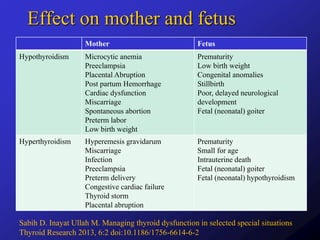
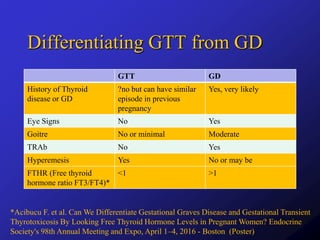
Thyroid hormones are essential for fetal development and maternal health during pregnancy, with dysfunction leading to various complications for both mother and baby. Approximately 2% of pregnancies exhibit obvious hypothyroidism, and management varies based on the type and severity of thyroid issues, including increased iodine intake and careful monitoring of thyroid hormone levels. Guidelines suggest that both overt and subclinical thyroid disease should be identified and managed appropriately to ensure optimal outcomes in pregnancy and postpartum periods.