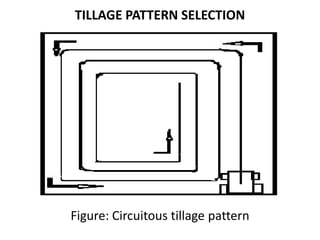
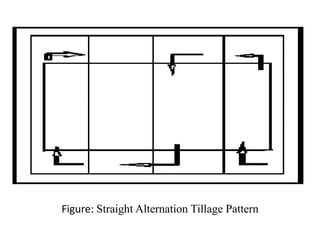
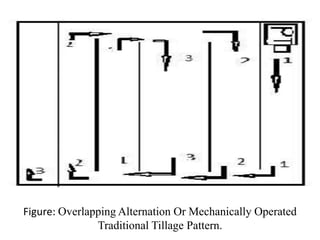
The research aimed to identify an effective tillage pattern that optimizes fuel economy in Bangladesh's agricultural sector. The study compared three tillage patterns and found that the traditional mechanically-operated pattern required the least time and fuel consumption. Results indicated that while traditional and alternating patterns had the same fuel use, the traditional method was most efficient overall, suggesting the need for further research on a larger scale.