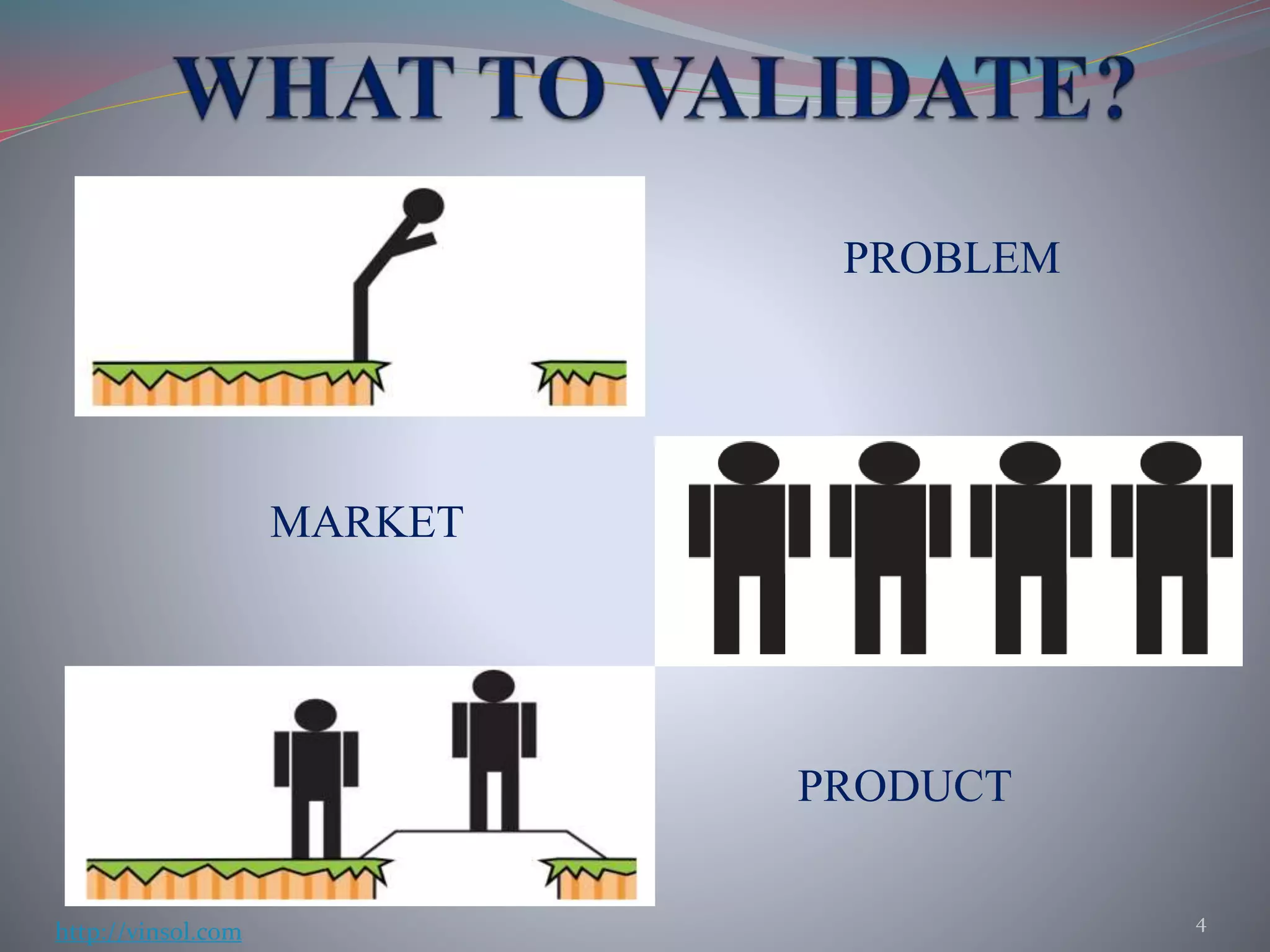
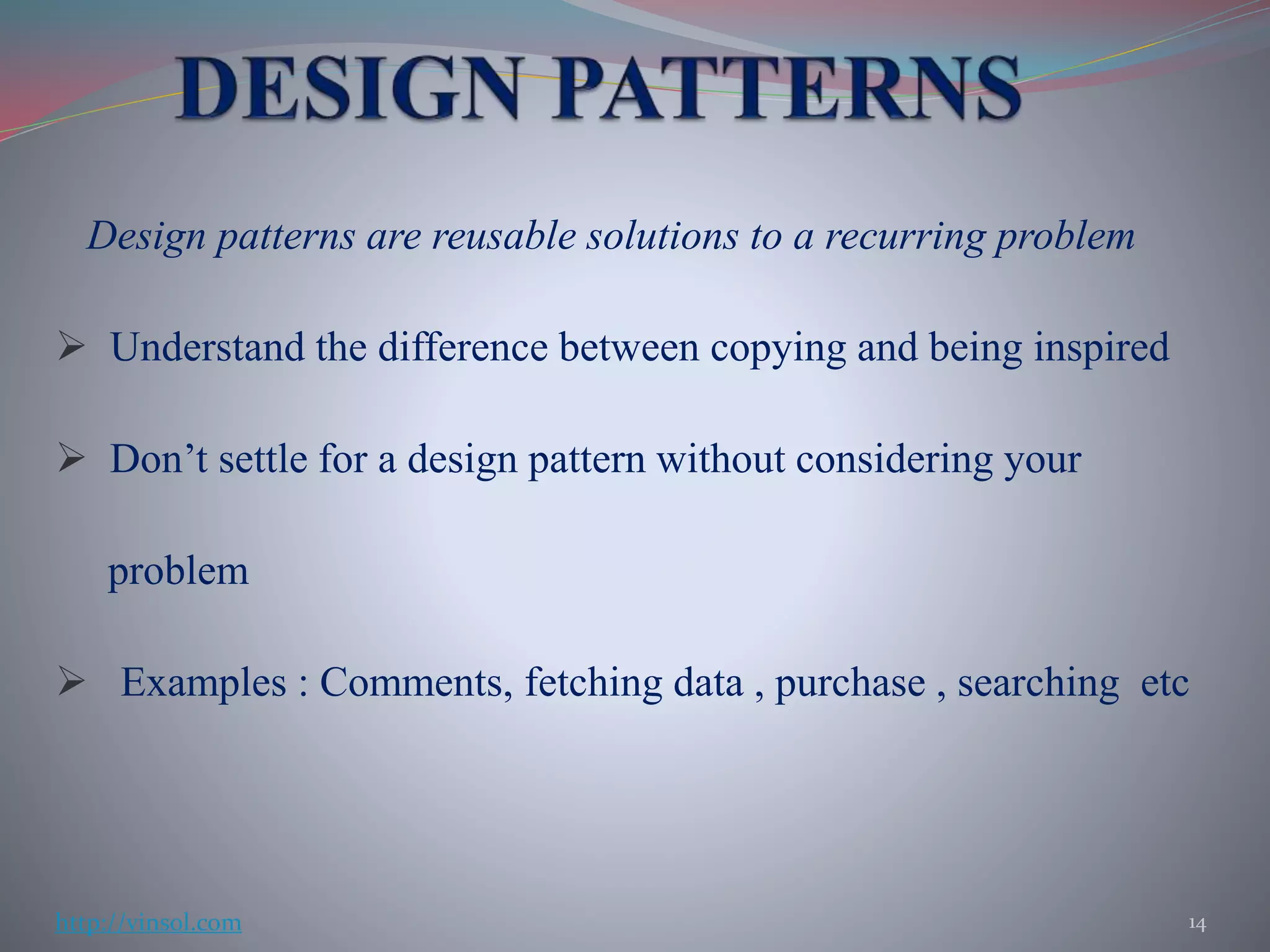
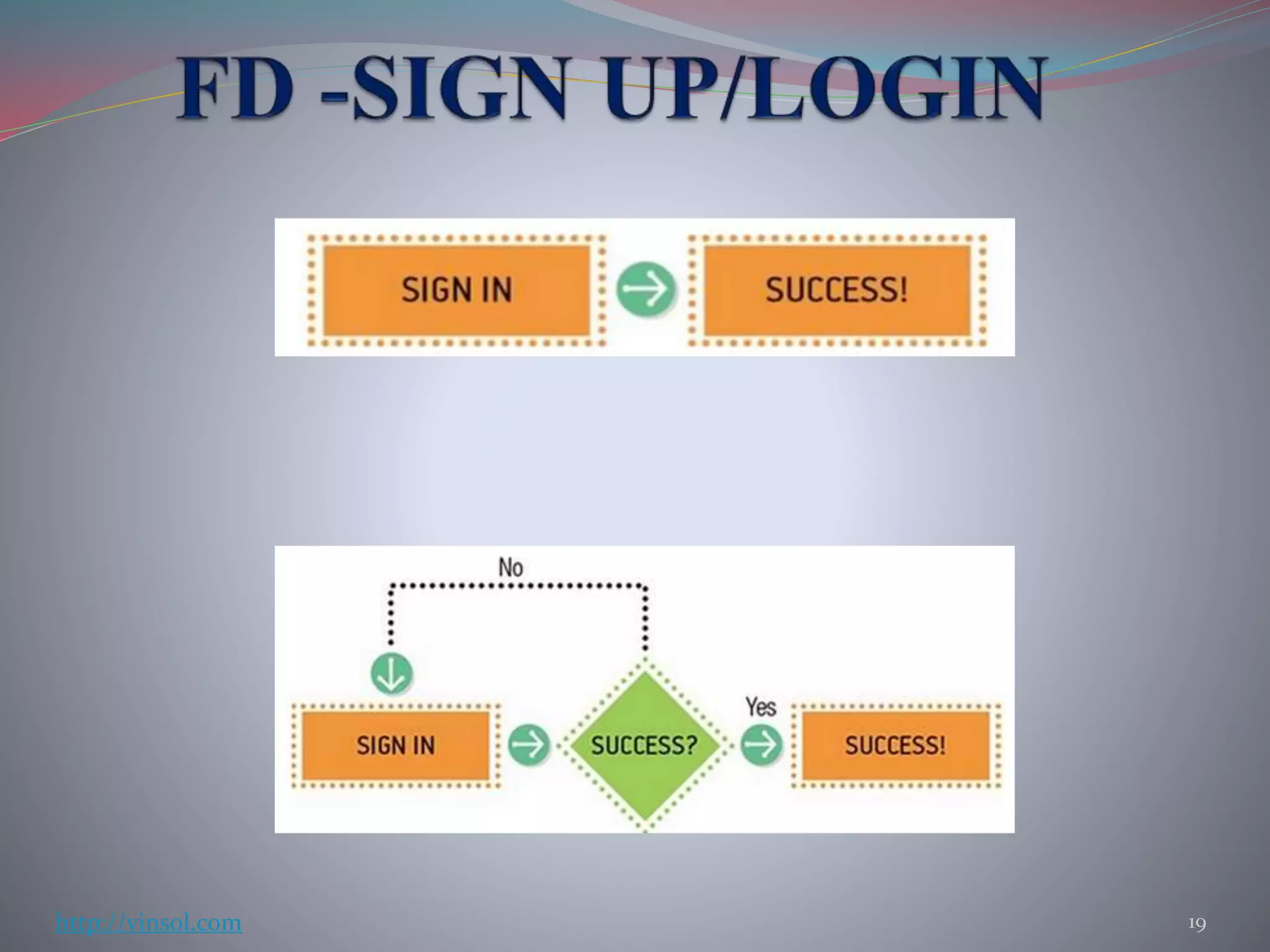
This document discusses Lean UX and validation techniques for products. Some key points include:
- Lean UX focuses on user-centered, agile, data-driven and hypothesis-driven approaches to product design.
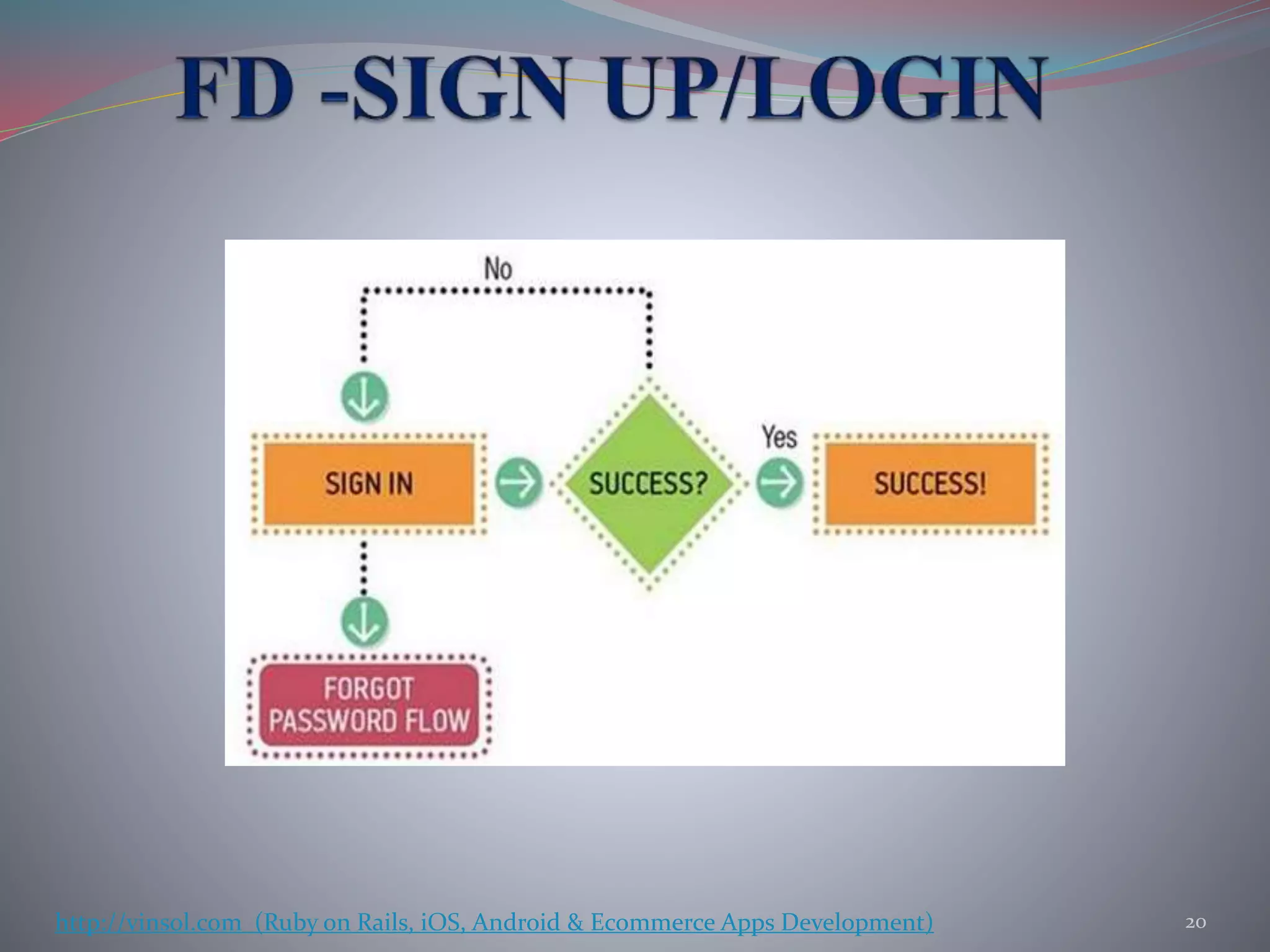
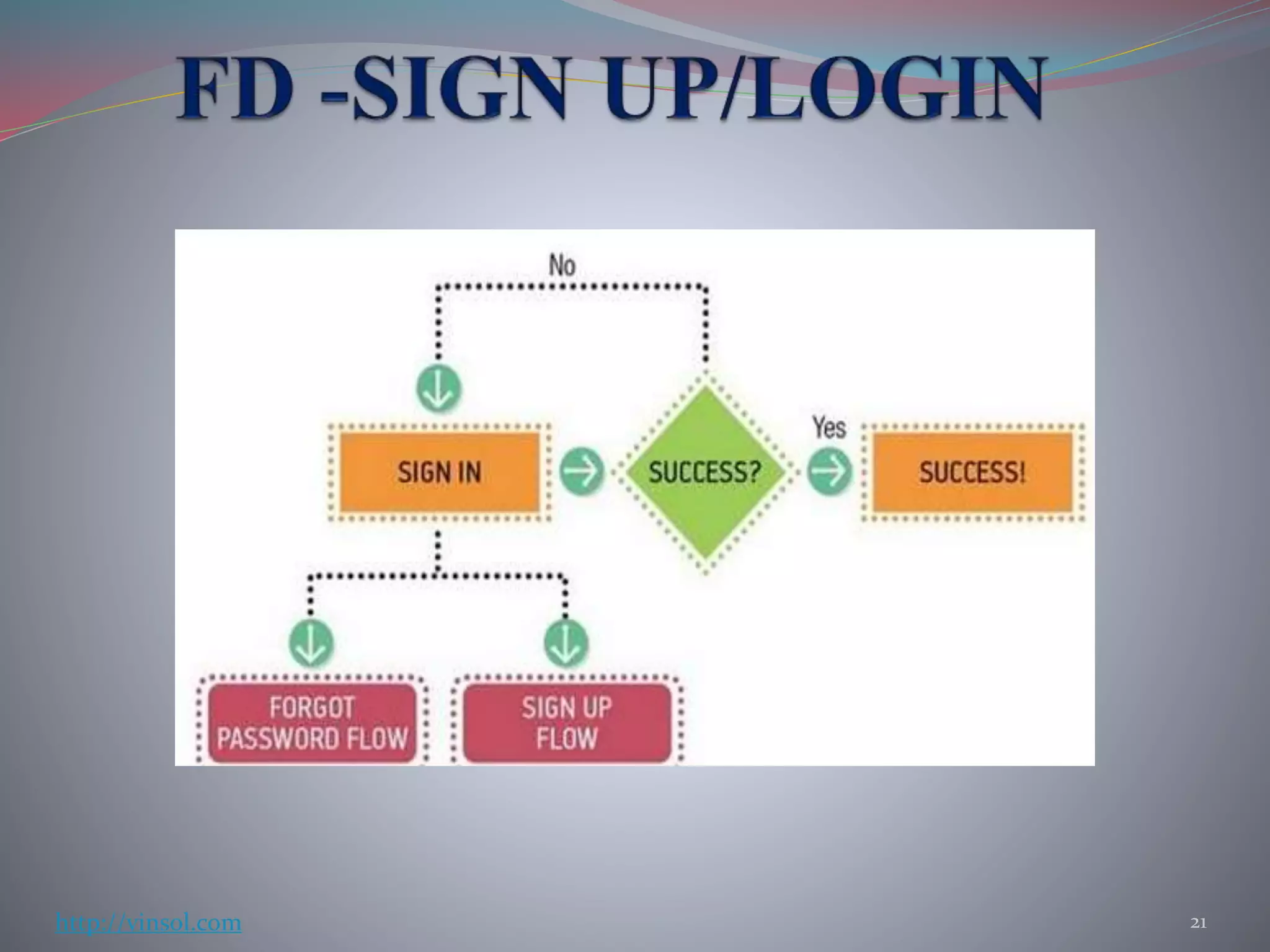
- Various validation techniques are described such as landing page tests, prototype testing, guerrilla user tests, and A/B testing to gather feedback and validate hypotheses.
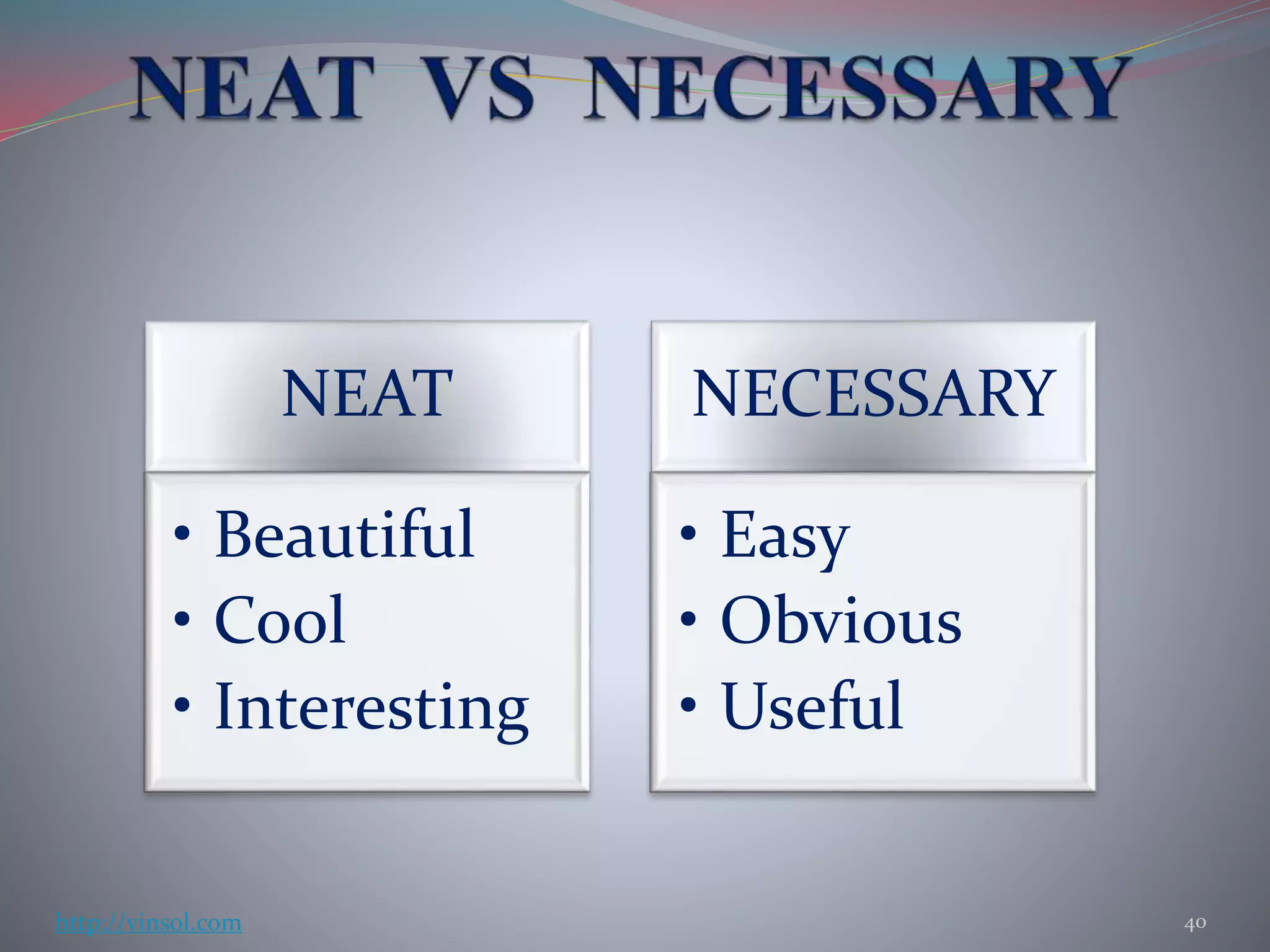
- An MVP or minimum viable product should be both minimum and viable, providing a small whole product to validate rather than an incomplete large product. Metrics like retention, revenue, and conversion can provide insights but require careful analysis.