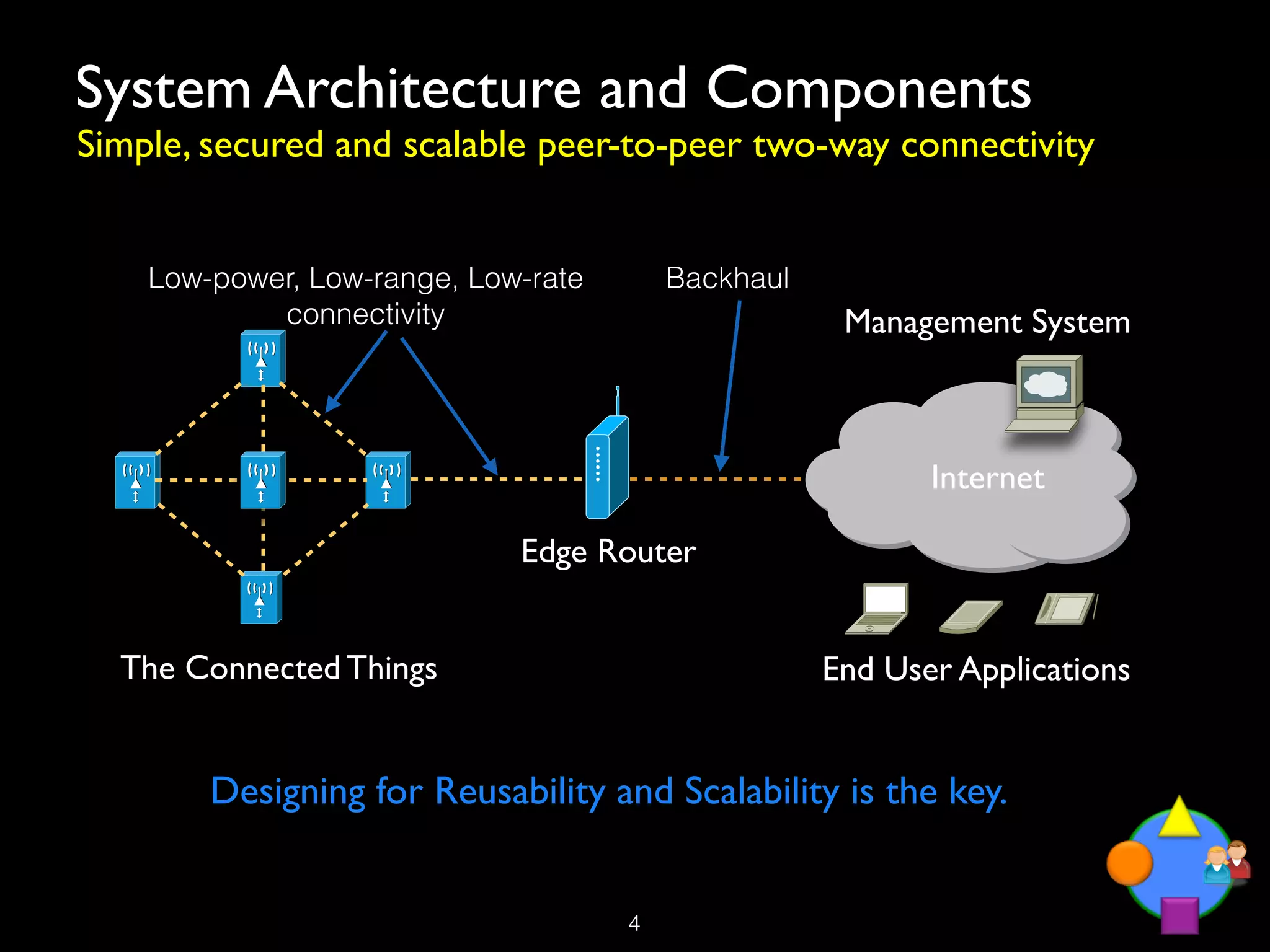
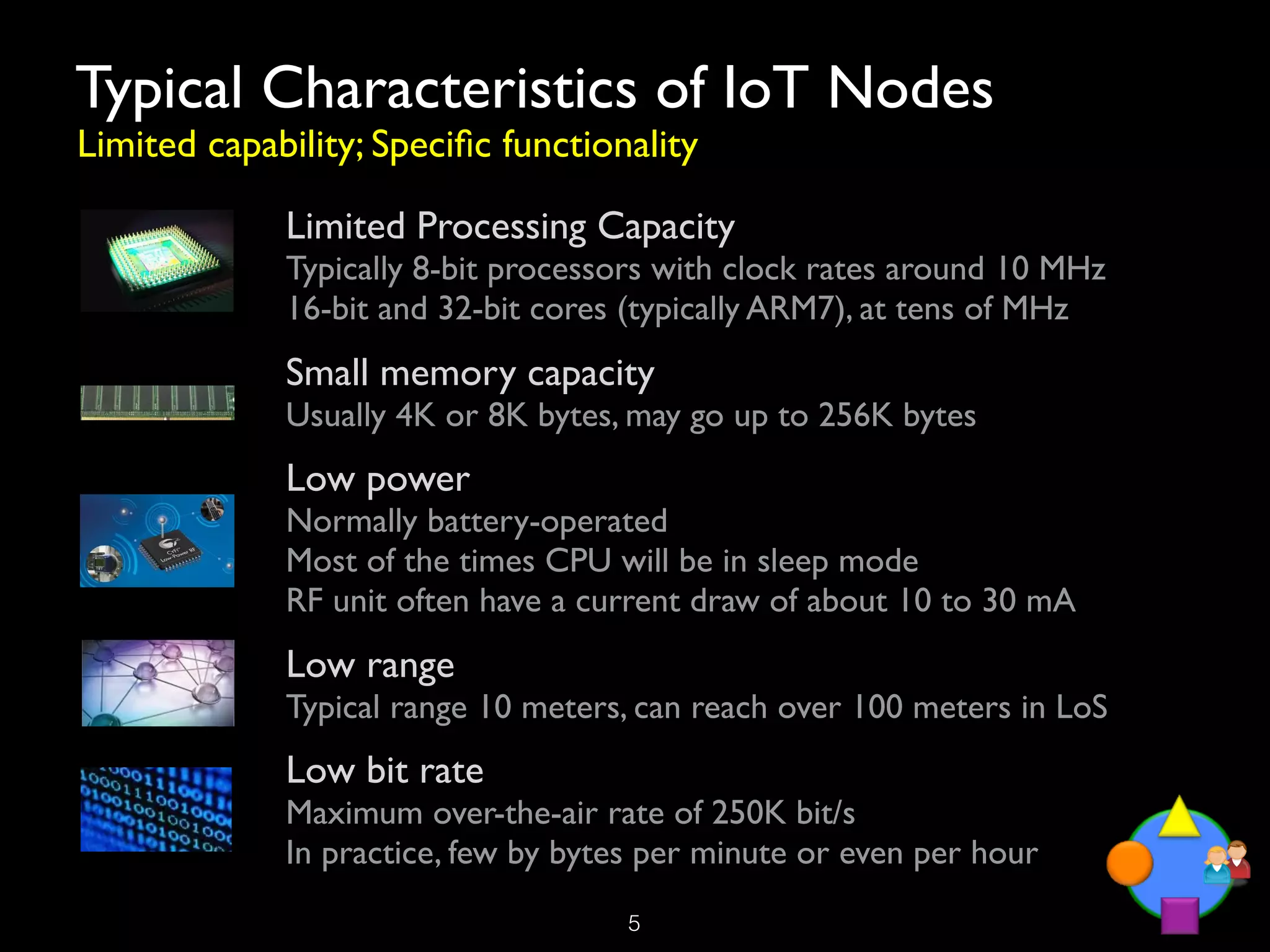
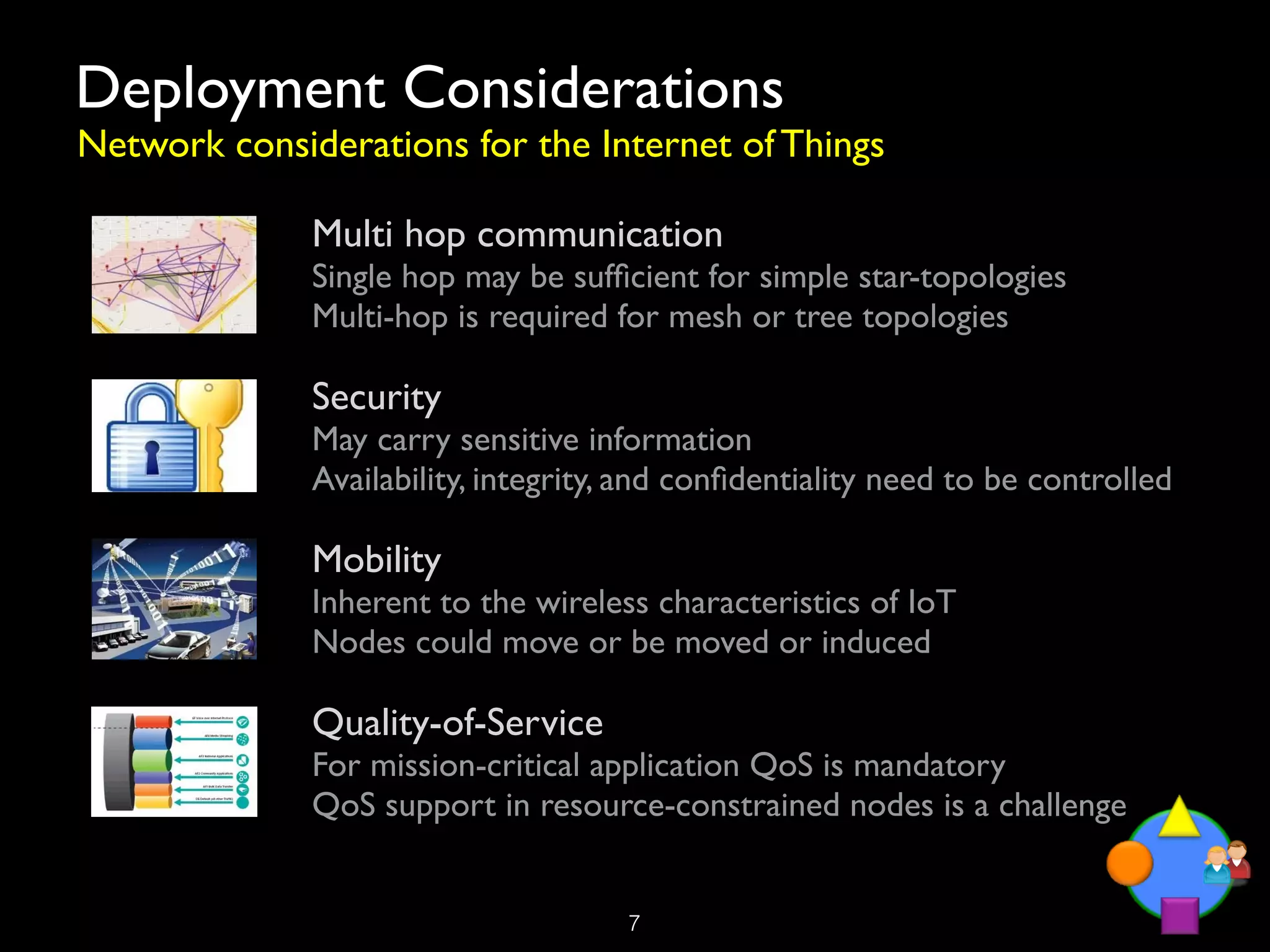
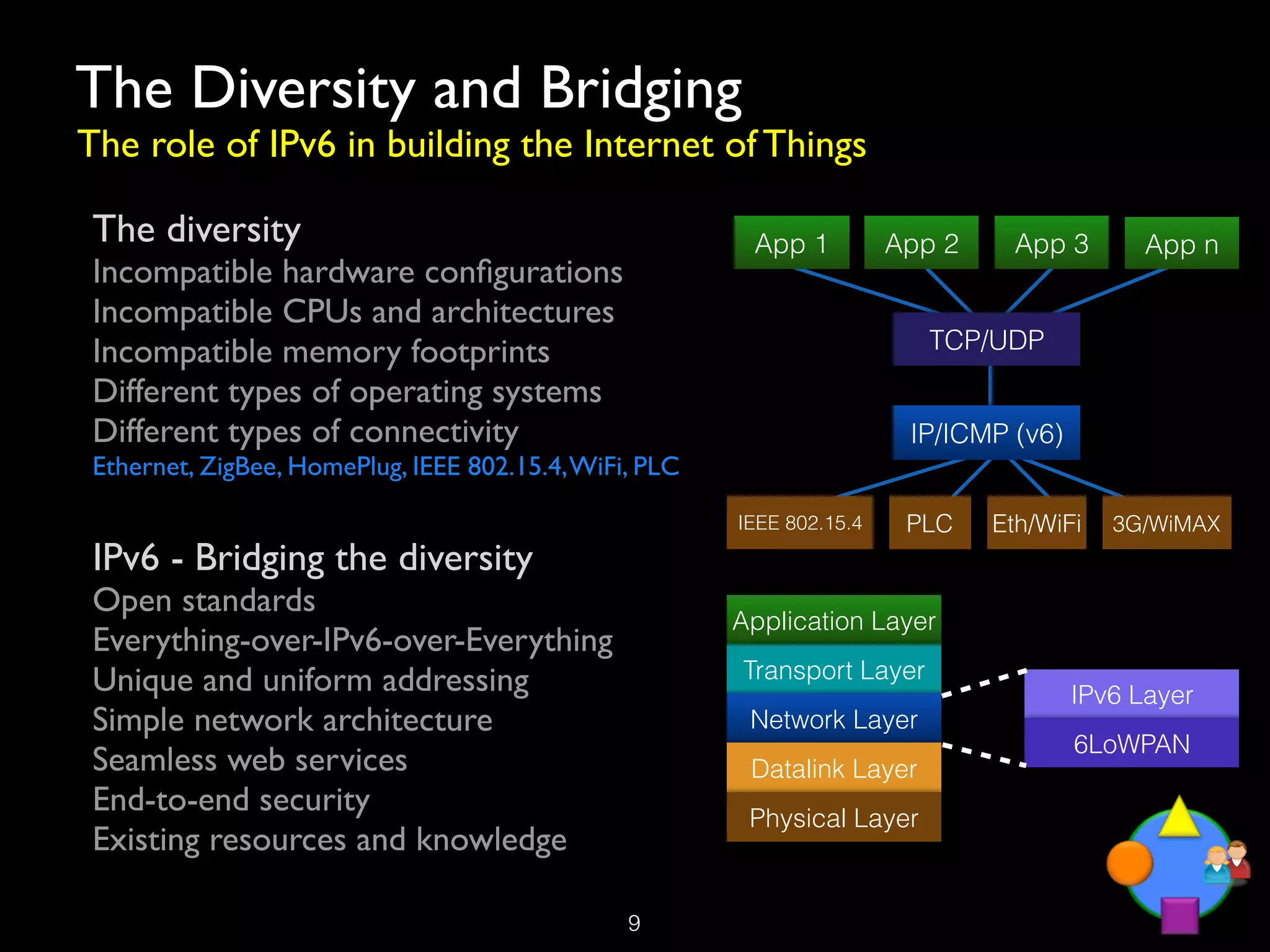
The document discusses the Internet of Things (IoT) as a transformative technology that addresses societal challenges, enhances living standards, and offers new business models. It outlines the architecture, deployment considerations, and trends of IoT, emphasizing its potential applications across various sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, and smart cities. Furthermore, it highlights the role of public authorities in governance, ethical considerations, and the challenges faced in IoT implementation.