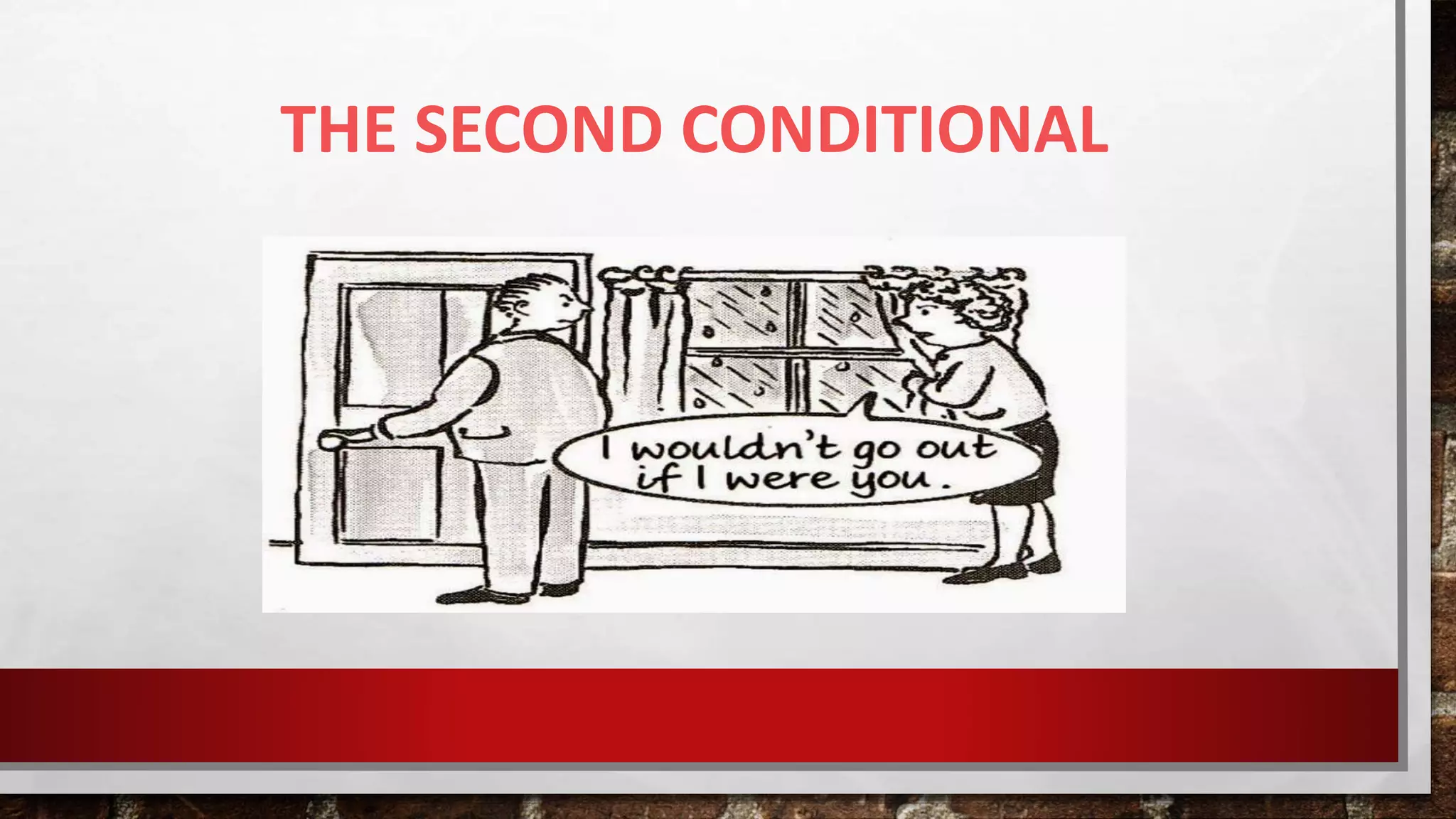
This document discusses the structure and use of the second conditional to describe hypothetical or unlikely situations. It begins by explaining that the second conditional uses past tense verbs to talk about possible present or future situations that are not real. It then provides examples of the typical "if-clause + would-clause" structure. The document outlines the specific verb tenses and forms used in the if-clause and would-clause of the second conditional construction. It also compares the second conditional to the first conditional and discusses how certain modal verbs like "might" and "could" can be used instead of "would" to express uncertainty.