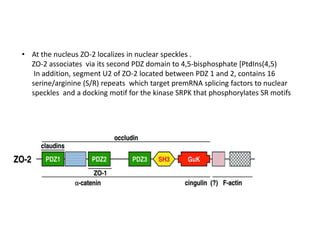
Tight junctions play an important role in regulating gene expression and cell proliferation. Two key proteins, ZO-1 and ZO-2, shuttle between the tight junctions and the nucleus in proliferating cells. ZO-1 expression is higher in contact-inhibited cells and suppresses proliferation. ZO-2 localizes to nuclear speckles in proliferating cells to regulate pre-mRNA splicing. The nuclear transport of these proteins allows tight junctions to influence gene transcription and cell cycle progression.