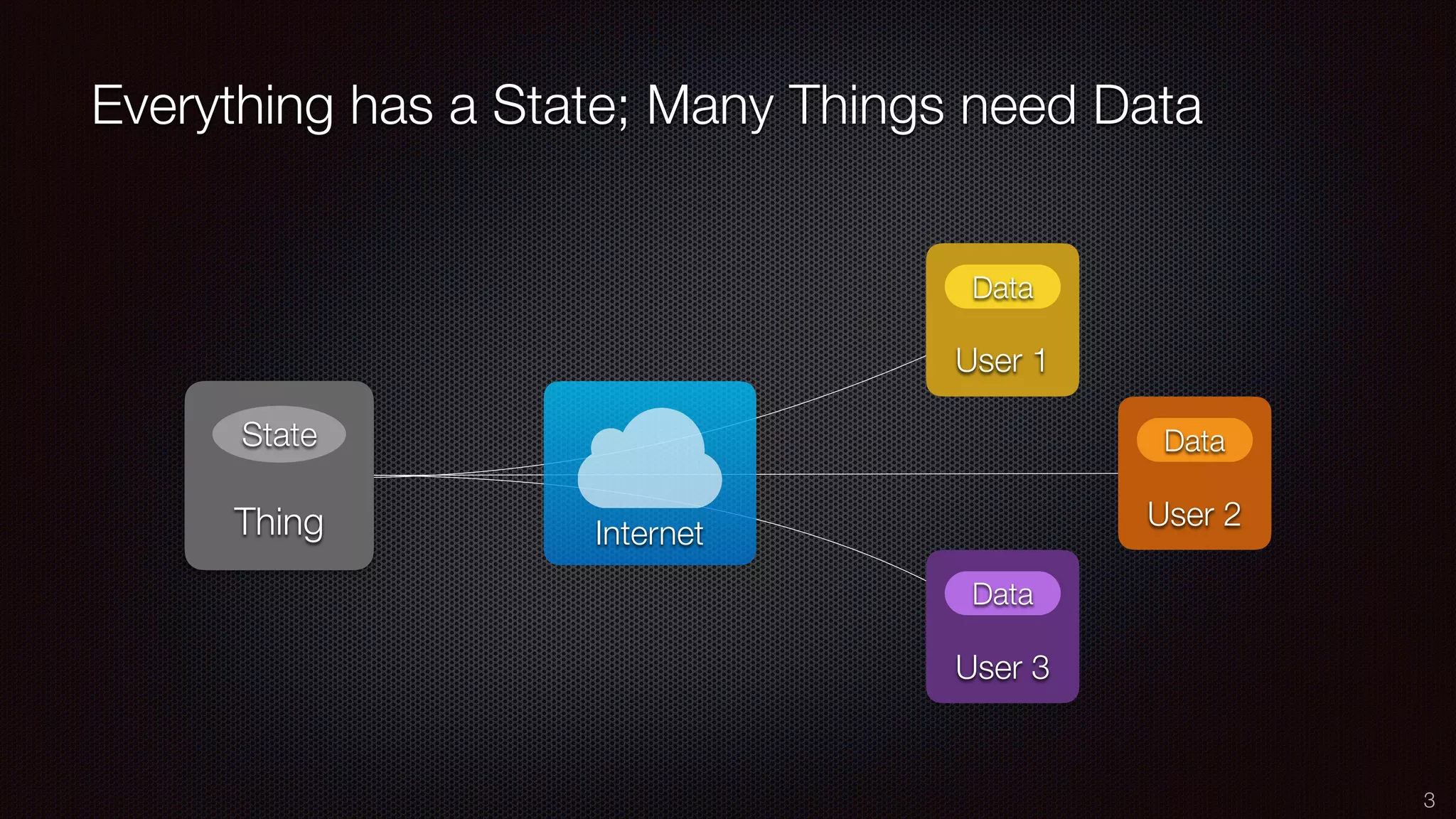
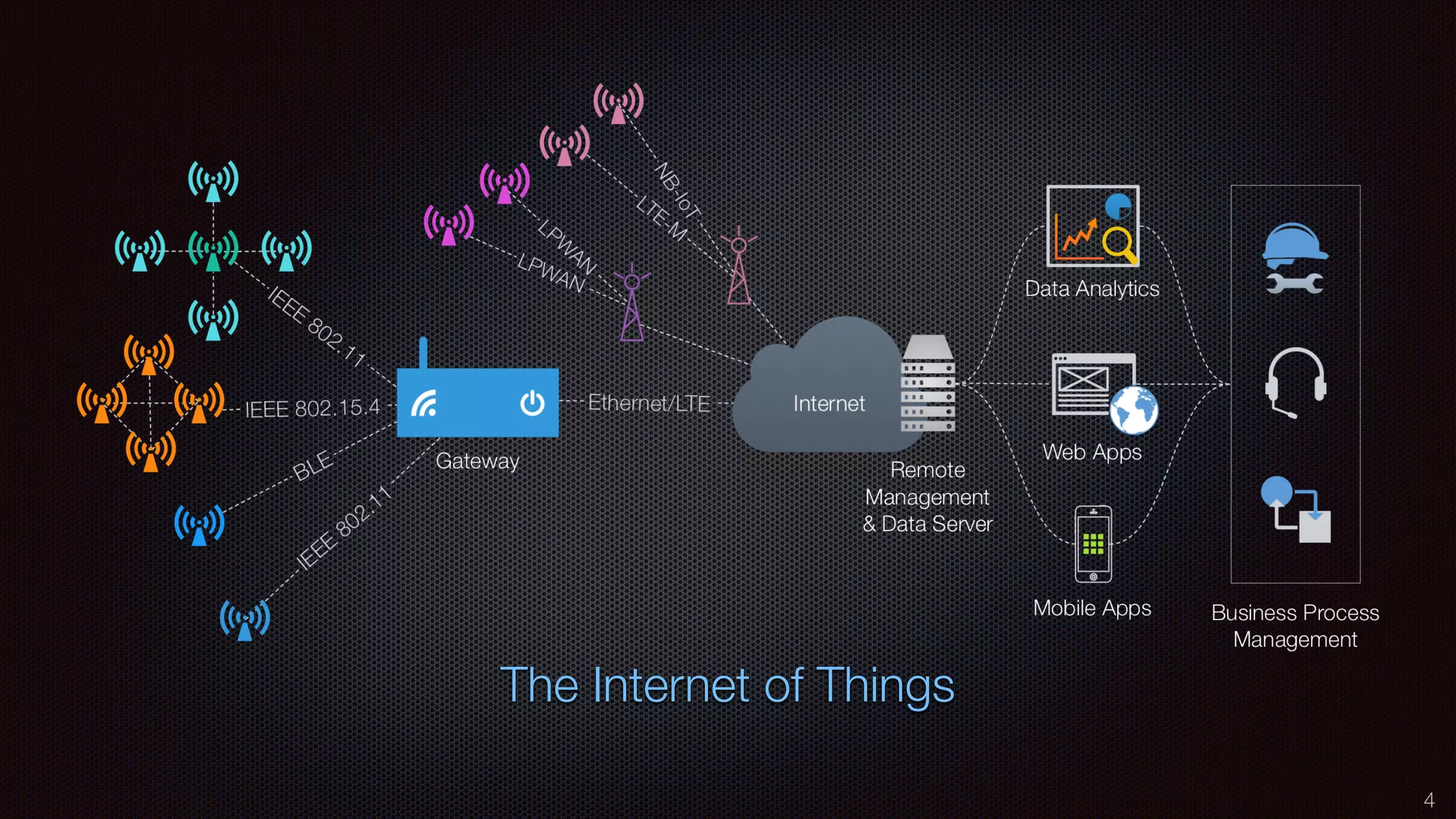
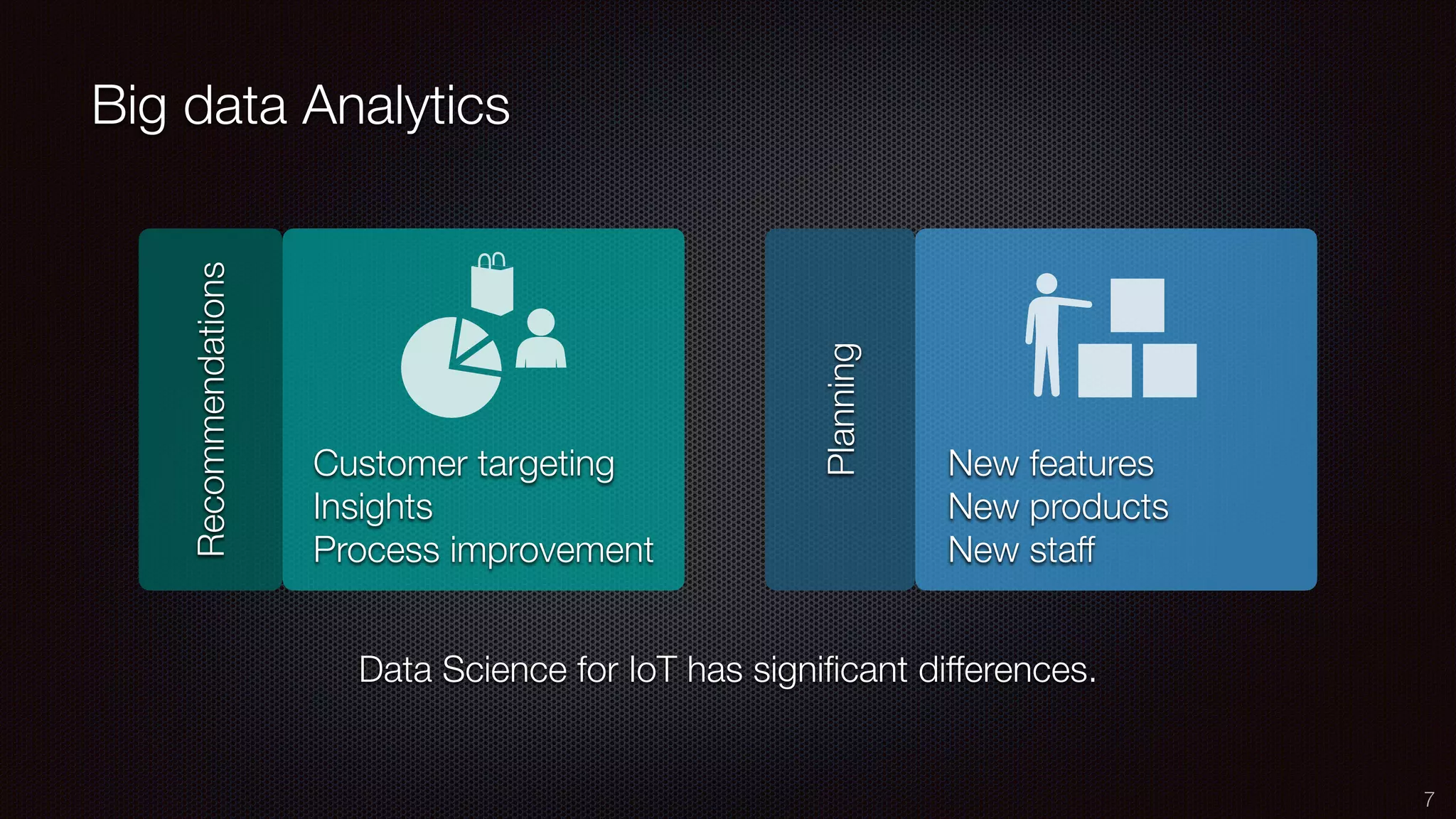
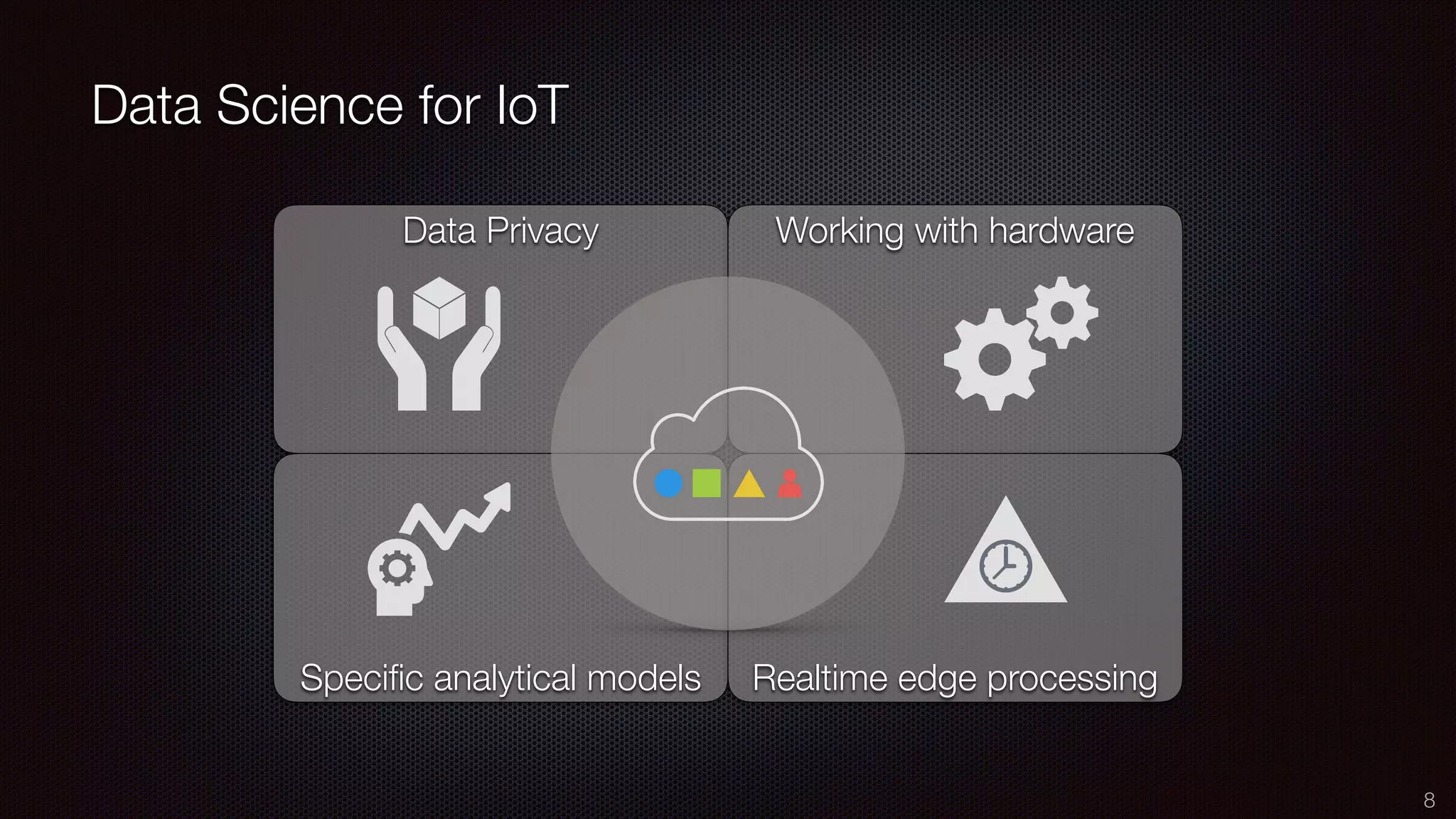
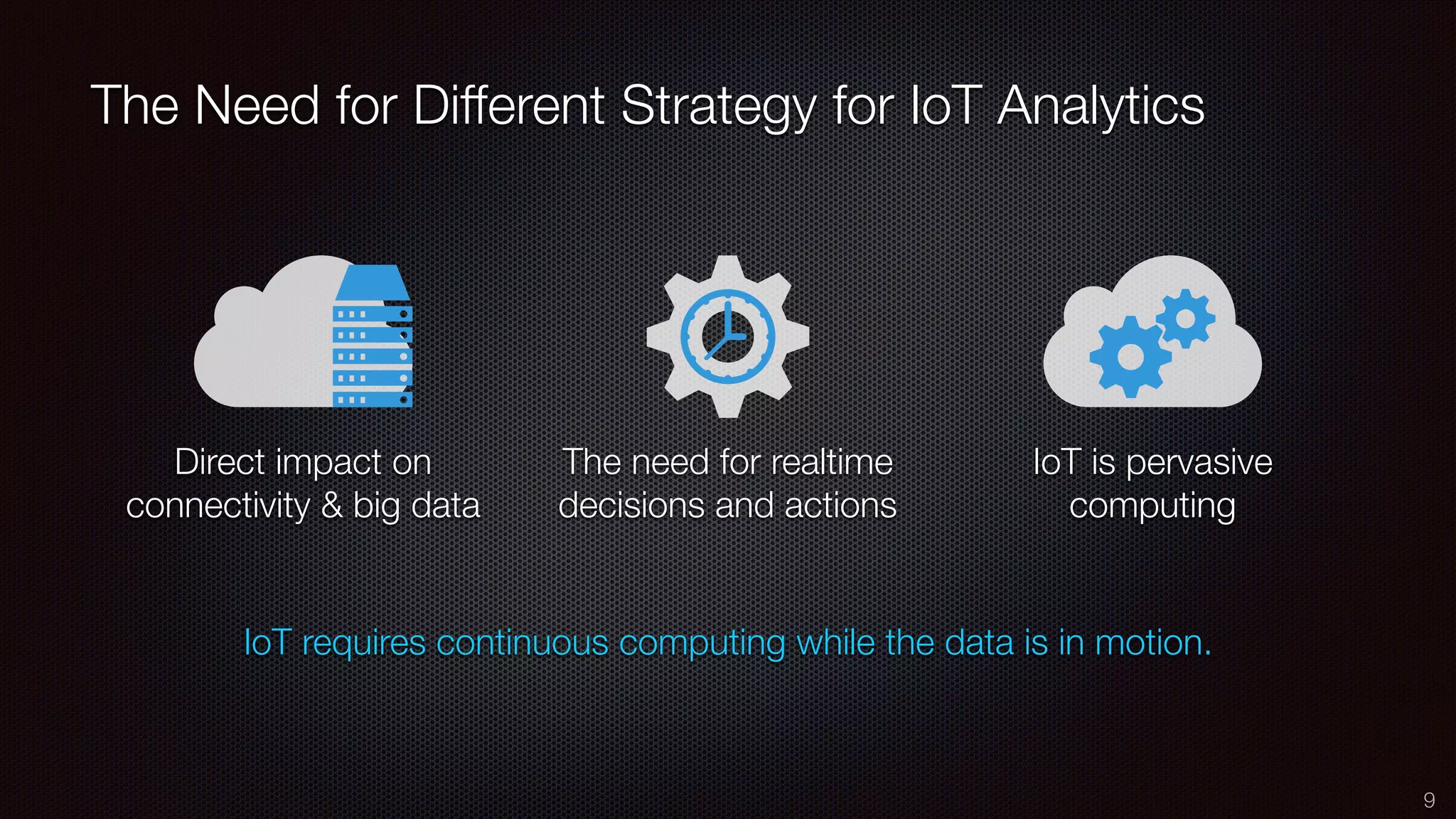
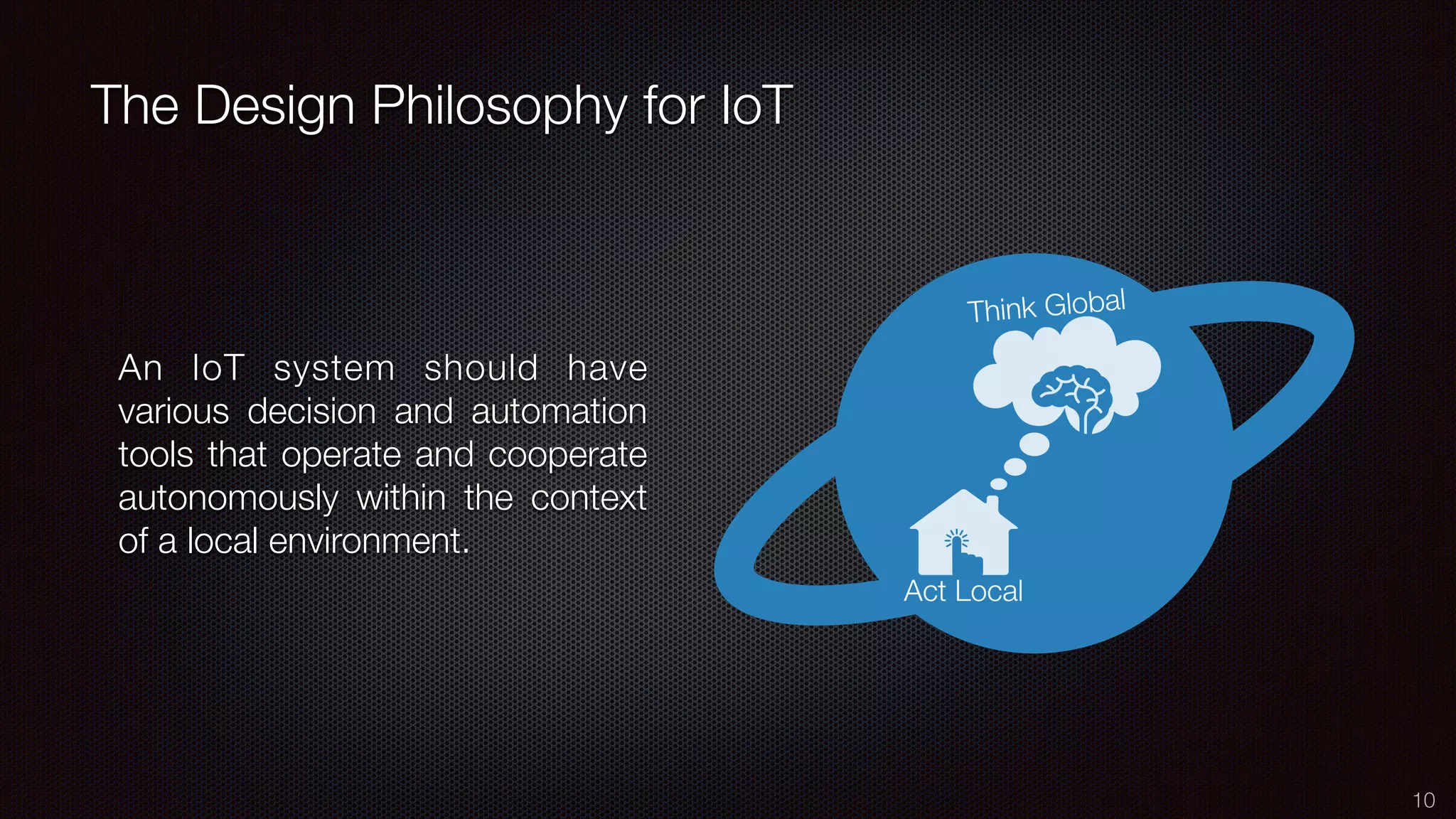
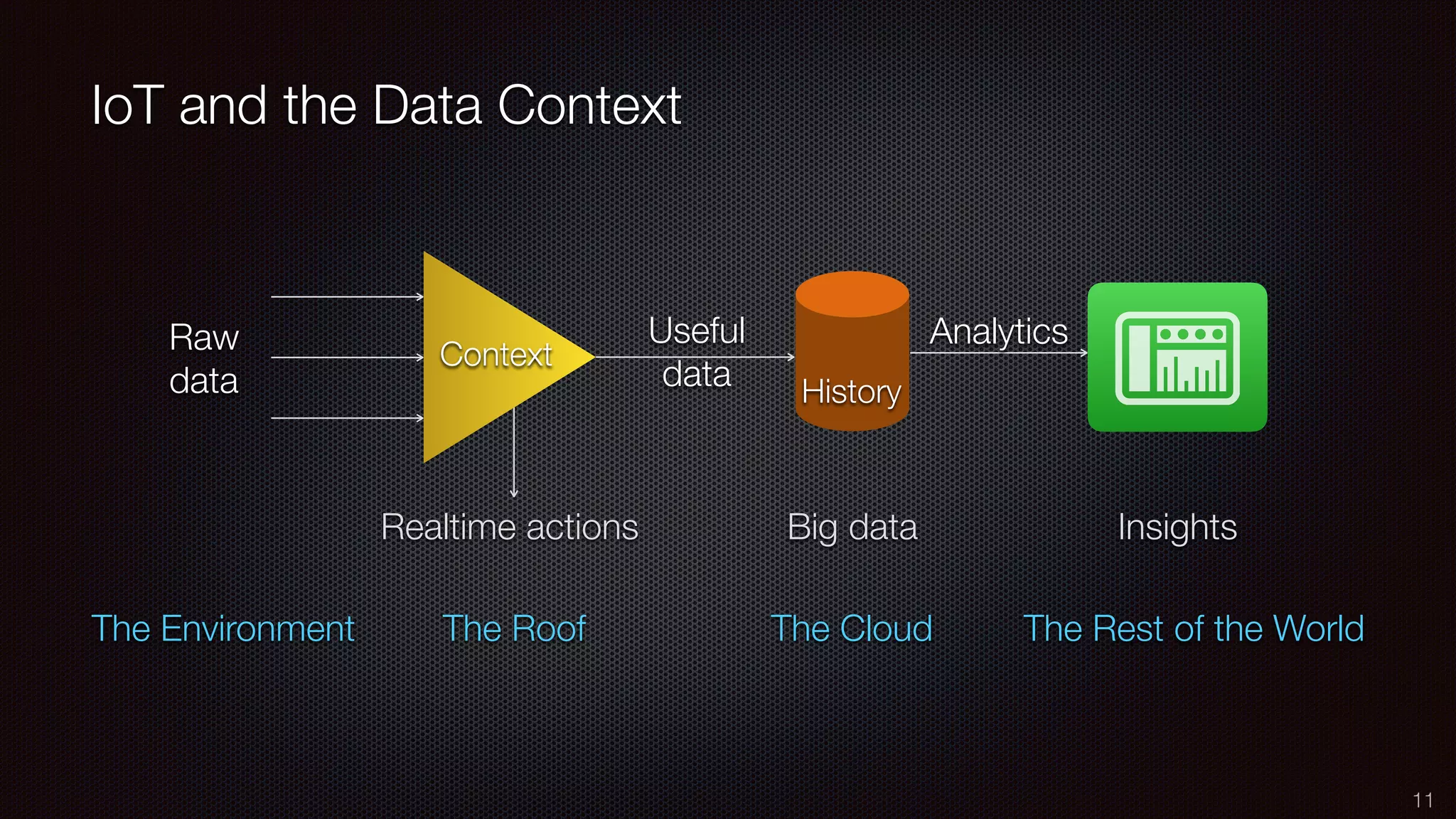
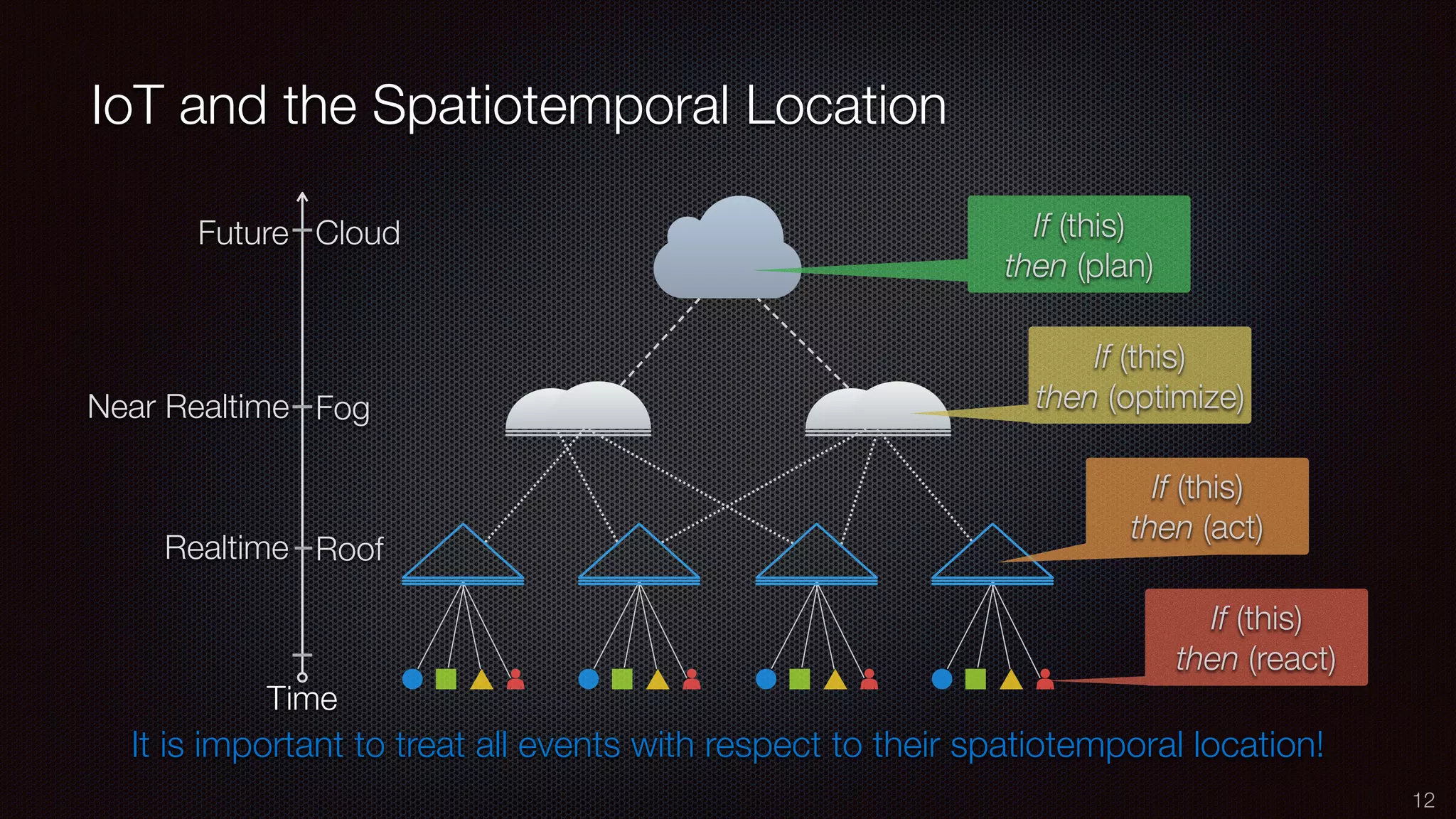
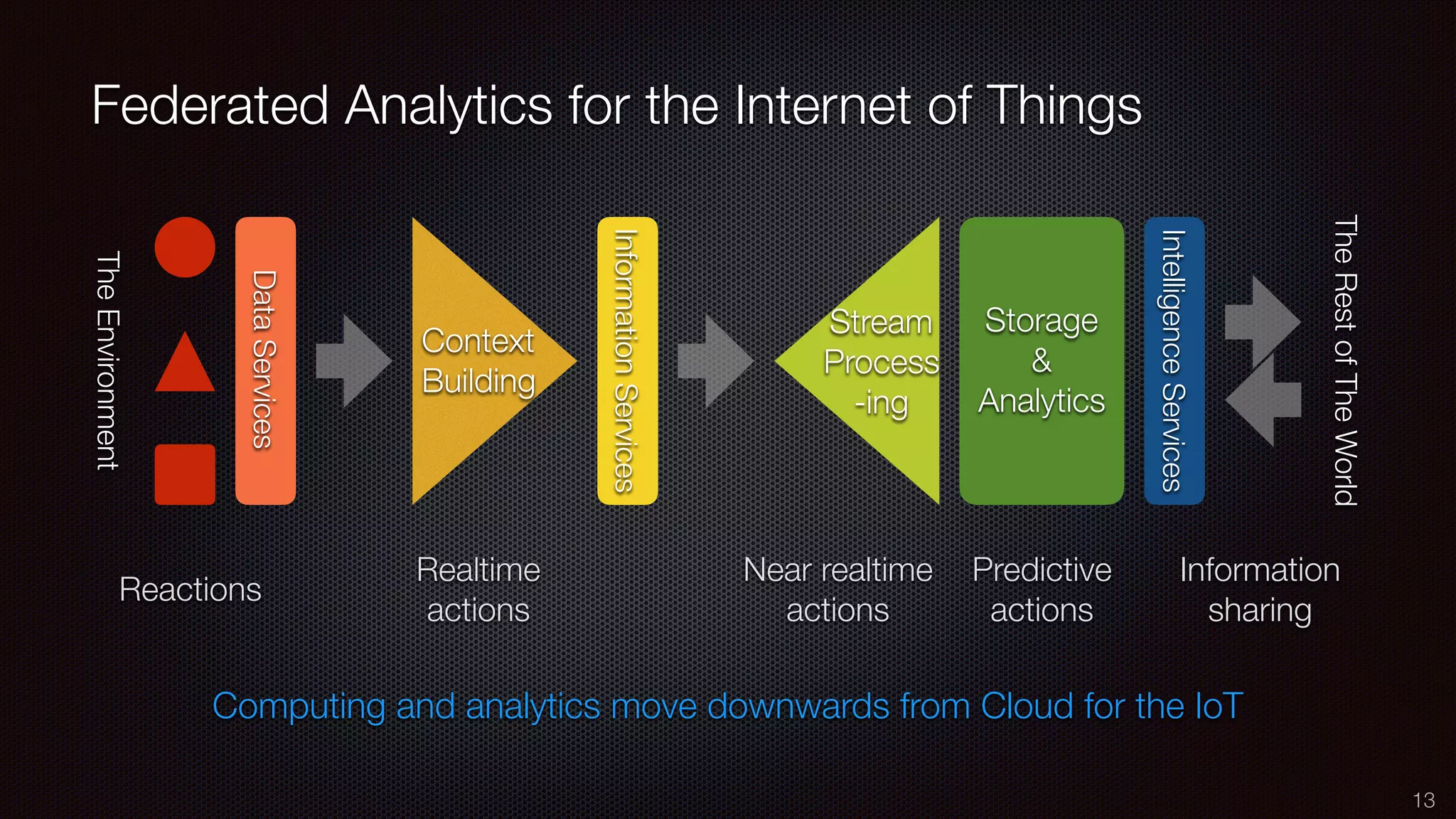
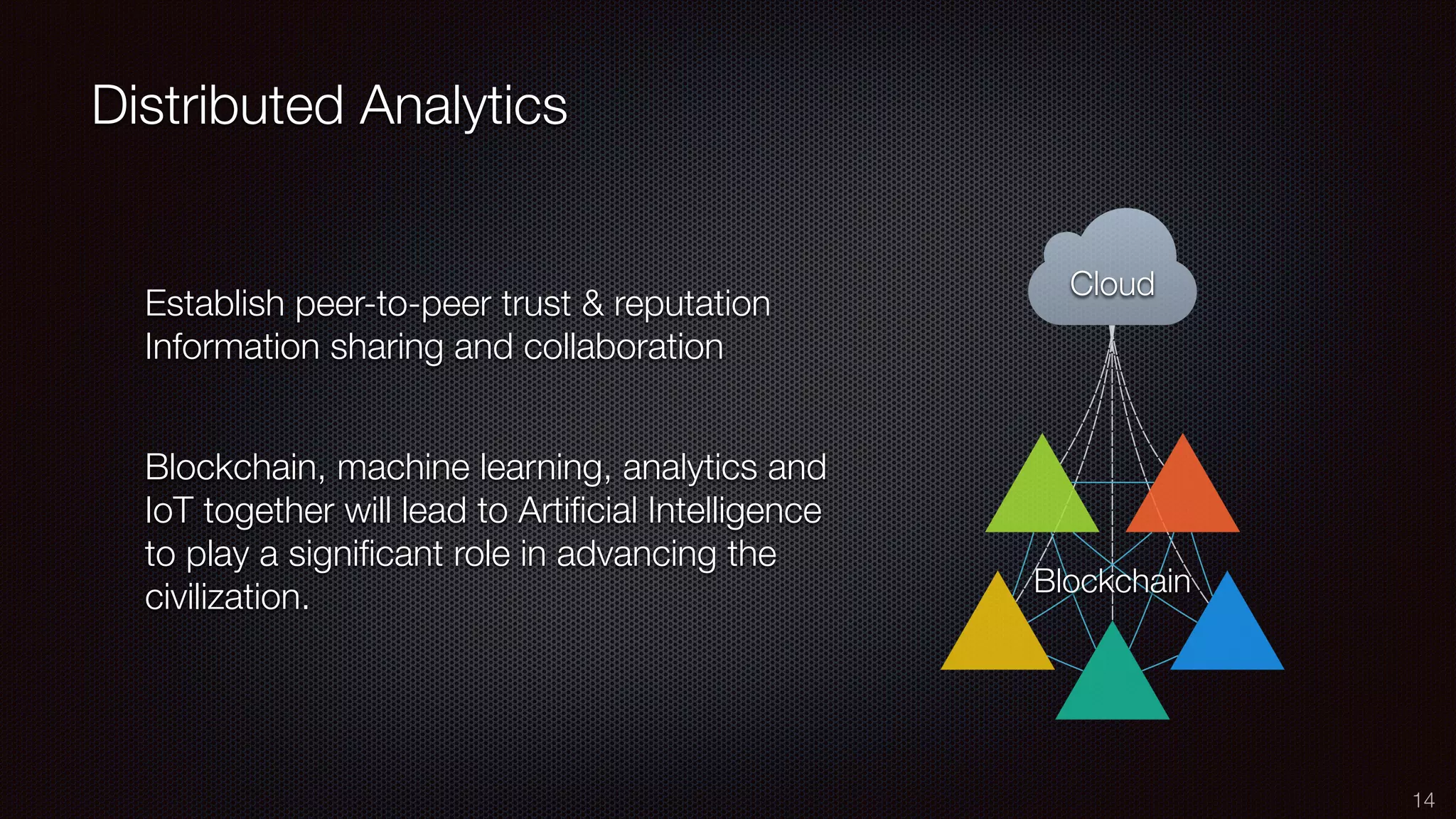
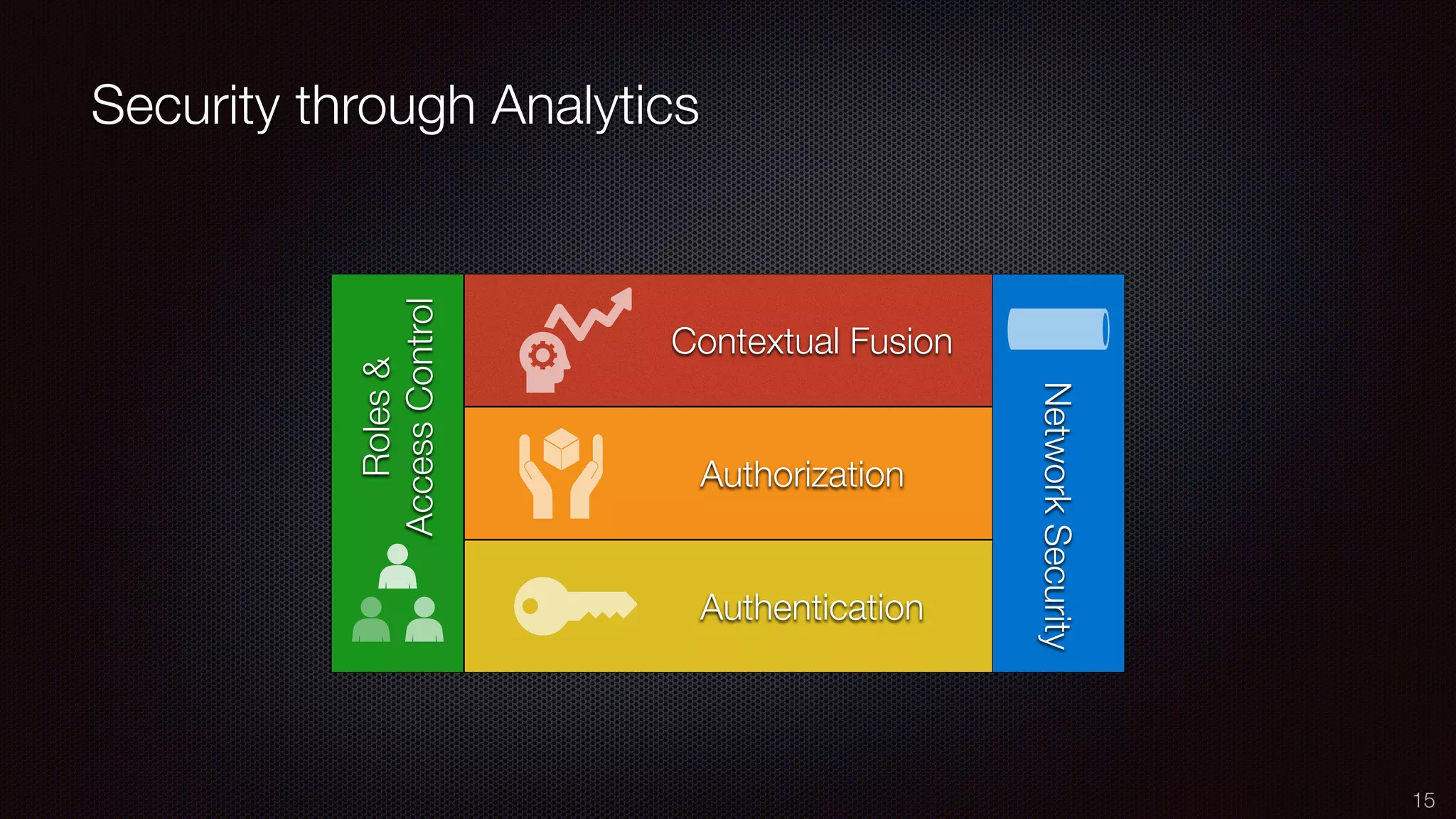
The document discusses the impact of the Internet of Things (IoT) on cloud computing, big data, and analytics, emphasizing its pervasive nature and the need for real-time decision-making. It outlines the importance of various technologies converging with IoT, including artificial intelligence and data science, to improve customer insights and process efficiencies. The document highlights the necessity for standard analytical models and collaborative frameworks to ensure interoperability and enhance security within IoT ecosystems.