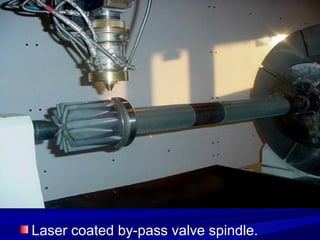
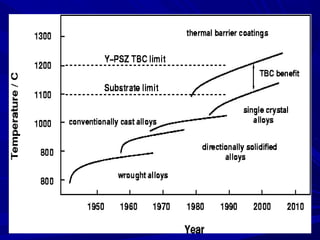
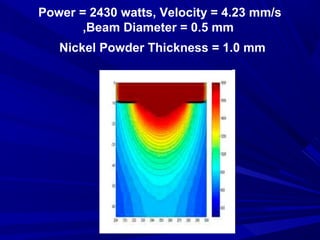
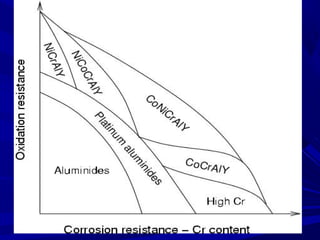
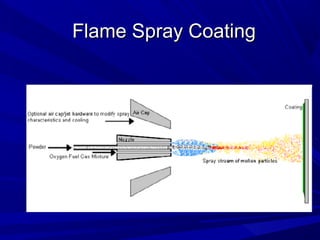
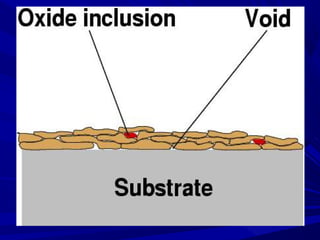
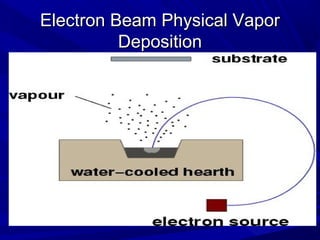
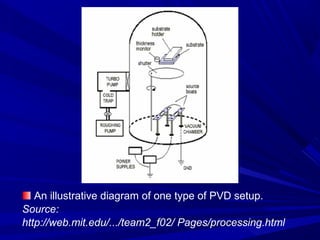
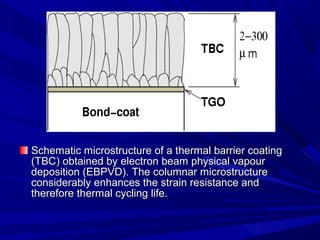
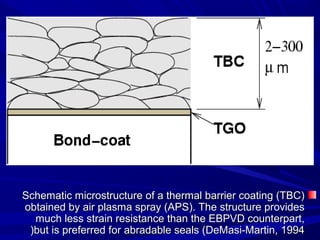
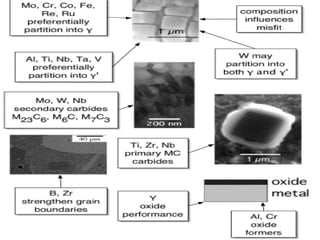
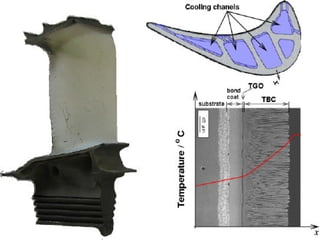
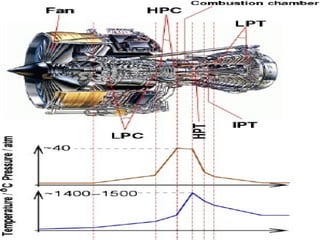
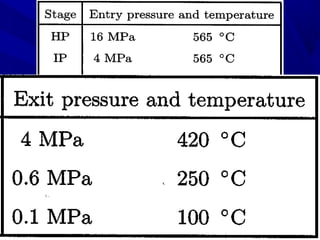
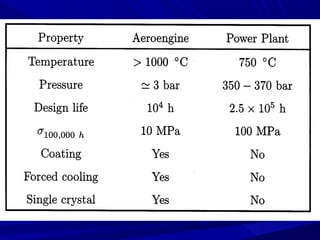
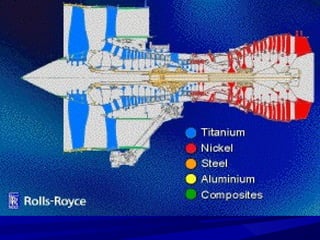
The document discusses thermal spray coatings as an essential surface engineering technique used to enhance material properties without changing their bulk composition. It outlines various surface treatment methods, including physical vapor deposition and plasma spray coatings, and their applications in improving durability, wear resistance, and thermal performance of engineering components. Key advantages include increased component life, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced operational efficiency.