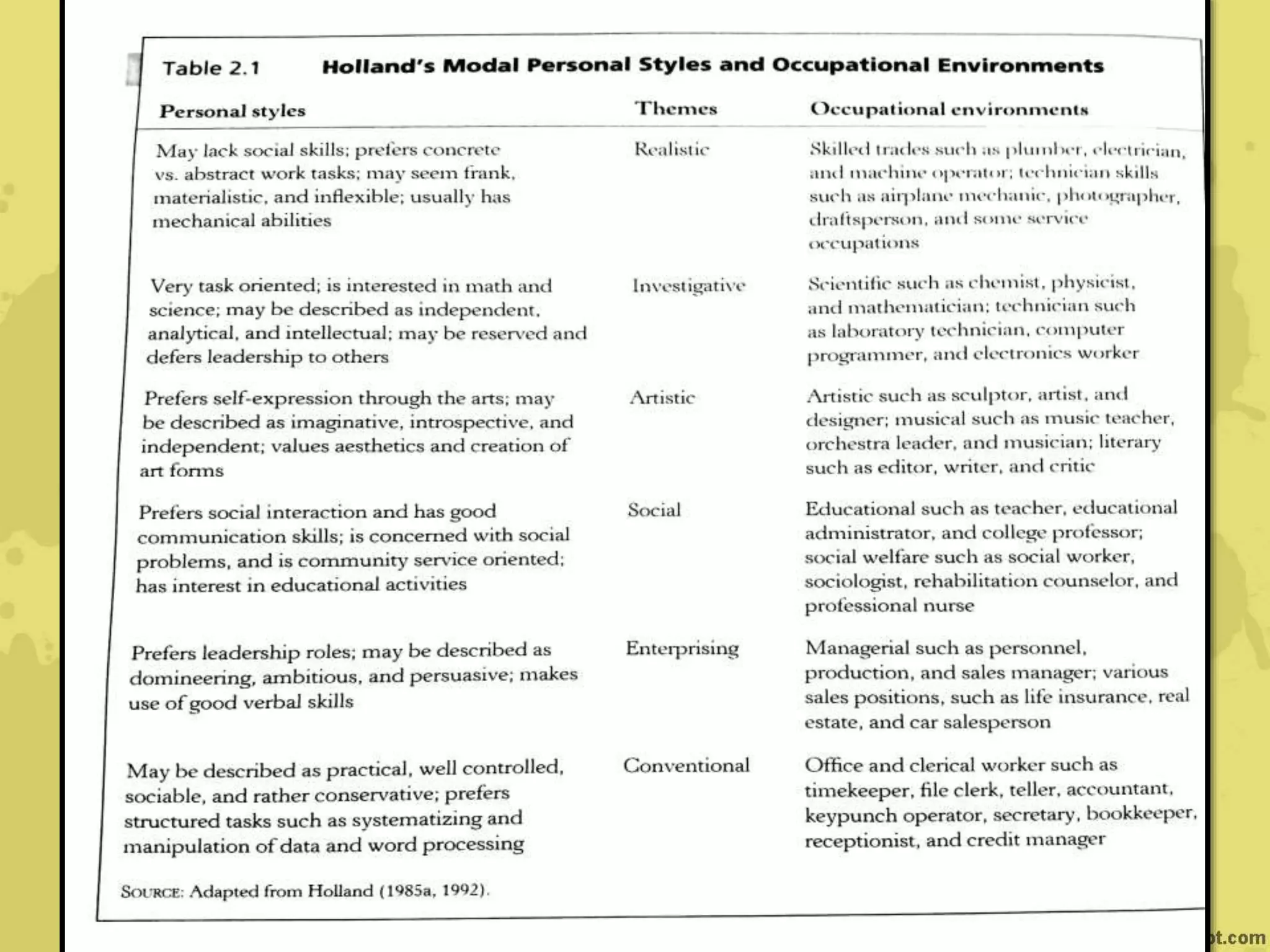
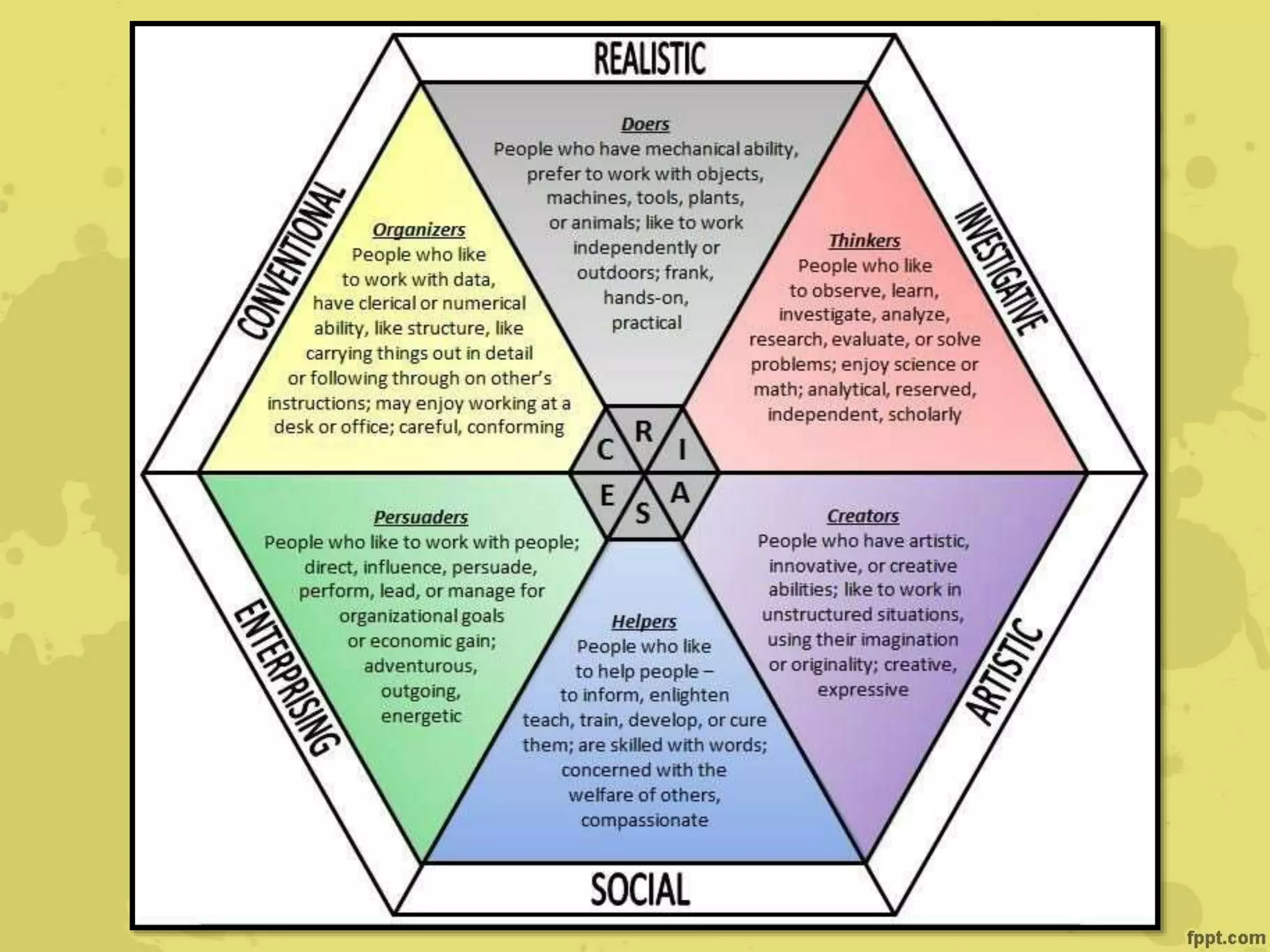
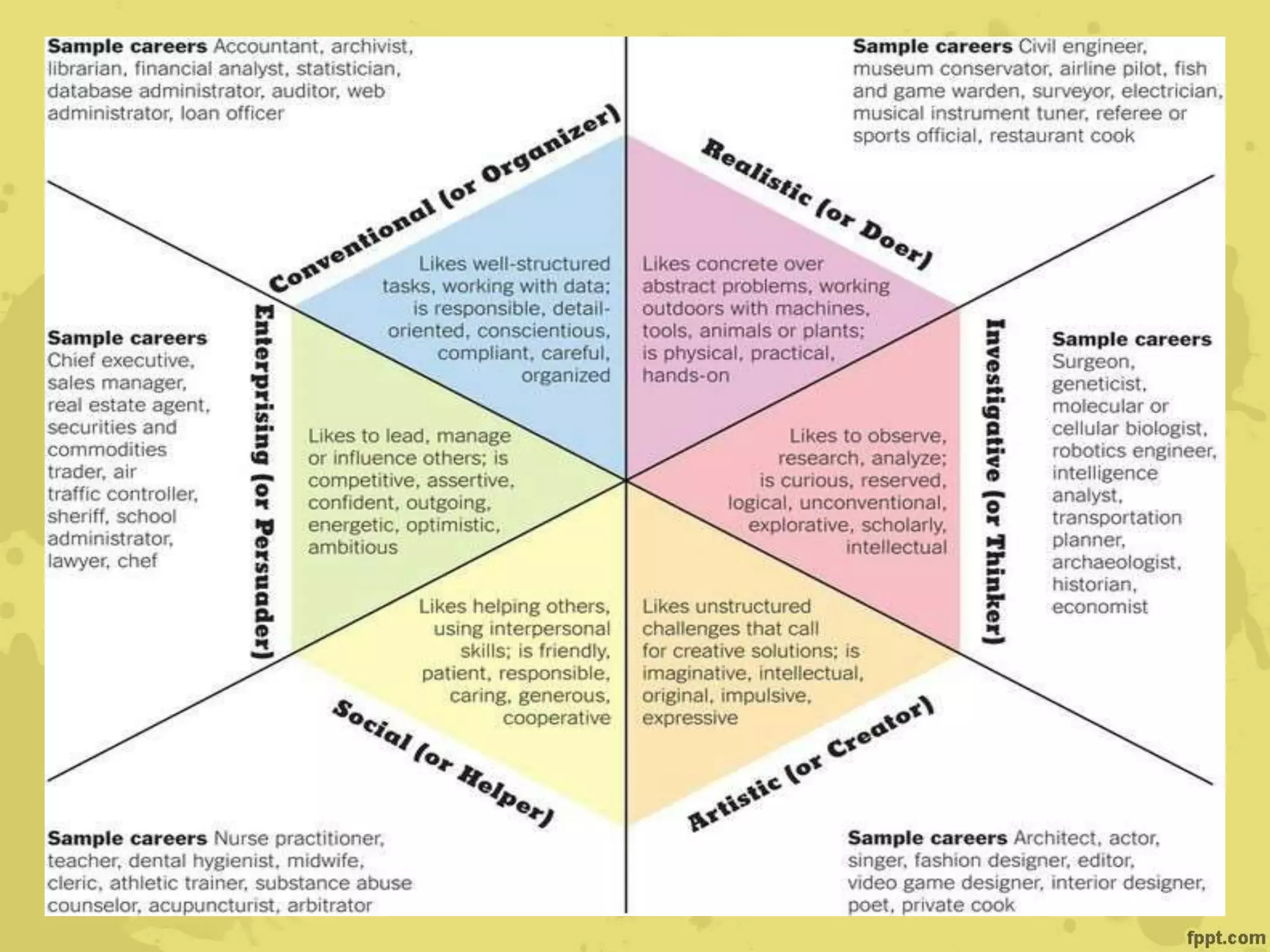
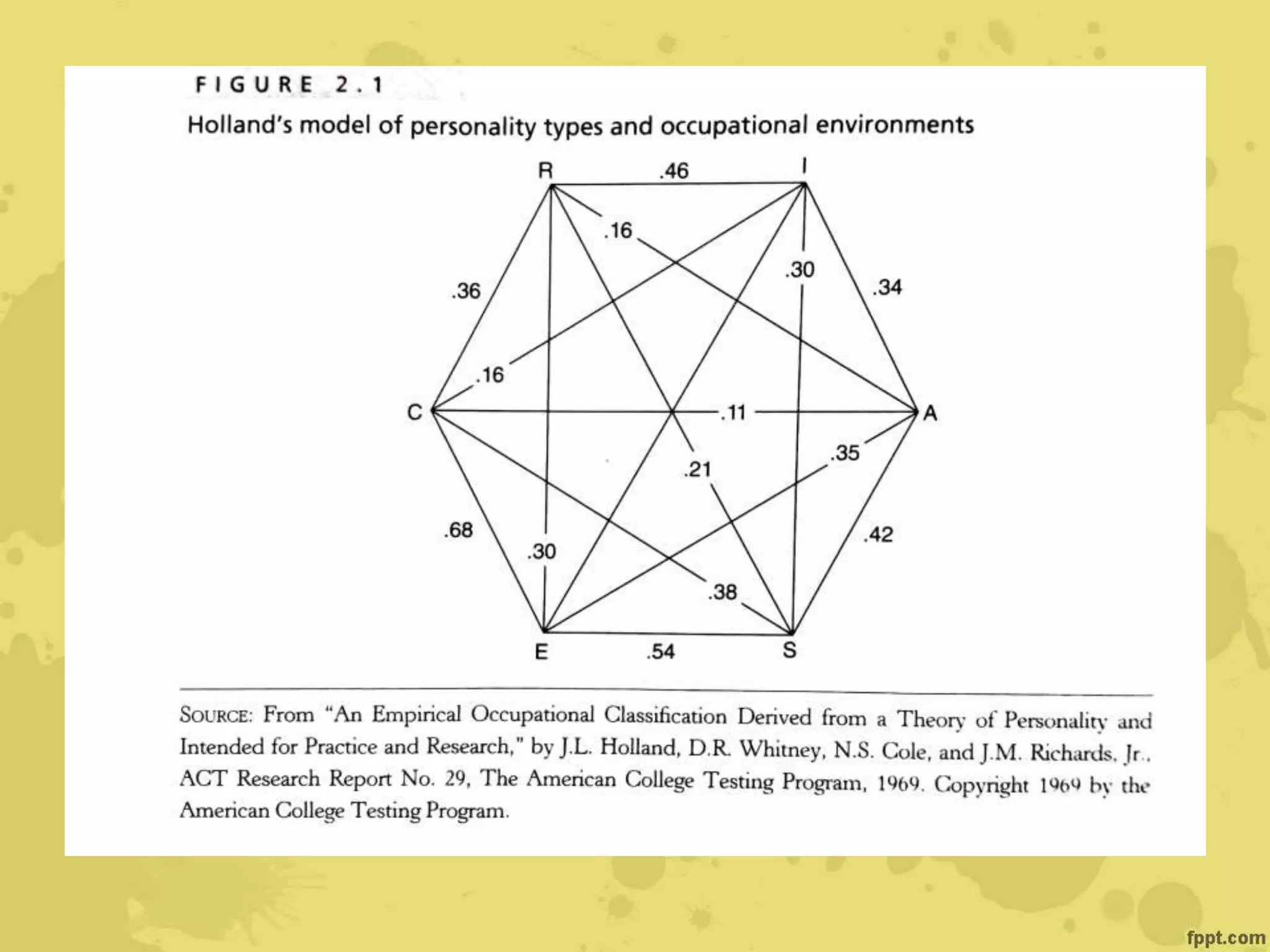
John Holland's theory proposes that individuals are attracted to certain careers based on their personalities and backgrounds. He identified six personality types - realistic, investigative, artistic, social, enterprising, and conventional - that are attracted to matching work environments. Career satisfaction depends on the congruence between one's personality type and their work. Krumboltz's social learning theory emphasizes how genetic, environmental, learning, and skills factors influence career choices over a person's lifespan. Cognitive information processing theories view career choice as involving problem-solving, decision-making, and the interaction of cognitive and affective processes.