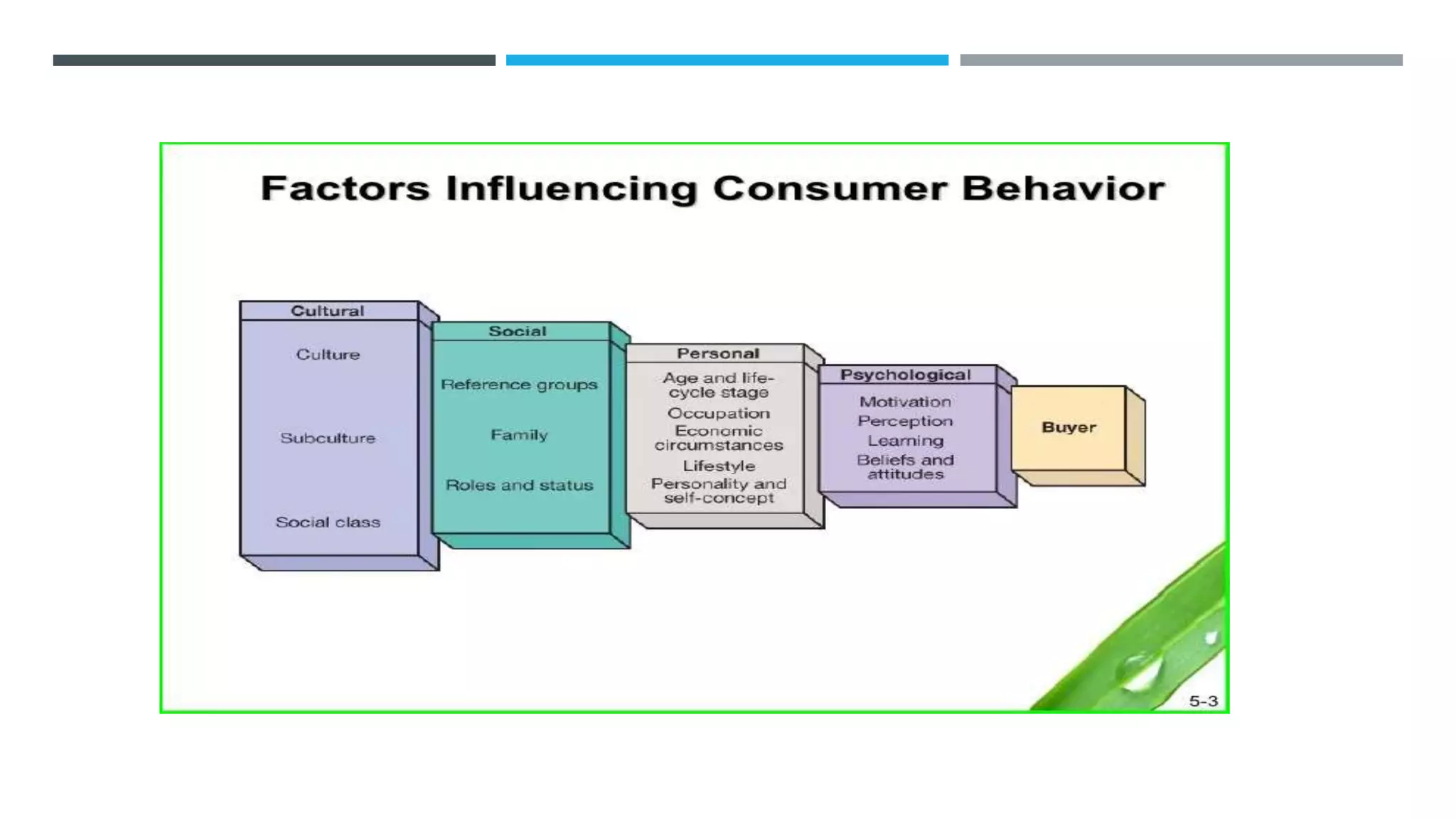
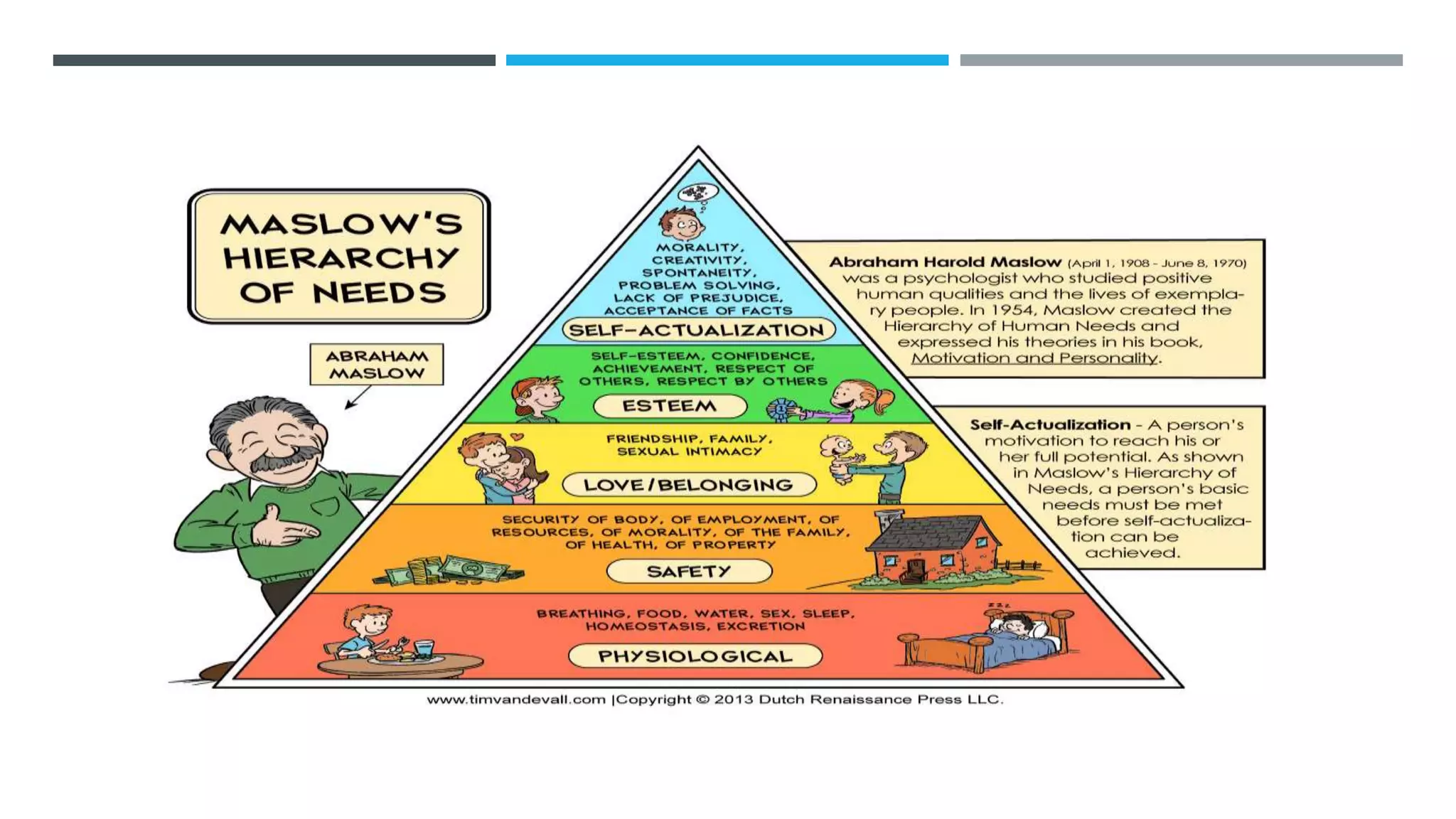
The document discusses the theory of consumer behavior, focusing on utility, which is the satisfaction derived from consuming goods, and the various cultural, social, personal, and psychological factors that influence this behavior. It explains concepts such as Maslow's hierarchy of needs, the indifference curve representing consumer preferences, and how changes in prices impact consumer decisions through the income and substitution effects. Additionally, it addresses demand curves, consumer surplus, and the paradox of value, illustrating the relationship between necessity and price.