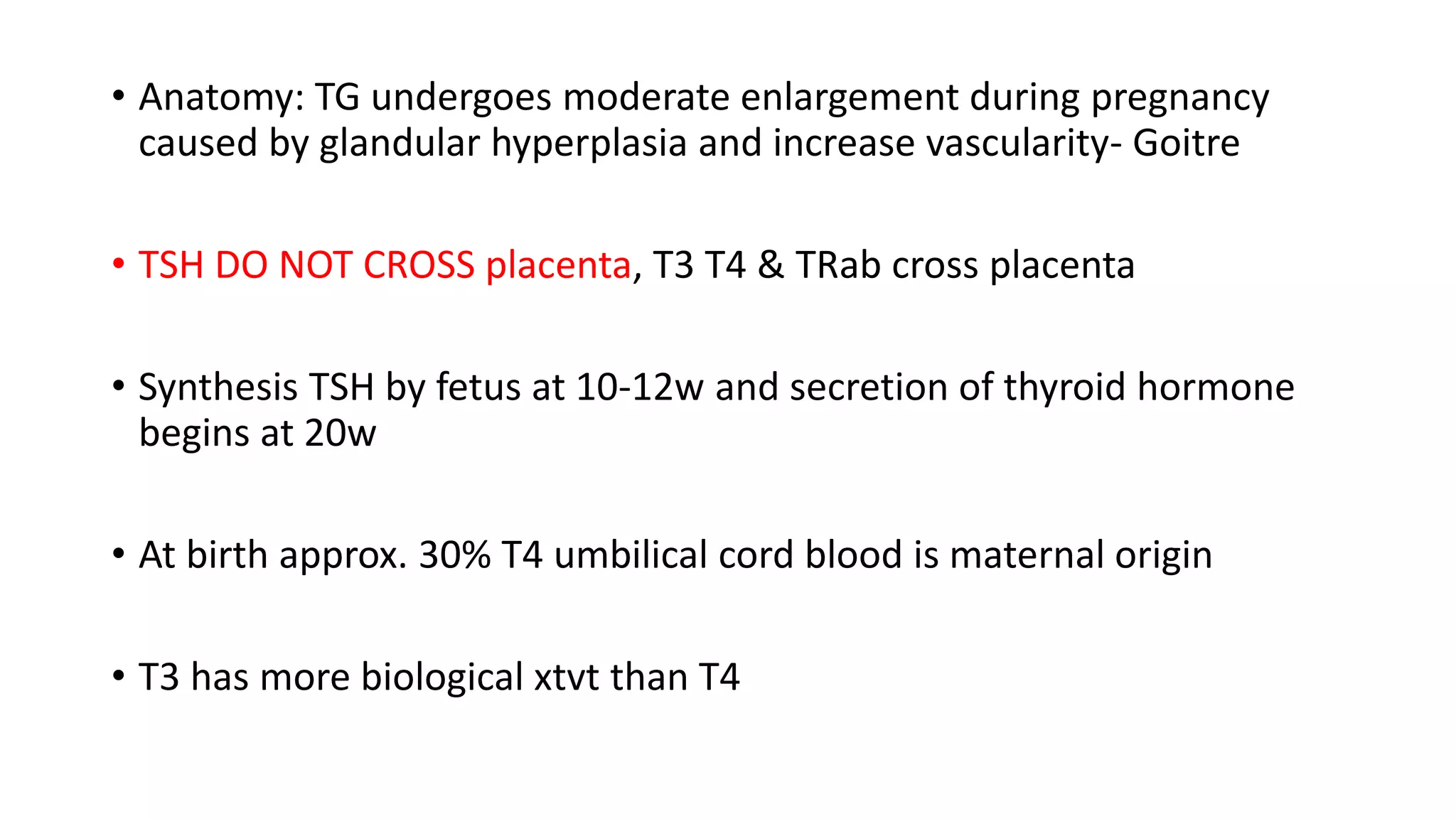
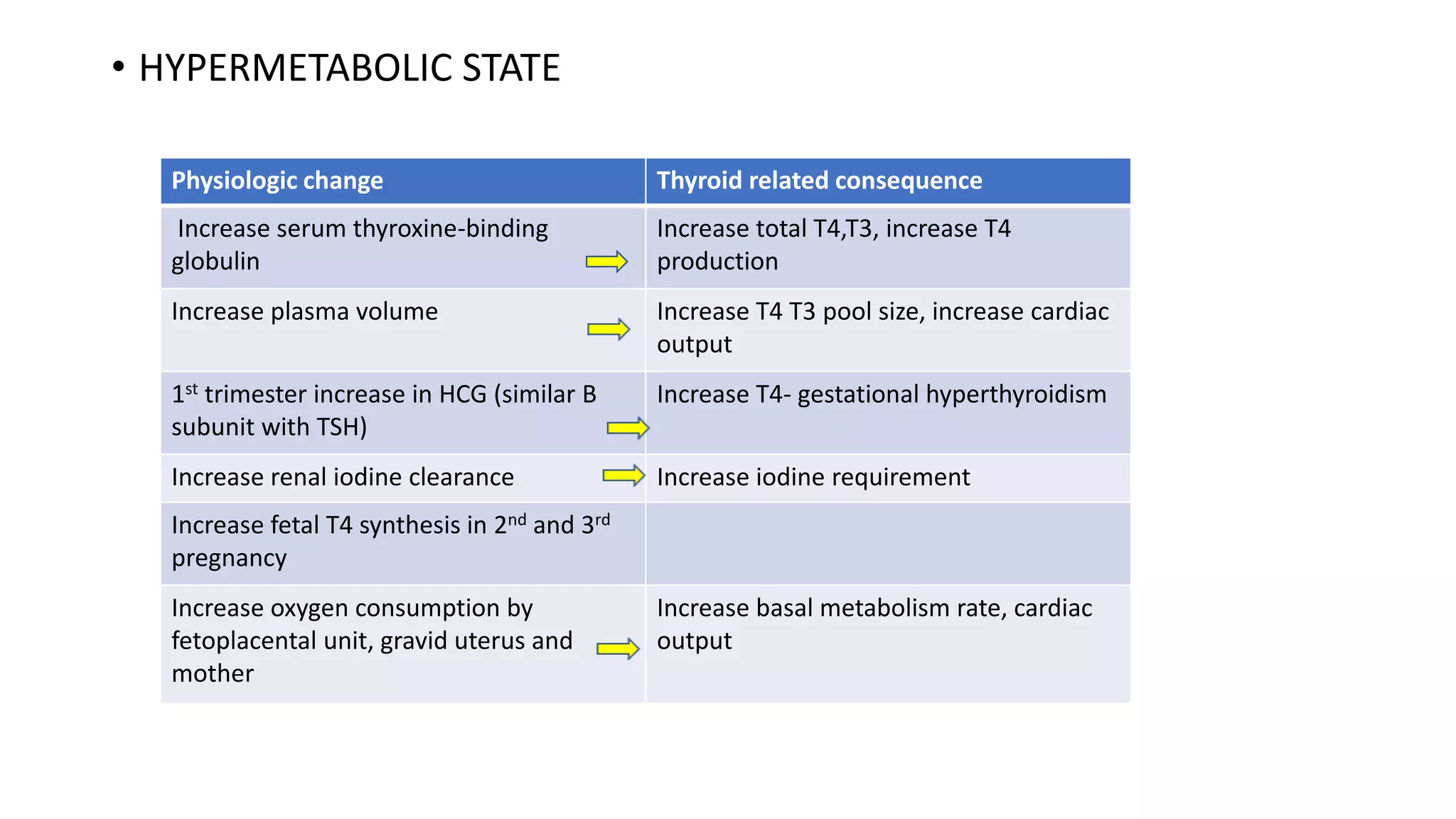
1) Thyroid hormone levels change physiologically during pregnancy, leading to changes in the thyroid gland and metabolism. The fetus's thyroid also matures during pregnancy.
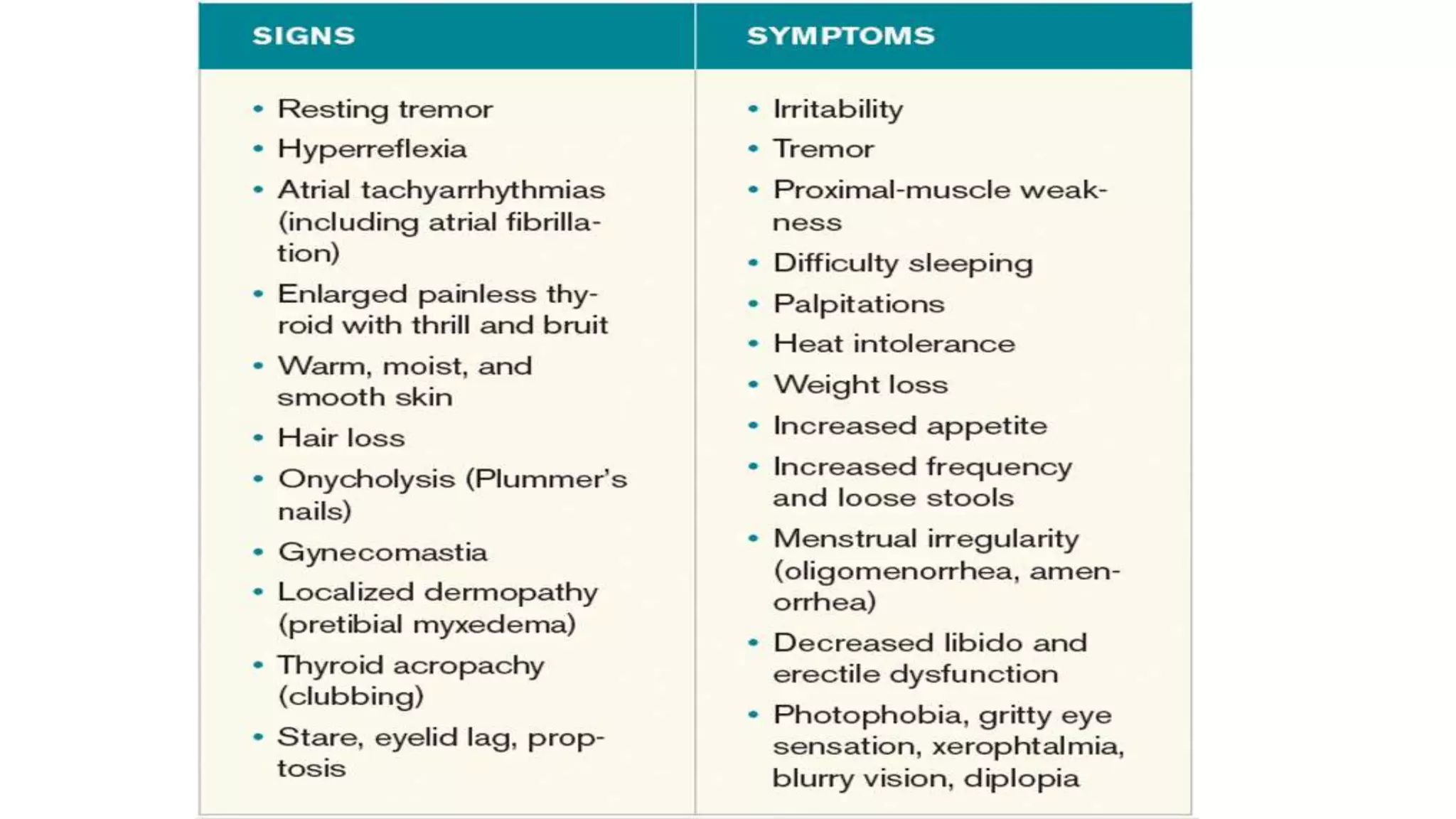
2) Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can impact maternal and fetal health, increasing risks of complications like miscarriage, preeclampsia, and preterm birth.
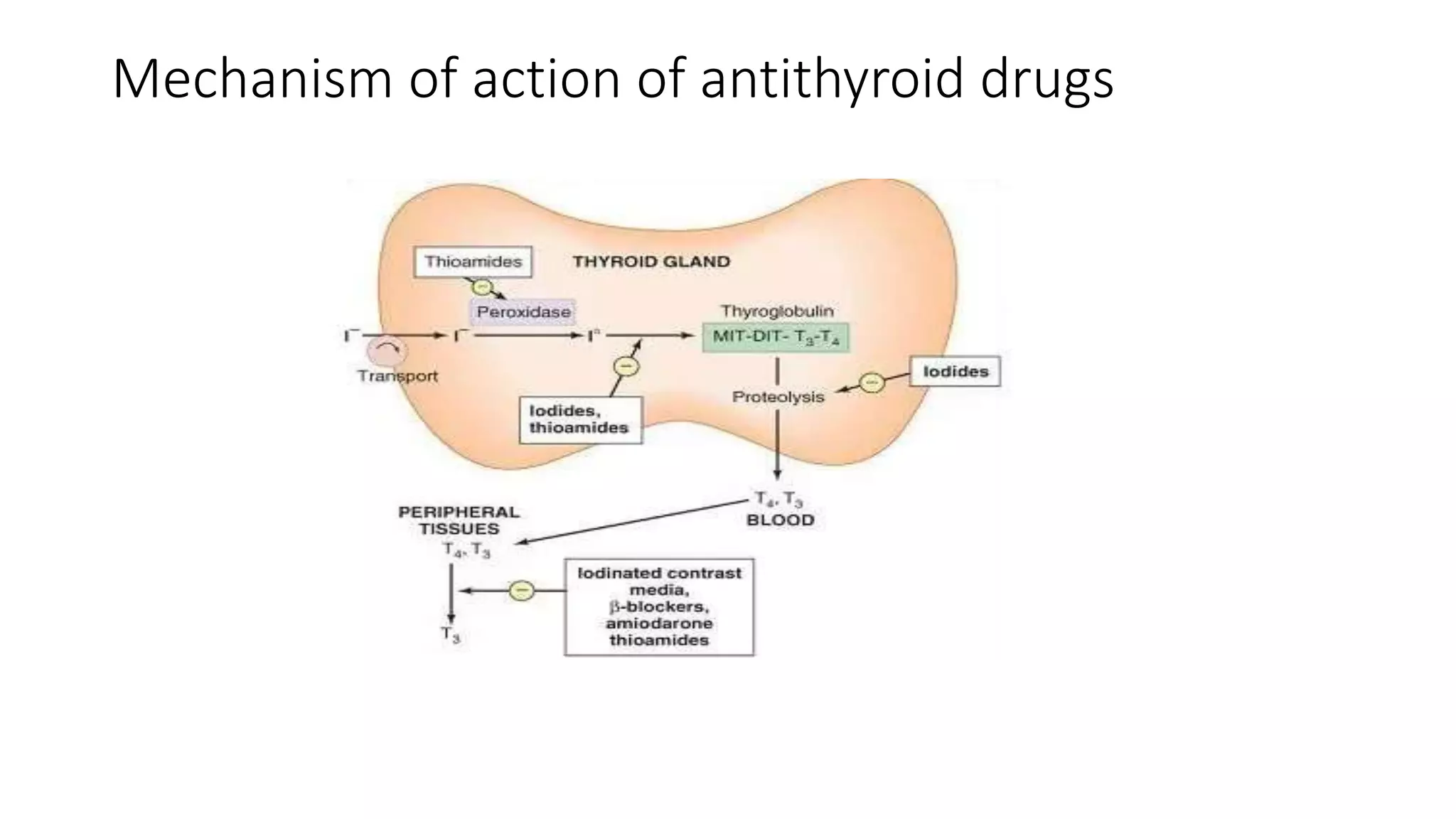
3) Graves' disease is a common cause of hyperthyroidism in pregnancy. Antithyroid medications are used for treatment but require careful management due to risks of congenital anomalies, especially with carbimazole in the first trimester.