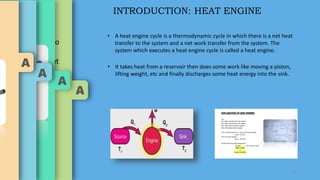
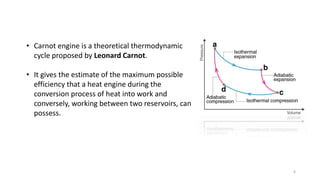
The document discusses heat engines, detailing their definition, efficiency, and classification, including a focus on the Carnot engine and cycle. It describes the first law of thermodynamics in relation to heat transfer and work done by heat engines, highlighting efficiency challenges faced by typical engines. The Carnot cycle is presented as an ideal model for achieving maximum efficiency in heat-to-work conversion.