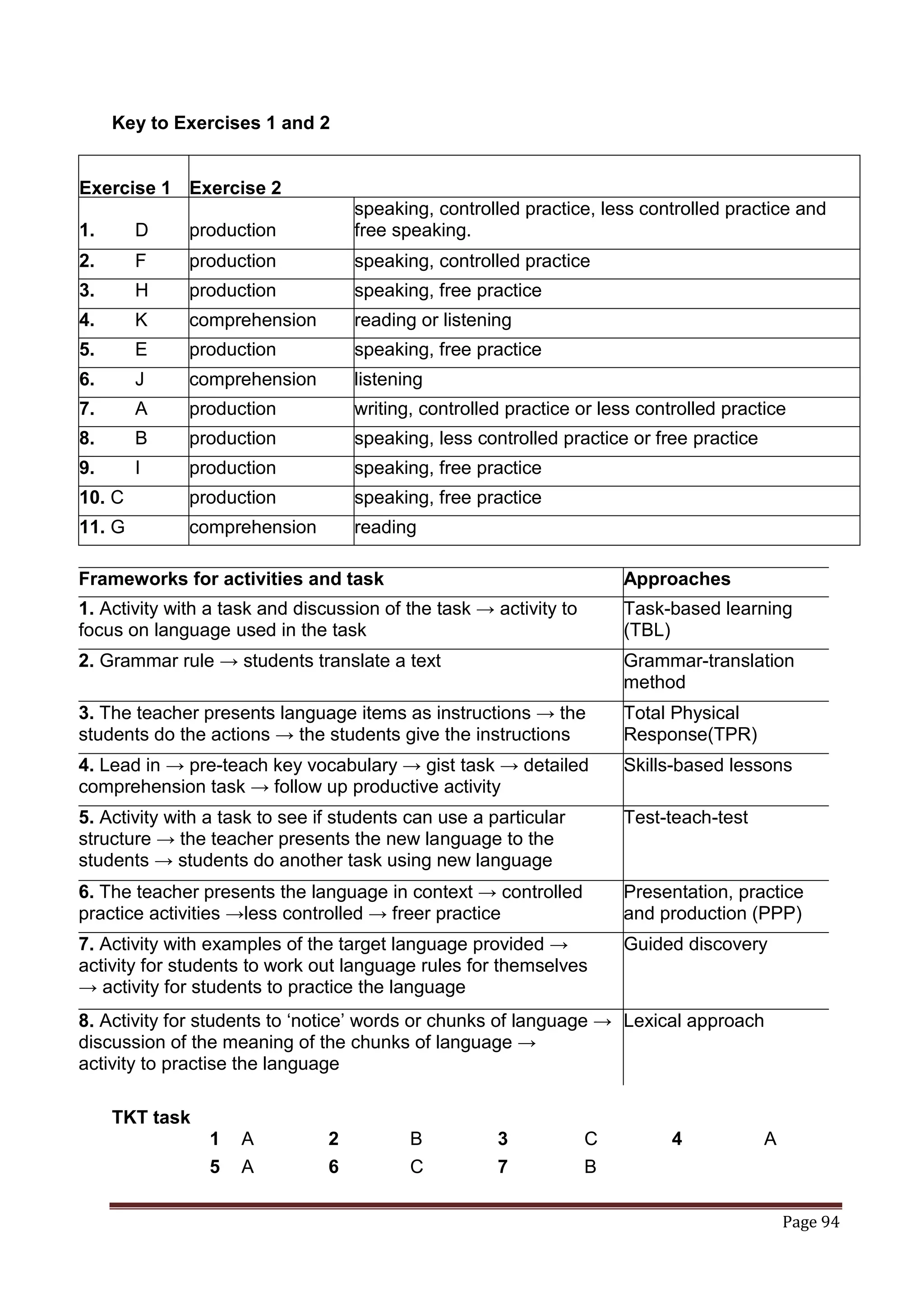
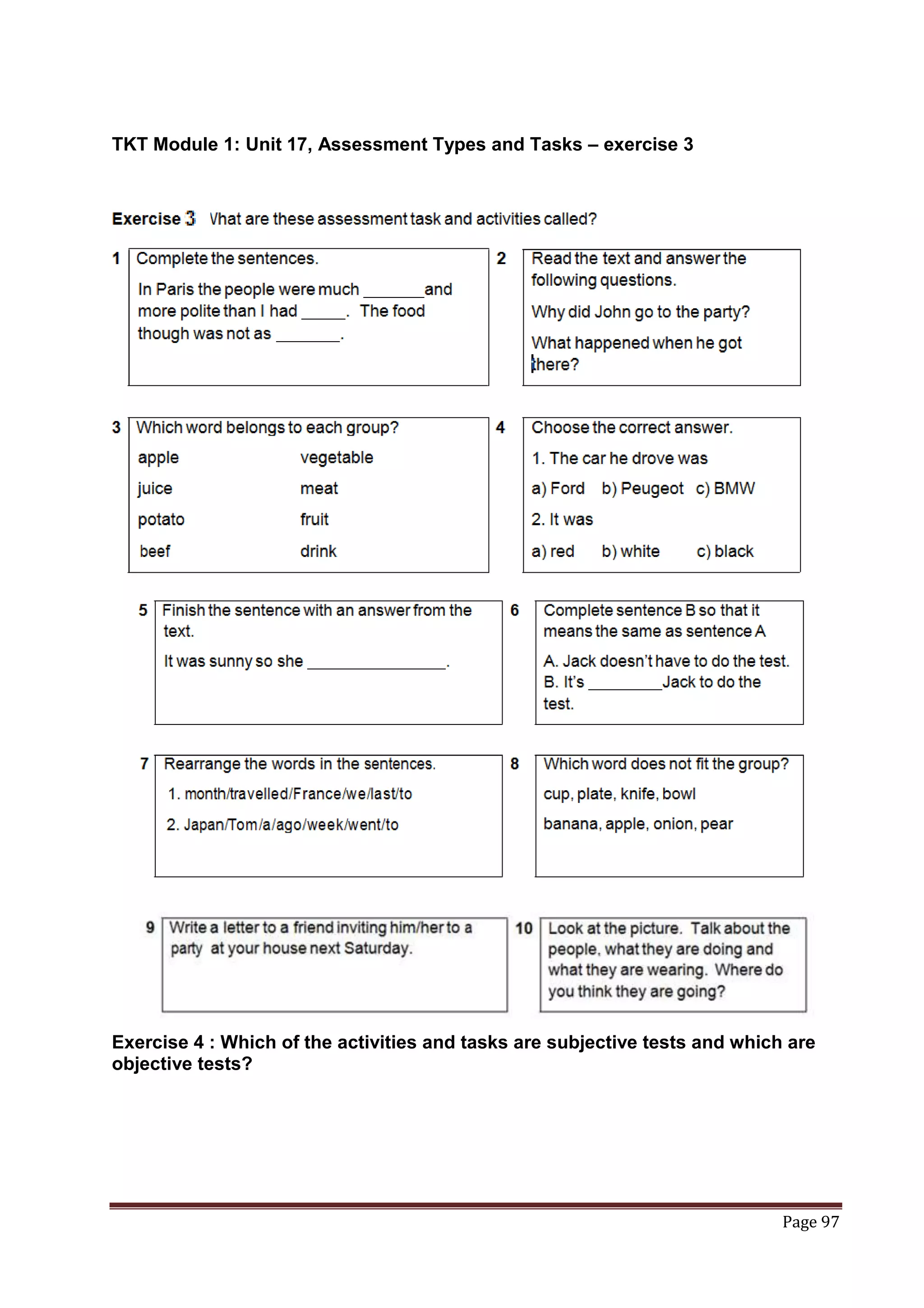
The document provides information about a book that aims to help candidates prepare and do well on the TKT (Teaching Knowledge Test) exam. The book is divided into three chapters that correspond to the three modules on the TKT exam. It contains practice exercises and tasks similar to those on the real TKT exam to help candidates understand the structure and learn tips to achieve the highest band score of 4. An English teacher from New York is quoted saying this book was a powerful tool that helped him feel confident enough to get band 4 on the TKT exam.