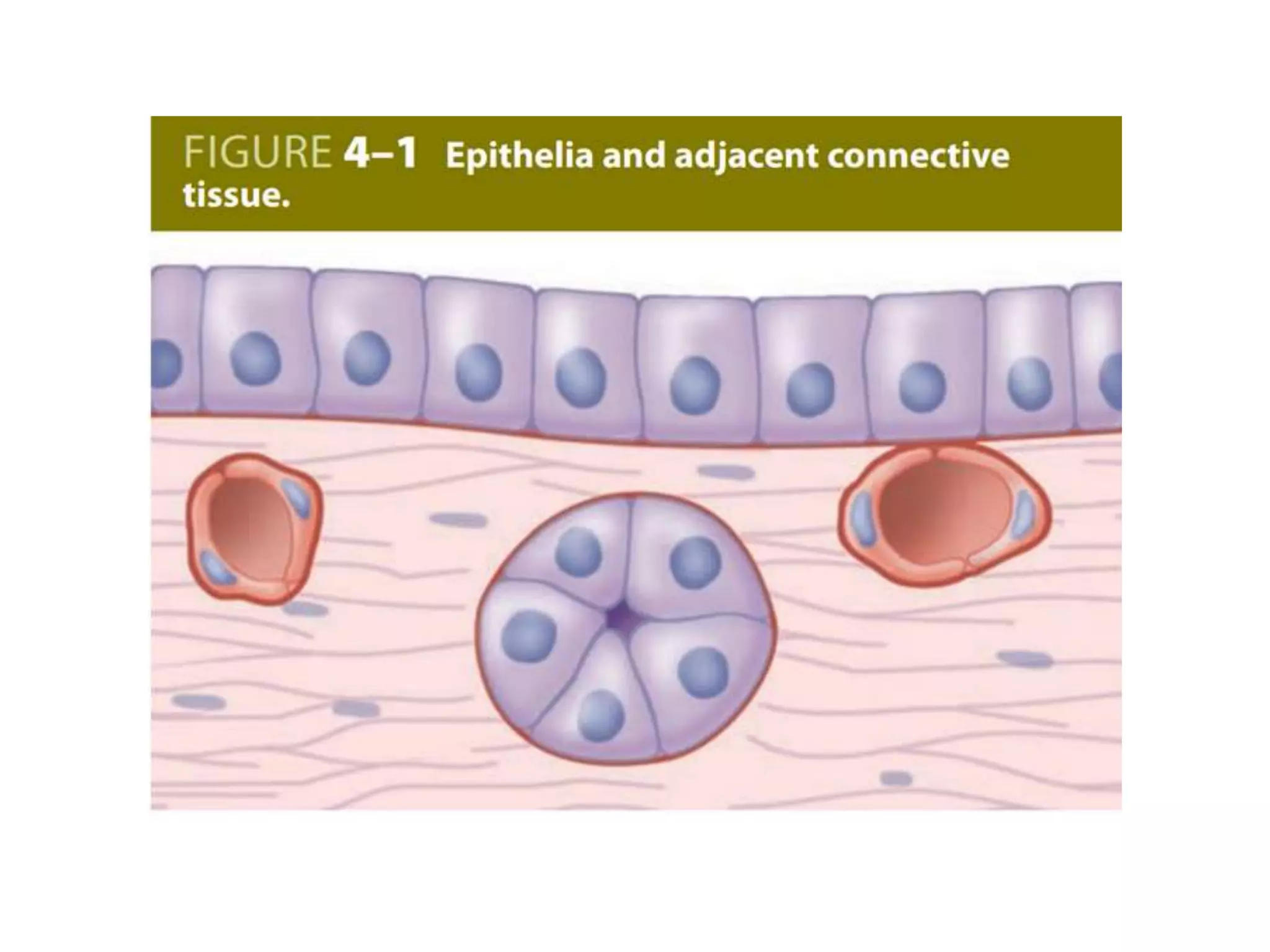
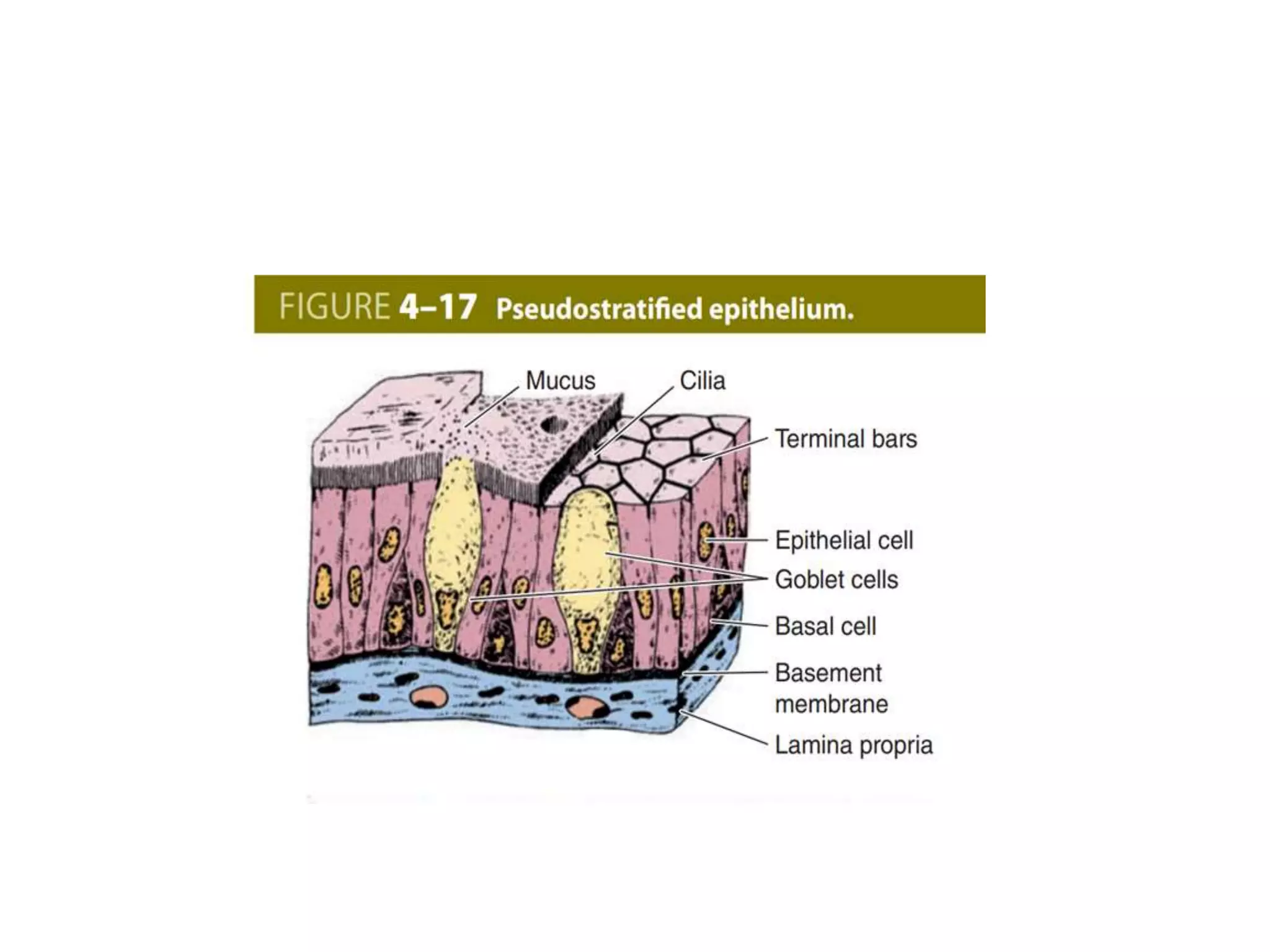
Epithelial tissue lines body surfaces and forms glands. It has several key functions, including protection, absorption, and secretion. Epithelial cells are closely packed and polarized. They communicate through junctions and microstructures. There are several types of epithelia defined by their cell shape, number of layers, and location in the body. Epithelial tissues contain secretory cells that produce molecules for exocrine and endocrine glands.