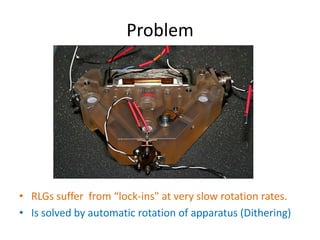
The document discusses various theories of relativity including Newtonian relativity, Einstein's theory of relativity, and Ritz's emission theory. It then describes the Sagnac effect, which is an interference phenomenon observed when light beams travel in opposite directions in a rotating frame. This effect disproved emission theory and supported relativity. The document concludes by explaining how the Sagnac effect is used in ring laser gyros to measure rotation and their use in inertial guidance systems, along with solutions to issues like lock-ins at slow rotation rates.