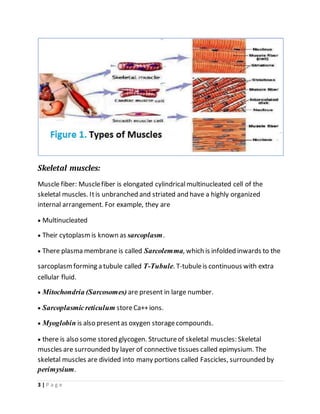
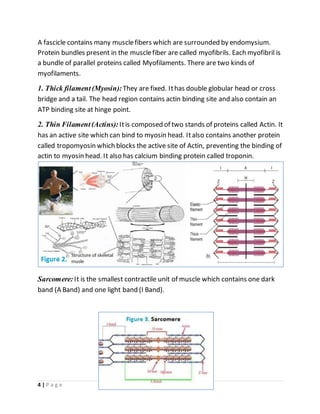
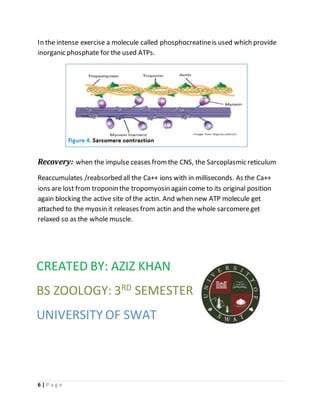
The muscular system allows for movement of the body through contraction of three main types of muscles - skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles. Skeletal muscles are striated and voluntary, attaching to bones via tendons, and composing around 40% of body weight. They contract through a sliding filament mechanism where actin and myosin filaments interact powered by ATP hydrolysis. Contraction is triggered by calcium release in the sarcoplasmic reticulum in response to neural stimulation. Relaxation occurs when calcium is reabsorbed, disengaging the filaments. In summary, the muscular system enables movement through contraction of striated skeletal muscles powered by the sliding filament interaction between actin and myosin filaments.