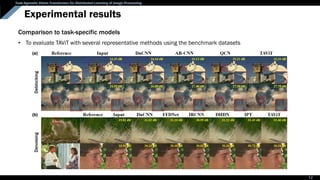
The document presents a task-agnostic vision transformer (TAVIT) designed for distributed learning in image processing, allowing multiple clients to train a single network using local data. It aims to enhance generalization and computational efficiency by learning various image processing tasks without sharing local data and combines task-specific client networks with a task-agnostic server model. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach compared to traditional methods in multi-task learning scenarios.

![Task-Agnostic Vision Transformer for Distributed Learning of Image Processing
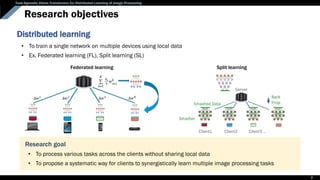
Research objectives
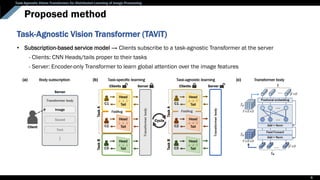
Distributed learning
• To train a single network on multiple devices using local data
• Ex. Federated learning (FL), Split learning (SL)
[1] https://proandroiddev.com/federated-learning-e79e054c33ef [2] Singh, Abhishek, et al. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.09145 (2019).
2
Federated learning Split learning
Parallel communication between each client Decomposition of a network into clients & server
Usually consider a common task such as classification](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tiptavitpresentation-221230122617-641d49de/85/TIP_TAViT_presentation-pdf-2-320.jpg)
![Task-Agnostic Vision Transformer for Distributed Learning of Image Processing
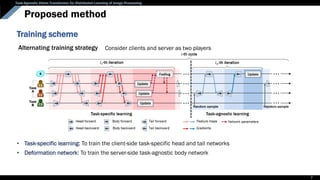
Background: Multi-task learning (MTL)
[1] https://pyimagesearch.com/2022/08/17/multi-task-learning-and-hydranets-with-pytorch/ [2] Kendall et al., 2017
4
• To enhance the generalization of model on one task by learning shared representations of related tasks
• To improve computational efficiency and reduces the overfitting problem
Unlike existing MTL models that learn similar tasks,
Our model is to learn multiple different image processing tasks
[1] [2]
Existing models](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tiptavitpresentation-221230122617-641d49de/85/TIP_TAViT_presentation-pdf-4-320.jpg)
![Task-Agnostic Vision Transformer for Distributed Learning of Image Processing
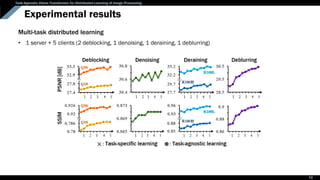
Background: Image processing using Transformer
[1] Vaswani, Ashish, et al. NeurIPS (2017). [2] Dosovitskiy, Alexey, et al. ICLR 2021. [3] Chen, Hanting, et al. CVPR 2021.
A network to solve sequence-to-
sequence tasks by using long-range
dependencies via self-attention
Transformer
5
An encoder-only architecture to
learn image recognition tasks
Vision Transformer (ViT)
NLP CV
Image Processing Transformer (IPT)
CNN heads/tails & Transformer body to
learn low-level vision tasks
Our model is to design a distributed learning framework using Transformer
that does not require centralized data
Distribute learning](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tiptavitpresentation-221230122617-641d49de/85/TIP_TAViT_presentation-pdf-5-320.jpg)