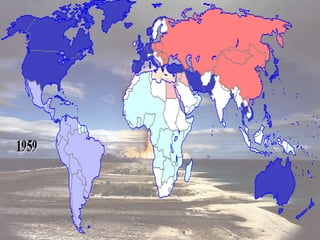
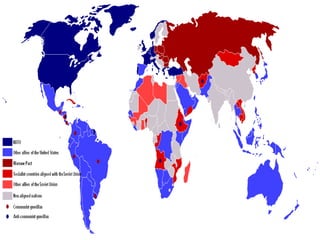
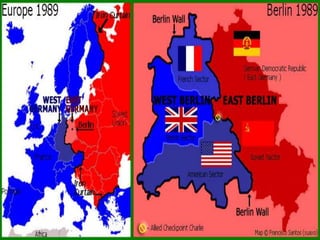
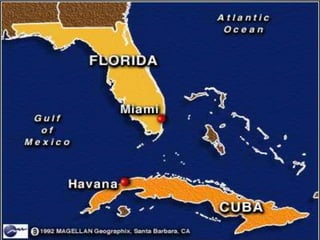
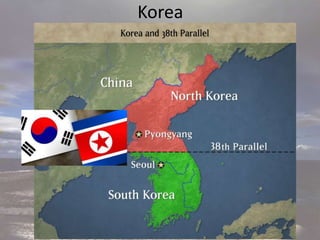
The document provides an overview of the Cold War period between the United States and USSR from 1945-1991. It discusses key events including the dropping of nuclear bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, which marked the start of the nuclear age. It also describes the ideological battle between capitalism in the West led by the US and communism in the East led by the USSR. The arms race and space race between the two superpowers is examined. Finally, the document outlines Gorbachev's reforms of perestroika and glasnost in the USSR, which ultimately led to the collapse of Soviet communism.