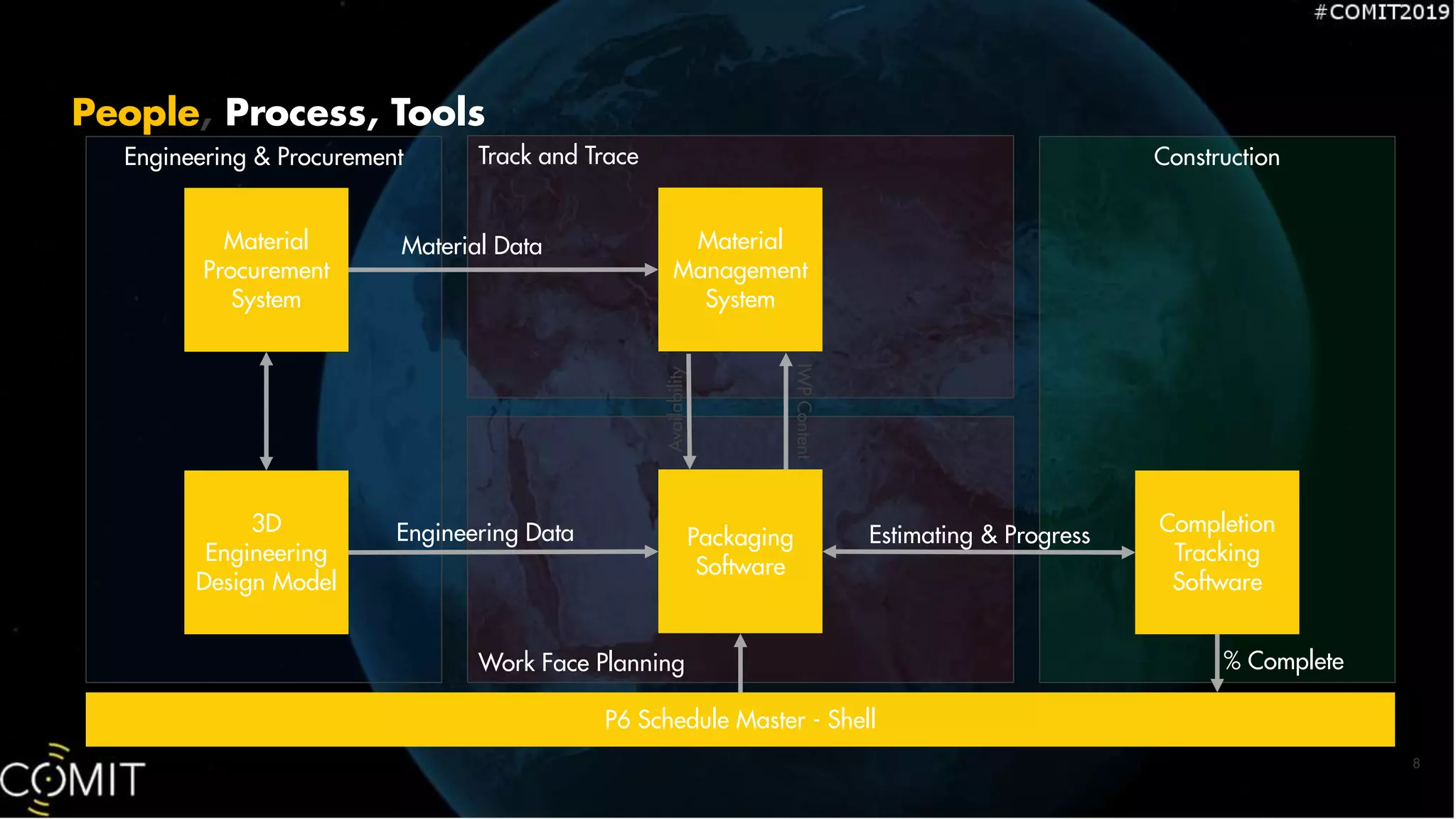
The document details the implementation of the Tiger AO4 project at Shell's manufacturing site in Geismar, Louisiana, which aims to enhance production capacity of linear alpha olefins. It emphasizes a construction strategy focused on safety, efficiency, and digital tool utilization, involving extensive planning and real-time data management to drive productivity. Key insights include the importance of early integration of software solutions and the need for strong data integrity to ensure effective project execution.