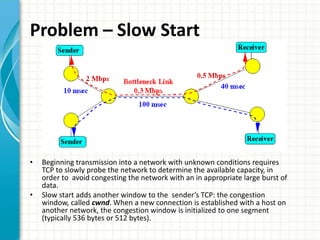
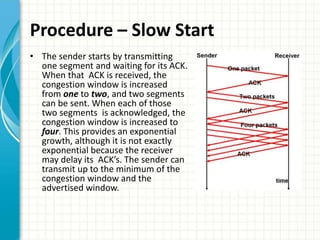
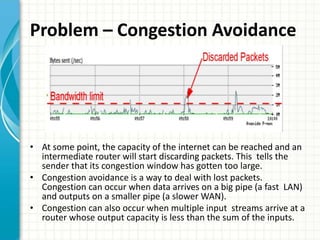
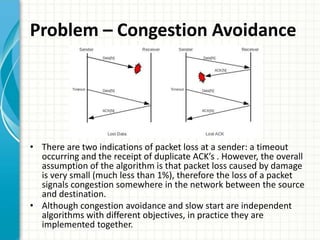
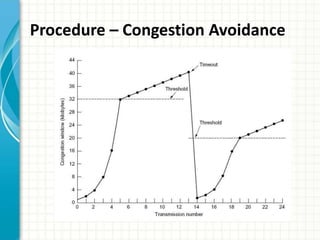
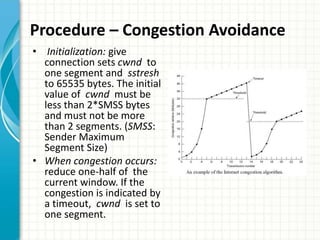
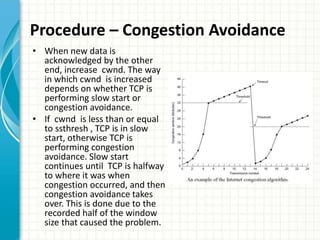
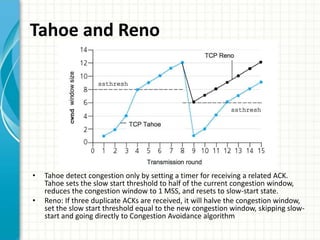
The document discusses slow start and congestion avoidance in TCP/IP. It begins by explaining the problems that slow start addresses, such as routers getting overloaded when a sender injects multiple segments before knowing the network conditions. Slow start solves this by starting transmission with a congestion window of one segment and exponentially increasing the window as acknowledgments are received. Congestion avoidance is then discussed, including how packet loss indicates the network is congested and transmission must slow down. The procedures of slow start, congestion avoidance, and how they work together are then outlined.