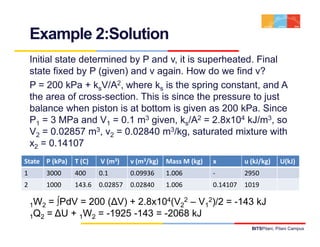
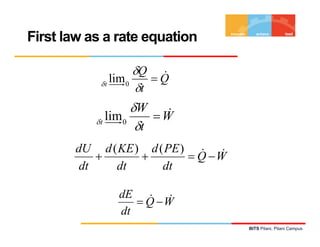
The document discusses the first law of thermodynamics as it applies to control volumes. It defines control volumes and explains that mass can cross their boundaries, so the net mass transfer into and out of the control volume must be tracked. The conservation of mass principle for control volumes is presented, along with equations relating the rate of change of mass within the control volume to the mass flow rates entering and exiting. The first law of thermodynamics is also expressed in rate equation form for a control volume with fixed mass.