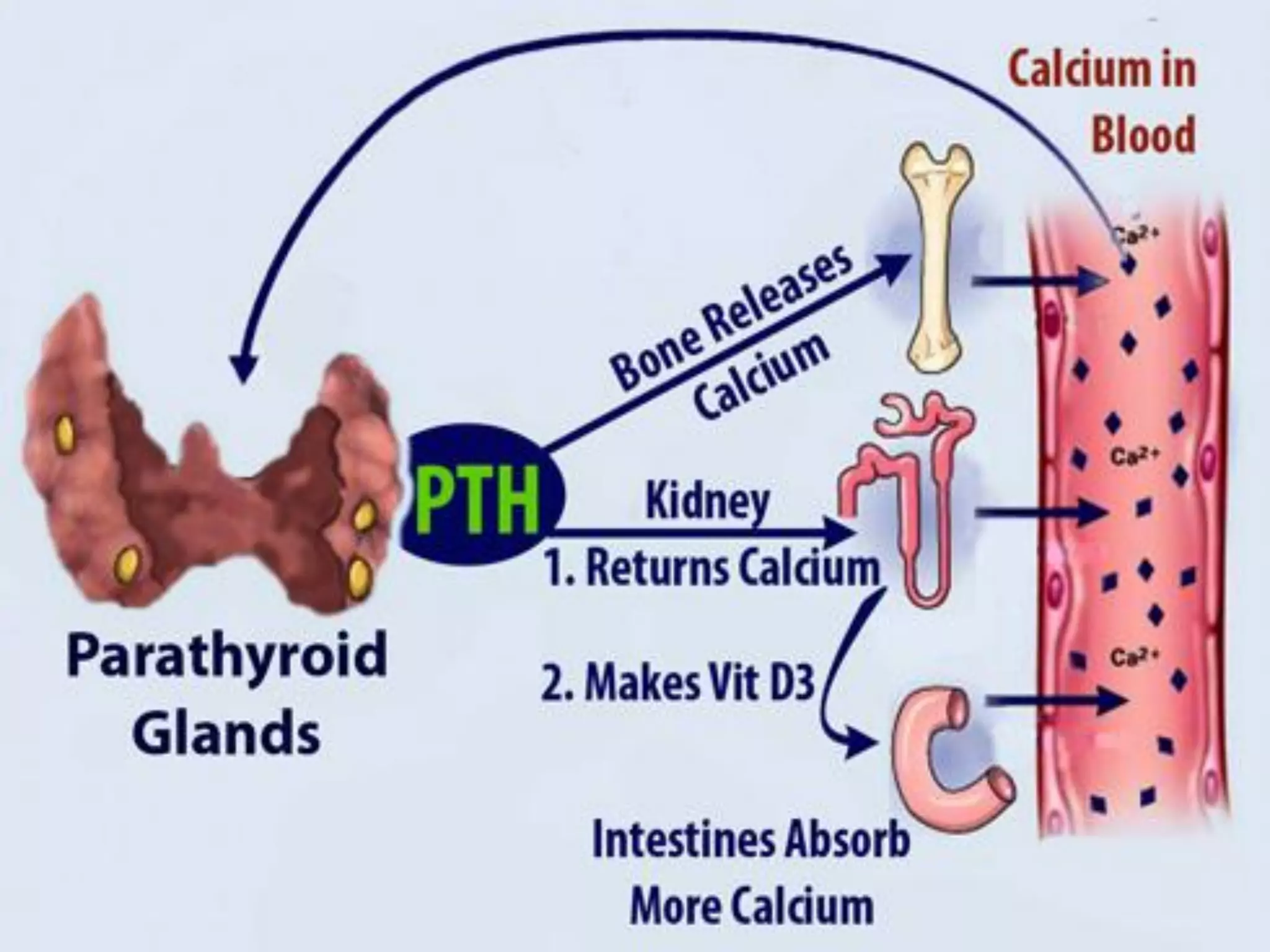
The parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck that produce parathyroid hormone (PTH), which regulates calcium and phosphate homeostasis. Conditions like hyperparathyroidism and hypoparathyroidism result from excess or decreased activity of these glands, respectively, leading to various health issues. Parathyroid tumors can cause hypercalcemia due to overproduction of PTH, which manifests in symptoms such as weakness and increased thirst in pets.