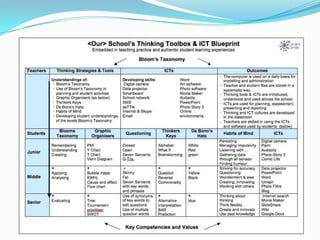
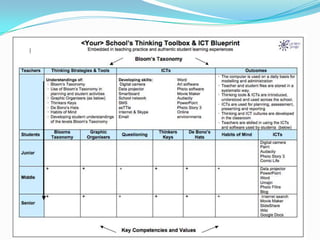
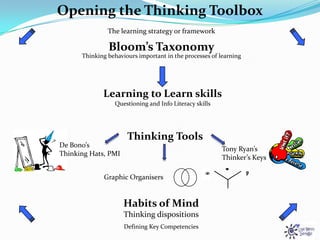
This document provides an overview of strategies and tools for developing creative and critical thinking skills. It discusses key thinking frameworks like Bloom's Taxonomy, which categorizes different thinking skills. Tools for opening the "thinking toolbox" are presented, including brainstorming, questioning techniques, and goal setting. The document also provides examples and templates for lesson planning using these thinking strategies and how to incorporate them into teaching and learning.