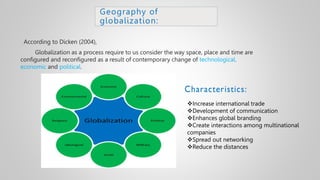
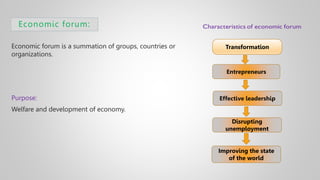
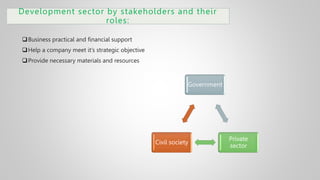
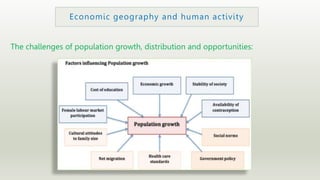
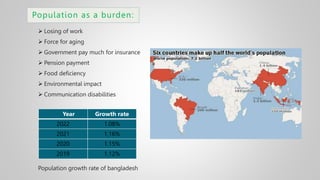
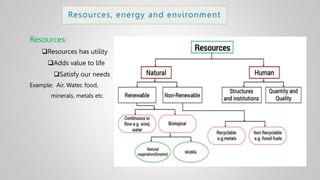
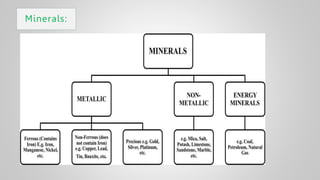
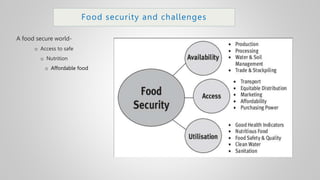
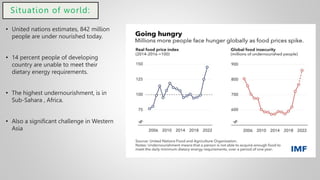
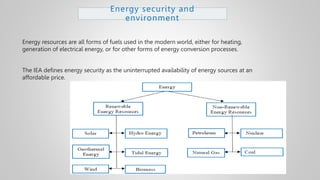
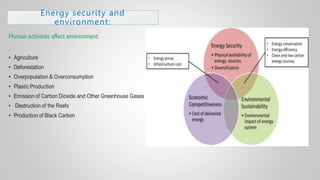
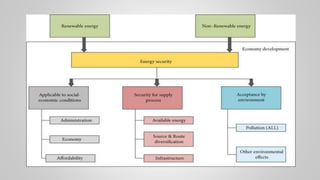
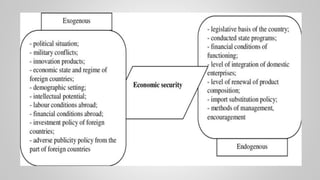
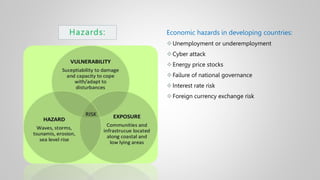
The document outlines various issues and challenges in economic development, including unemployment, poverty, and the effects of globalization, while emphasizing the roles of government and non-government stakeholders. It also addresses economic geography's impact on human activity concerning population growth, resource management, and energy security. Key points include the importance of economic zones and forums for facilitating trade and development, as well as the need for sustainable practices to ensure food and energy security in developing countries.