More Related Content Similar to Tissue Types.pdf Similar to Tissue Types.pdf (20) 2. 2
Introduction
• Similar cells with a common function are
called tissues.
• The study of tissues is called histology.
• There are four (4) primary or major tissue types:
1. Epithelial Tissue
2. Connective Tissue
3. Muscle Tissue
4. Nervous Tissue
3. 3
Intercellular Junctions
Tight junctions
• Close space between cells
• Located among cells that
form linings
Desmosomes
• Form “spot welds” between cells
• Located among outer skin cells
Gap junctions
• Tubular channels between cells
• Located in cardiac muscle cells
Tight junction
Cell membrane
Cell membrane
Cell membrane
Desmosome
Gap junction
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
4. 4
Epithelial Tissue
• General characteristics:
• Cover organs and the body
• Line body cavities
• Line hollow organs
• Have a free surface
• Have a basement membrane
• Are avascular
• Cells readily divide
• Cells tightly packed
• Cells often have desmosomes
• Function in protection, secretion, absorption, and excretion
• Classified according to cell shape and number of cell layers
5. 5
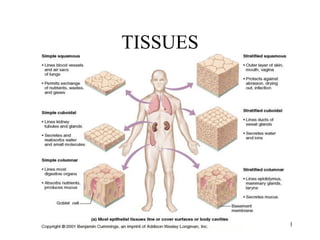
Epithelial Tissue
• Simple squamous:
• Single layer of flat cells
• Substances pass easily through
• Line air sacs
• Line blood vessels
• Line lymphatic vessels
• Simple cuboidal:
• Single layer of cube-shaped cells
• Line kidney tubules
• Cover ovaries
• Line ducts of some glands
(b)
(a)
Free surface
of tissue
Simple
squamous
epithelium
Basement
Nucleus
Connective
tissue
Copyright
©
The
McGraw-Hill
Companies,
Inc.
Permission
required
for
reproduction
or
display.
b,d: © Ed Reschke
Nucleus
Basement
membrane
Free surface
of tissue
Simple
cuboidal
epithelium
Connective
tissue
Lumen
(a) (b)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer
6. 6
• Simple columnar:
• Single layer of elongated cells
• Nuclei usually near the basement
• Membrane at same level
• Sometimes possess cilia
• Sometimes possess microvilli
• Often have goblet cells
• Line uterus, stomach, intestines
• Pseudostratified columnar:
• Single layer of elongated cells
• Nuclei at two or more levels
• Appear striated
• Often have cilia
• Often have goblet cells
• Line respiratory passageways
Nucleus
Basement
membrane
Microvilli
(free surface
of tissue)
Connective
tissue
Mucus
Cytoplasm
Goblet cell
(a) (b)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer.
(a) (b)
Cilia
(free surface
of tissue)
Goblet cell
Basement
membrane
Nucleus
Connective
tissue
Cytoplasm
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Dennis Strete, photographer
Epithelial Tissue
7. 7
• Stratified squamous:
• Many cell layers
• Top cells are flat
• Can accumulate keratin
• Outer layer of skin
• Line oral cavity, vagina, and
anal canal
• Stratified cuboidal:
• 2-3 layers
• Cube-shaped cells
• Line ducts of mammary glands,
sweat glands, salivary glands, and
the pancreas
Basement
membrane
Layer of
dividing
cells
Connective
tissue
Free surface
of tissue
Squamous
cells
(b)
(a)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer
(a) (b)
Stratified
cuboidal
epithelium
Free surface
of tissue
Lumen
Basement
membrane
Connective
tissue
Nucleus
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer.
Epithelial Tissue
8. 8
• Stratified columnar:
• Top layer of elongated cells
• Cube-shaped cells in deeper
layers
• Line part of male urethra and
part of pharynx
• Transitional:
• Many cell layers
• Cube-shaped and elongated
cells
• Line urinary bladder,
ureters, and part of urethra
(b)
(a)
Lumen
Stratified
columnar
epithelium
Connective
tissue
Basement
membrane
Free surface
of tissue
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer
Stretched
transitional
epithelium
Basement
membrane
Underlying
connective tissue
Basement
membrane
Underlying
connective tissue
Unstretched
transitional
epithelium
(b)
(a)
(d)
(c)
Free surface
of tissue
Free surface
of tissue
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b,d: © Ed Reschke
Epithelial Tissue
9. 9
Glandular Epithelium
• Composed of cells that are specialized to produce and
secrete substances
• There are two (2) types:
• Endocrine glands are ductless (key word: hormone)
• Exocrine glands have ducts
• Unicellular exocrine gland:
• Composed of one cell
• Goblet cell
• Multicellular exocrine gland:
• Composed of many cells
• Sweat glands, salivary glands, etc.
• Simple and compound
10. 10
Structural Types of
Exocrine Glands
Duct
Secretory portion
Tissue surface
Simple tubular Simple branched
tubular
Simple branched
alveolar
Simple coiled
tubular
Compound tubular Compound alveolar
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
11. 11
Types of Glandular Secretions
• Merocrine Glands
• Fluid product
• Salivary glands
• Pancreas gland (?)
• Sweat glands
•Serous Fluid
•Mucus
• Apocrine Glands
• Cellular product
• Portions of cells
• Mammary glands
• Ceruminous glands
• Holocrine Glands
• Secretory products
• Whole cells
• Sebaceous glands
(a) Merocrine gland (b) Apocrine gland (c) Holocrine gland
Secretion
Pinched off
portion of cell
(secretion)
Intact
cell
Disintegrating cell
and its contents
(secretion)
New cell
forming by
mitosis and
cytokinesis
12. 12
Connective Tissues
• General characteristics:
• Most abundant tissue type
• Many functions:
• Bind structures
• Provide support and protection
• Serve as frameworks
• Fill spaces
• Store fat
• Produce blood cells
• Protect against infections
• Help repair tissue damage
• Have an extracellular matrix
• Have varying degrees of vascularity
• Have cells that usually divide
13. 13
Connective Tissue
Major Cell Types Present
• Fibroblasts
• Fixed cell
• Most common cell
• Large, star-shaped
• Produce fibers
• Macrophages
• Wandering cell
• Phagocytic
• Important in injury or
infection
• Mast cells
• Fixed cell
• Release heparin
• Release histamine
14. 14
Connective Tissue
Fiber Types Present
• Collagenous fibers
• Thick
• Composed of collagen
• Great tensile strength
• Abundant in dense CT
• Hold structures together
• Tendons, ligaments
• Elastic fibers
• Bundles of microfibrils
embedded in elastin
• Fibers branch
• Elastic
• Vocal cords, air passages
• Reticular fibers
• Very thin collagenous fibers
• Highly branched
• Form supportive networks
15. 15
Connective Tissues
• Connective Tissue Proper:
• Loose connective tissue
• Adipose tissue
• Reticular connective tissue
• Dense connective tissue
• Elastic connective tissue
• Specialized Connective Tissue:
• Cartilage
• Bone
• Blood
16. 16
Connective Tissue Types
• Loose Connective Tissue
• Mainly fibroblasts
• Fluid to gel-like matrix
• Collagenous fibers
• Elastic fibers
• Bind skin to structures
• Beneath most epithelia
• Blood vessels nourish
nearby epithelial cells
• Between muscles
• Adipose Tissue
• Adipocytes
• Cushions
• Insulates
• Store fats
• Beneath skin
• Behind eyeballs
• Around kidneys and heart
Elastic
fiber
(a) (b)
Collagenous
fiber
Fibroblast
Ground
substance
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Dennis Strete, photographer
Fat droplet
(a) (b)
Nucleus
Cell
membrane
Cytsol
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Dennis Strete, photographer
17. 17
Connective Tissue Types
• Reticular Connective Tissue
• Composed of reticular fibers
• Supports internal organ walls
• Walls of liver, spleen,
lymphatic organs
• Dense Connective Tissue
• Packed collagenous fibers
• Elastic fibers
• Few fibroblasts
• Bind body parts together
• Tendons, ligaments, dermis
• Poor blood supply
Collagenous
fibers
Fibroblast
White blood
cell
(a) (b)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer
Fibroblasts
Collagenous
fibers
(a) (b)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Dennis Strete, photographer
18. 18
Connective Tissue Types
• Elastic Connective Tissue
• Abundant in elastic fibers
• Some collagenous fibers
• Fibroblasts
• Attachments between bones
• Walls of large arteries, airways, heart
• Bone (Osseous Tissue)
• Solid matrix
• Supports
• Protects
• Forms blood cells
• Attachment for muscles
• Skeleton
• Osteocytes in lacunae
Elastic fibers
Collagenous
fibers
Fibroblast
(a) (b)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer
21
Canaliculi
Osteocyte
in lacuna
Central
canal
Lamella
Nucleus
Osteocyte
Cell process in
canaliculus
(a) (b)
Osteon
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Dennis Strete, photographer
19. 19
Connective Tissue Types
• Cartilage
• Rigid matrix
• Chondrocytes in lacunae
• Poor blood supply
• Three (3) types:
• Hyaline Cartilage
• Elastic Cartilage
• Fibrocartilage
• Hyaline cartilage
• Most abundant
• Ends of bones
• Nose, respiratory passages
• Embryonic skeleton
• Elastic cartilage
• Flexible
• External ear, larynx
• Fibrocartilage
• Very tough
• Shock absorber
• Intervertebral discs
• Pads of knee and pelvic girdle
20. 20
Connective Tissue Types
Three (3) types of cartilage:
Hyaline Cartilage Elastic Cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Chondrocyte
Nucleus
Extracellular
matrix
(a) (b)
Lacuna
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer
Chondrocyte
Elastic fibers
Nucleus
Extracellular
matrix
(a) (b)
Lacuna
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer
Chondrocyte
Nucleus
Collagenous
fiber
Extracellular
matrix
(a) (b)
Lacuna
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer
21. 21
Connective Tissue Types
• Blood
• Fluid matrix called plasma
• Red blood cells
• White blood cells
• Platelets
• Transports
• Defends
• Involved in clotting
• Throughout body in blood
vessels
• Heart
Red blood
cells
Plasma
(extracellular
matrix of blood)
Platelets
White blood
cell
(a) (b)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer
22. 22
Types of Membranes
1. Serous Membranes
• Line body cavities that
do not open to the
outside
• Reduce friction
• Inner lining of thorax
and abdomen
• Cover organs of thorax
and abdomen
• Secrete serous fluid
2. Mucous Membranes
• Line tubes and organs
that open to outside world
• Lining of mouth, nose,
throat, etc.
• Secrete mucus
3. Cutaneous Membranes
• Covers body
• Skin
4. Synovial Membranes
• Composed entirely of
connective tissue
• Lines joints
• There are four (4) types of epithelial membranes:
23. 23
Muscle Tissues
• General characteristics:
• Muscle cells also called
muscle fibers
• Contractile
• Three (3) types:
• Skeletal muscle
• Smooth muscle
• Cardiac muscle
• Skeletal muscle
• Attached to bones
• Striated
• Voluntary
• Smooth muscle
• Walls of organs
• Skin
• Walls of blood vessels
• Involuntary
• Non-striated
• Cardiac muscle
• Heart wall
• Involuntary
• Striated
• Intercalated discs
24. 24
Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscle Smooth Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Striations
Portion of a
muscle fiber
Nuclei
(a) (b)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
(a) (b)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Dennis Strete, photographer
Intercalated
disc
Nucleus
Striations
(a) (b)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer
25. 25
Nervous Tissue
• Found in brain, spinal cord, and
peripheral nerves
• Functional cells are neurons
• Neuroglial cells support and
bind nervous tissue components
• Sensory reception
• Conduction of nerve impulses
Cell
membrane
Neuroglial
cells
Cytoplasm
Cellular
process
Nucleus
(a) (b)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
b: © Ed Reschke.