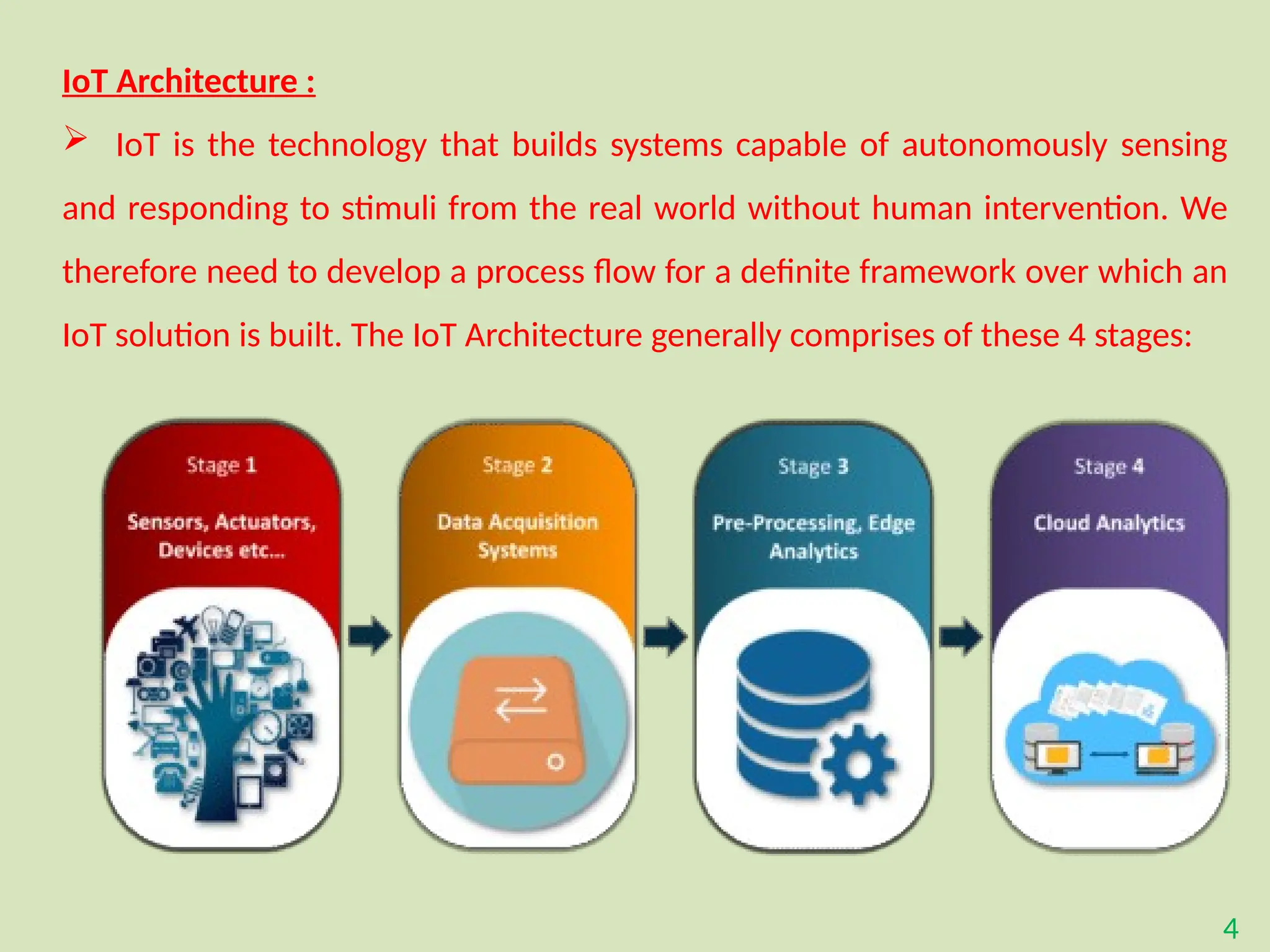
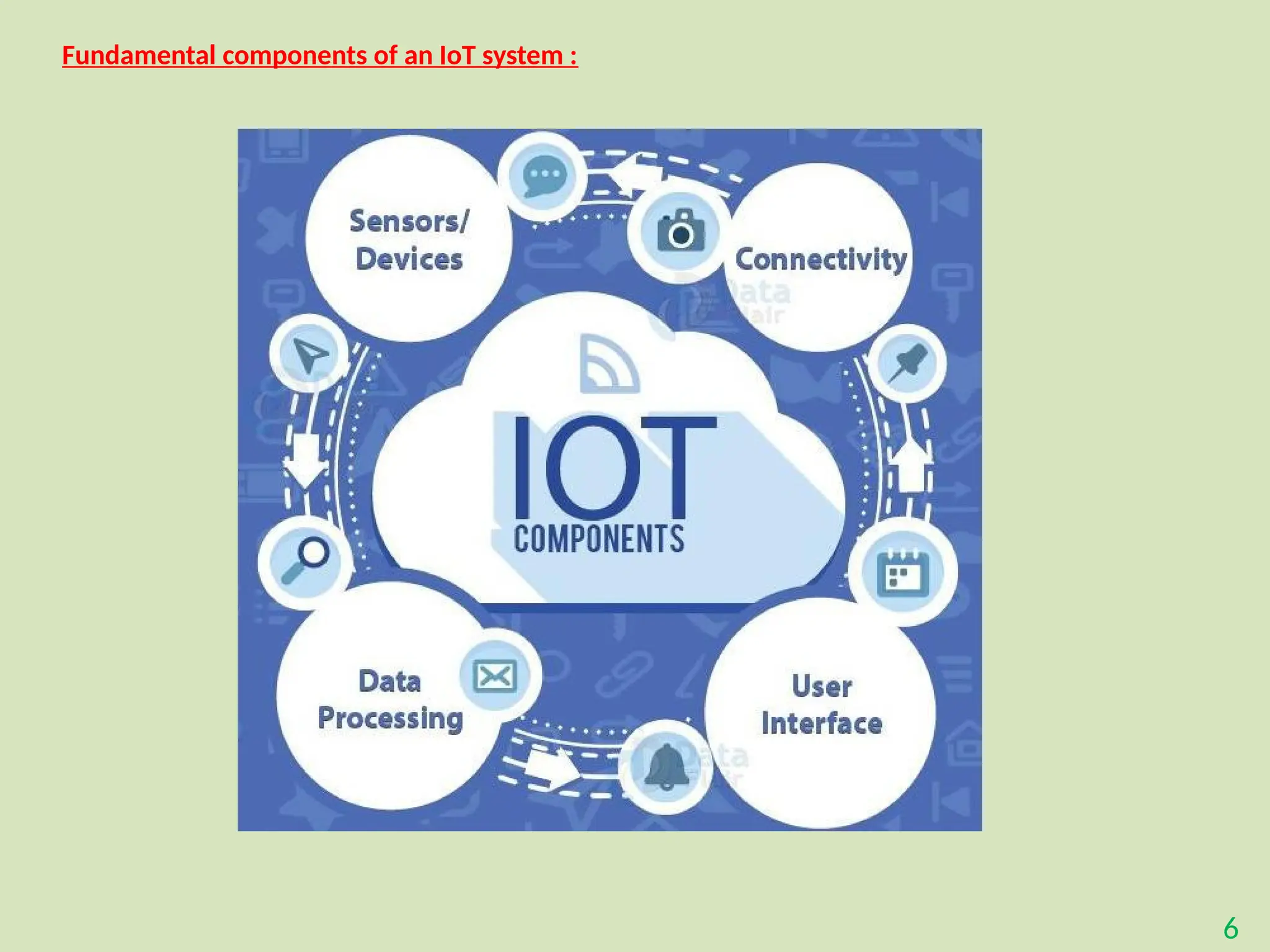
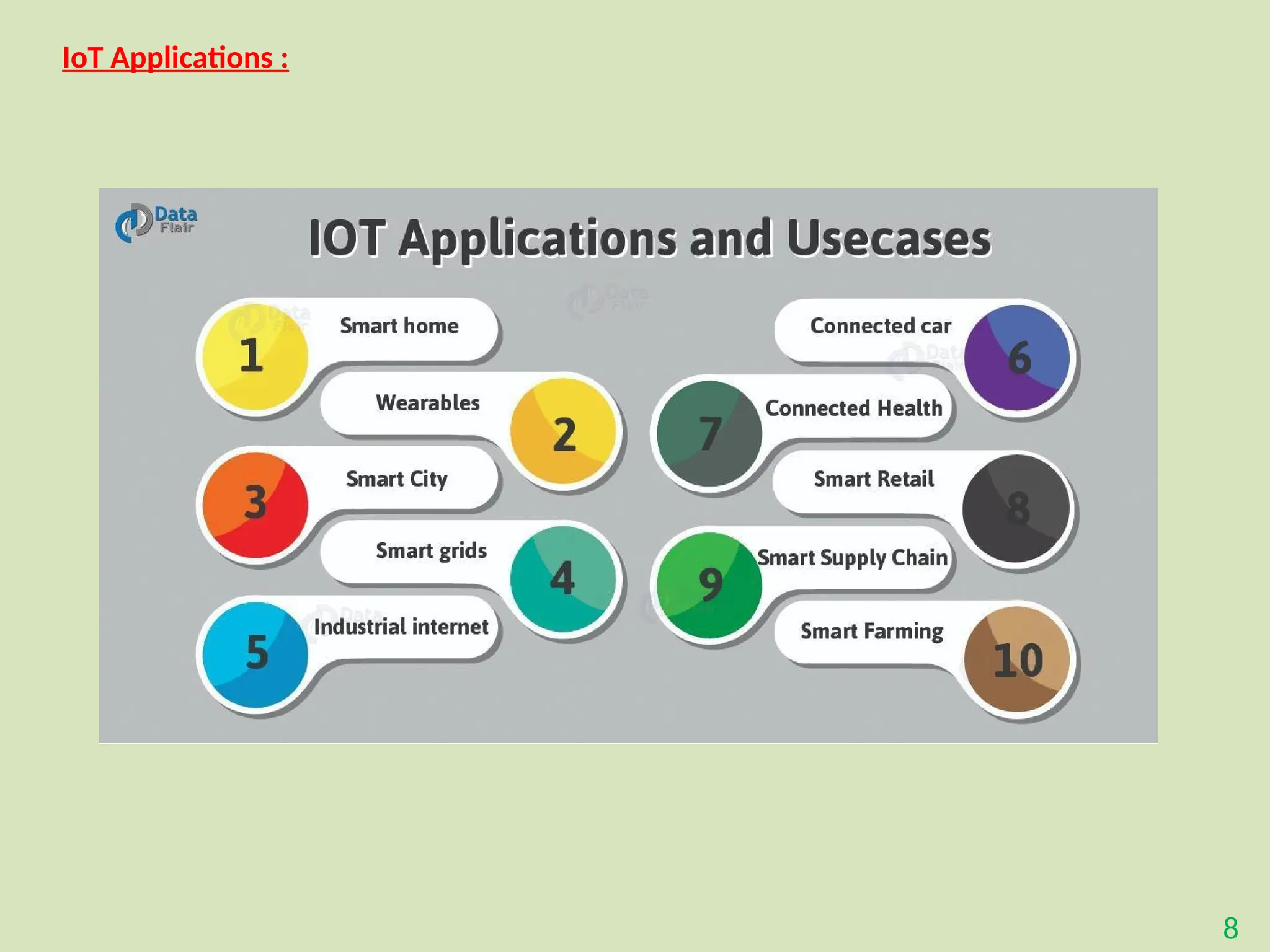
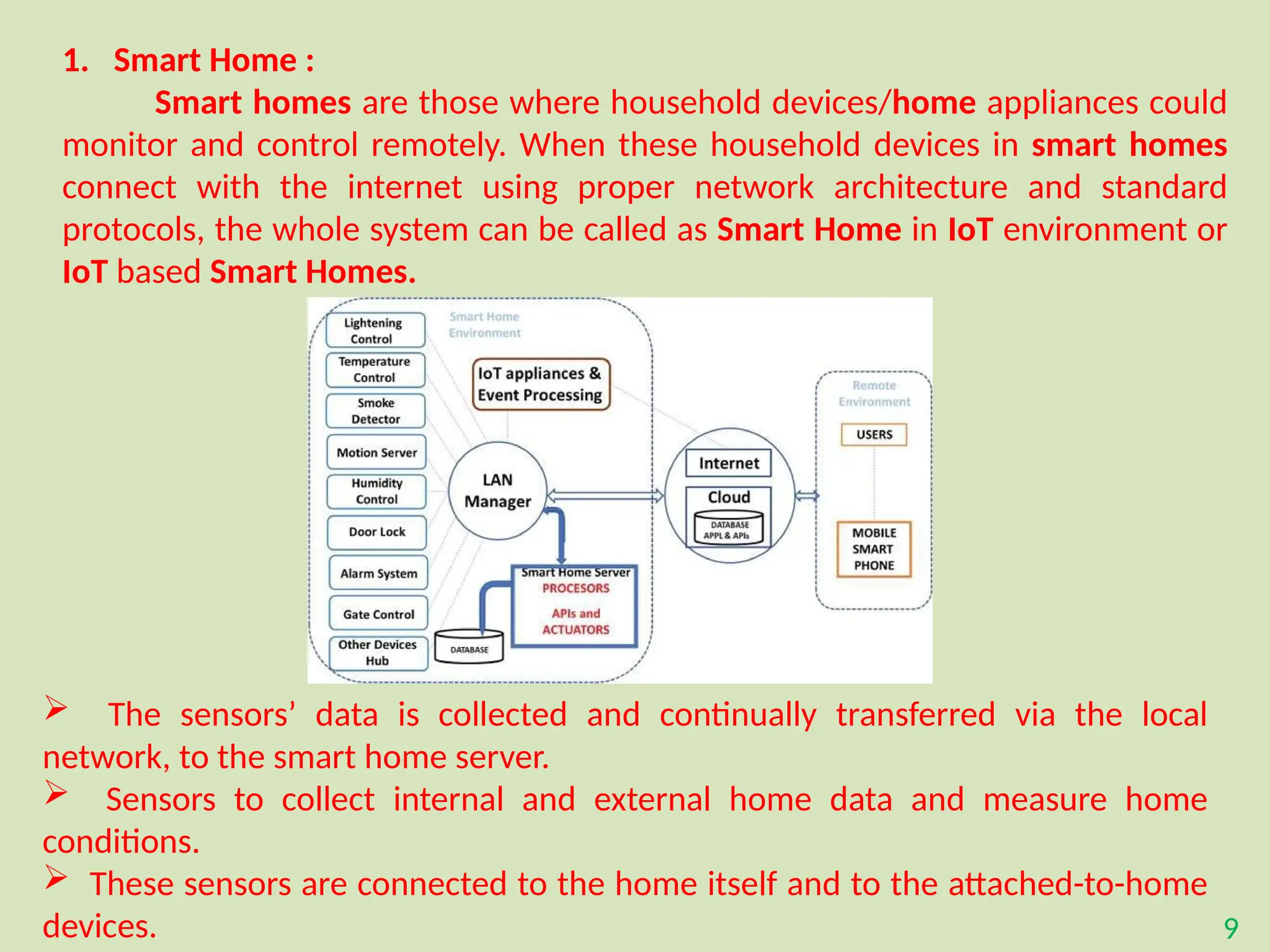
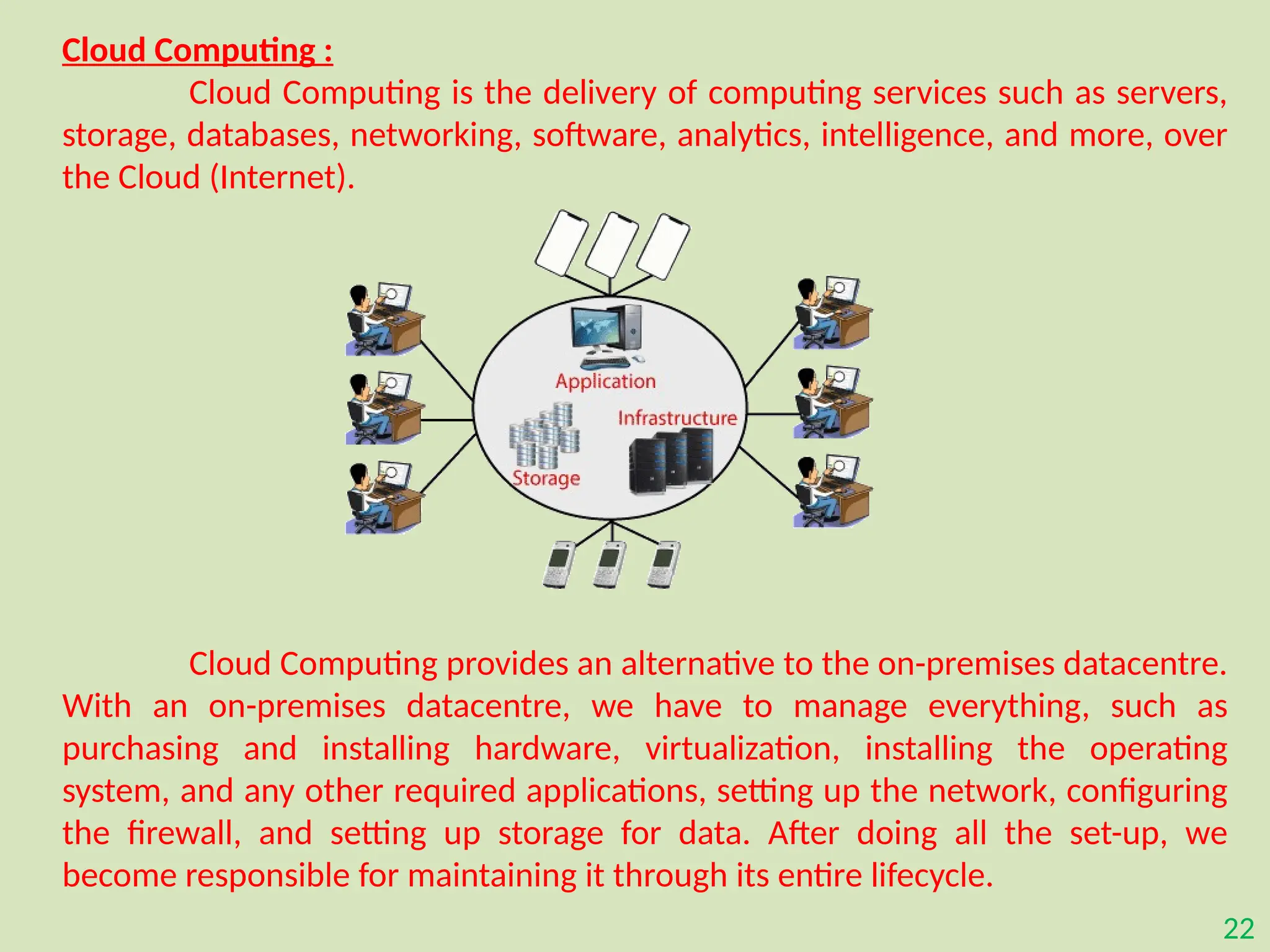
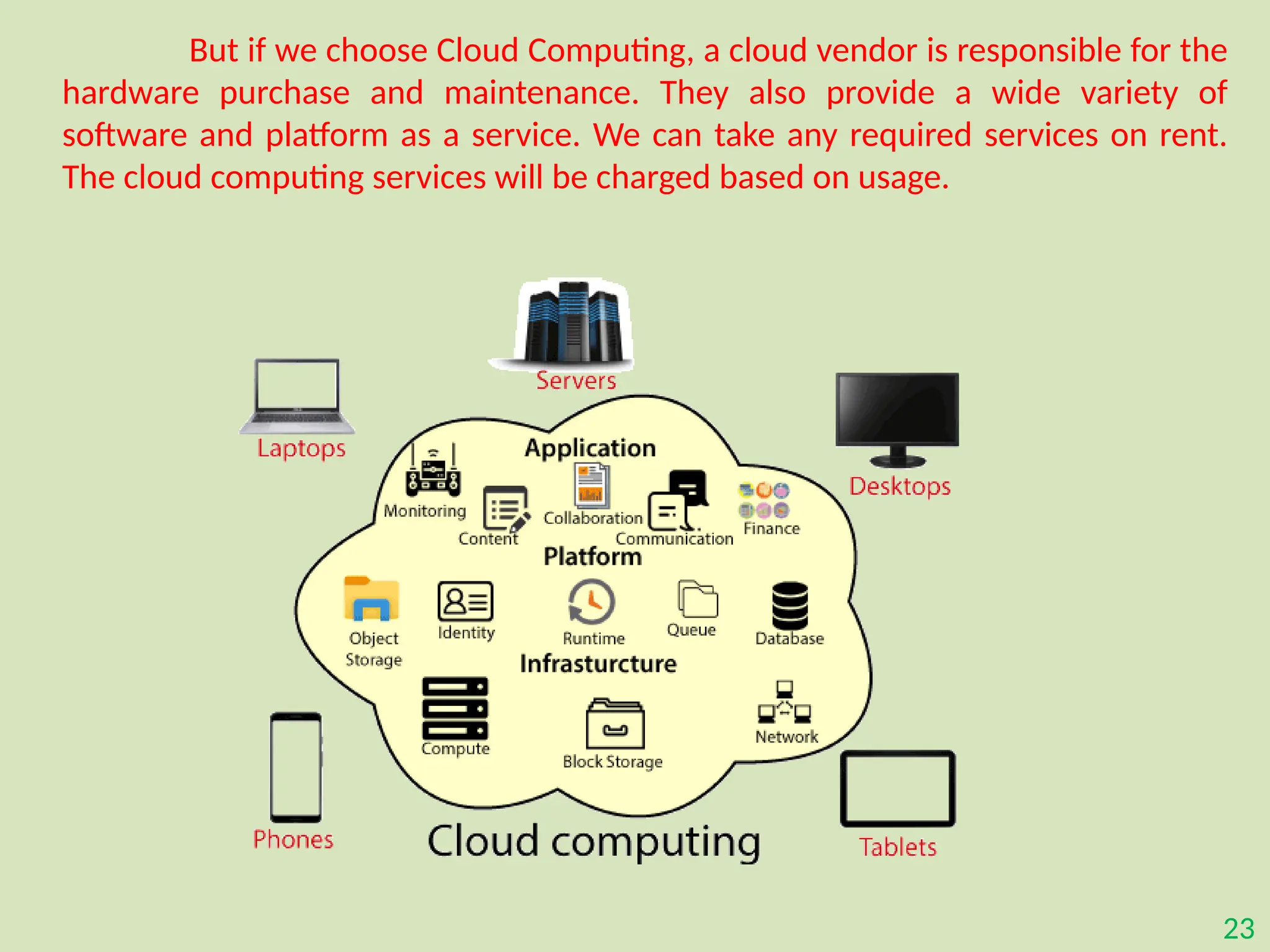
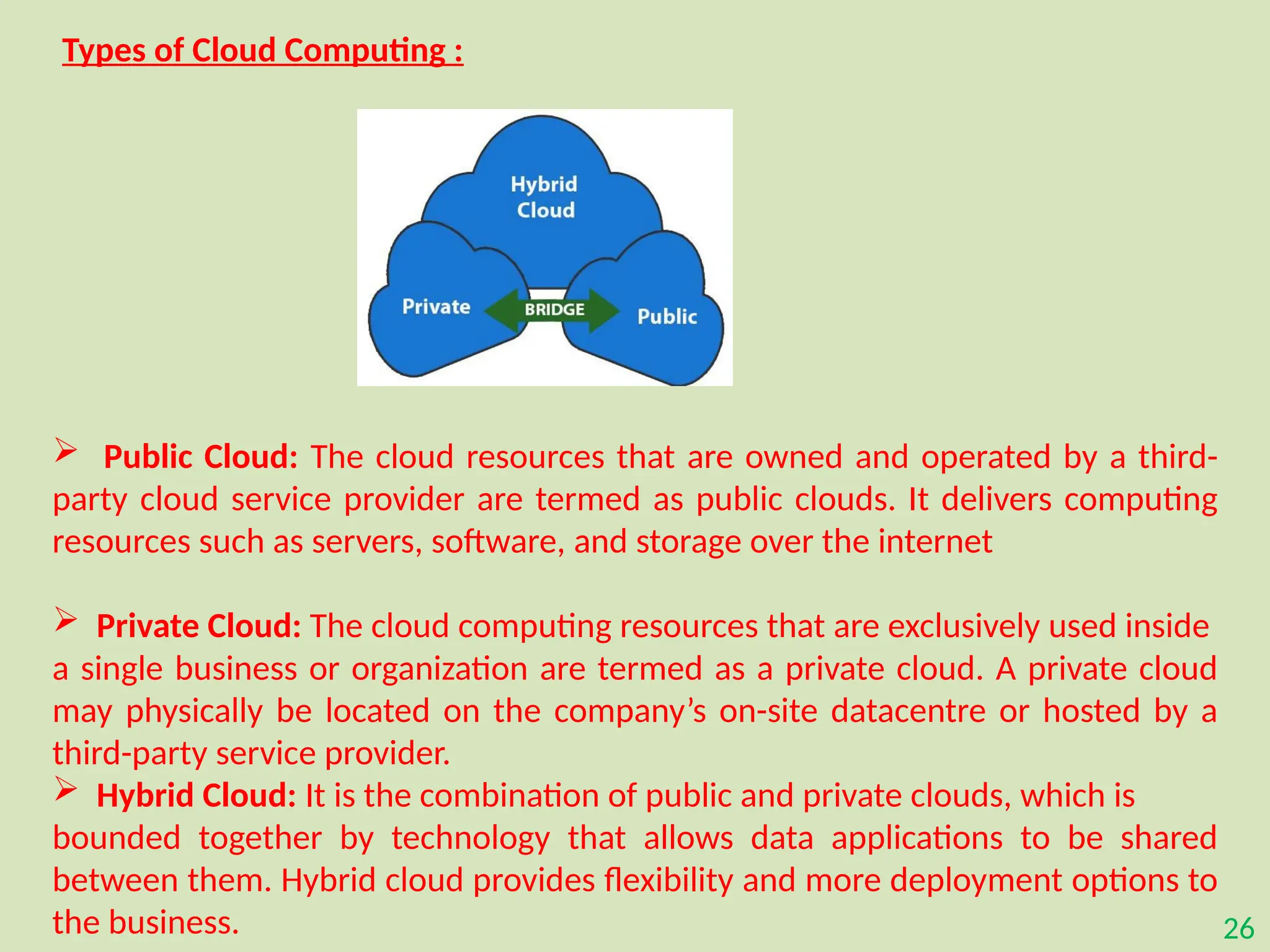
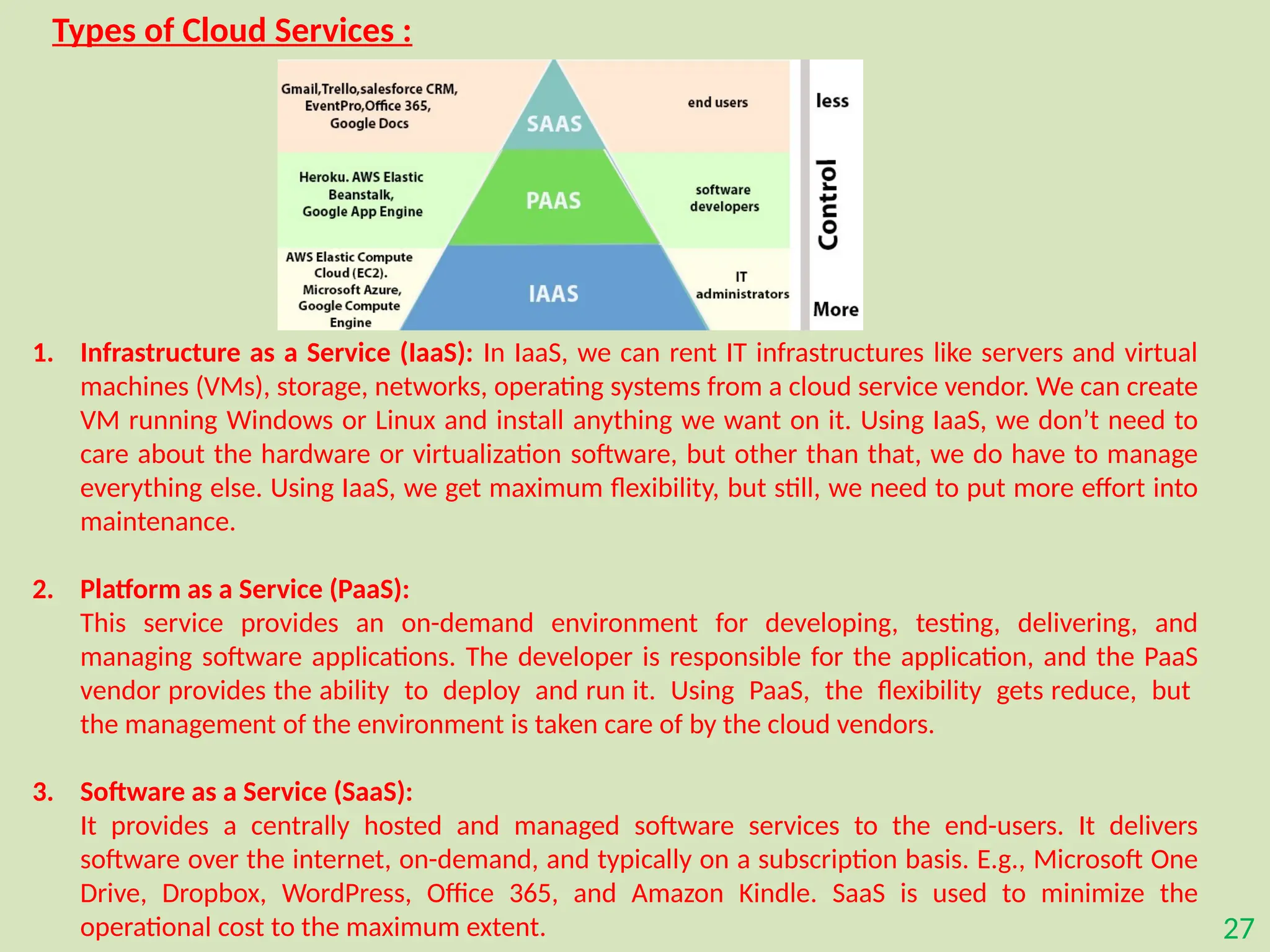
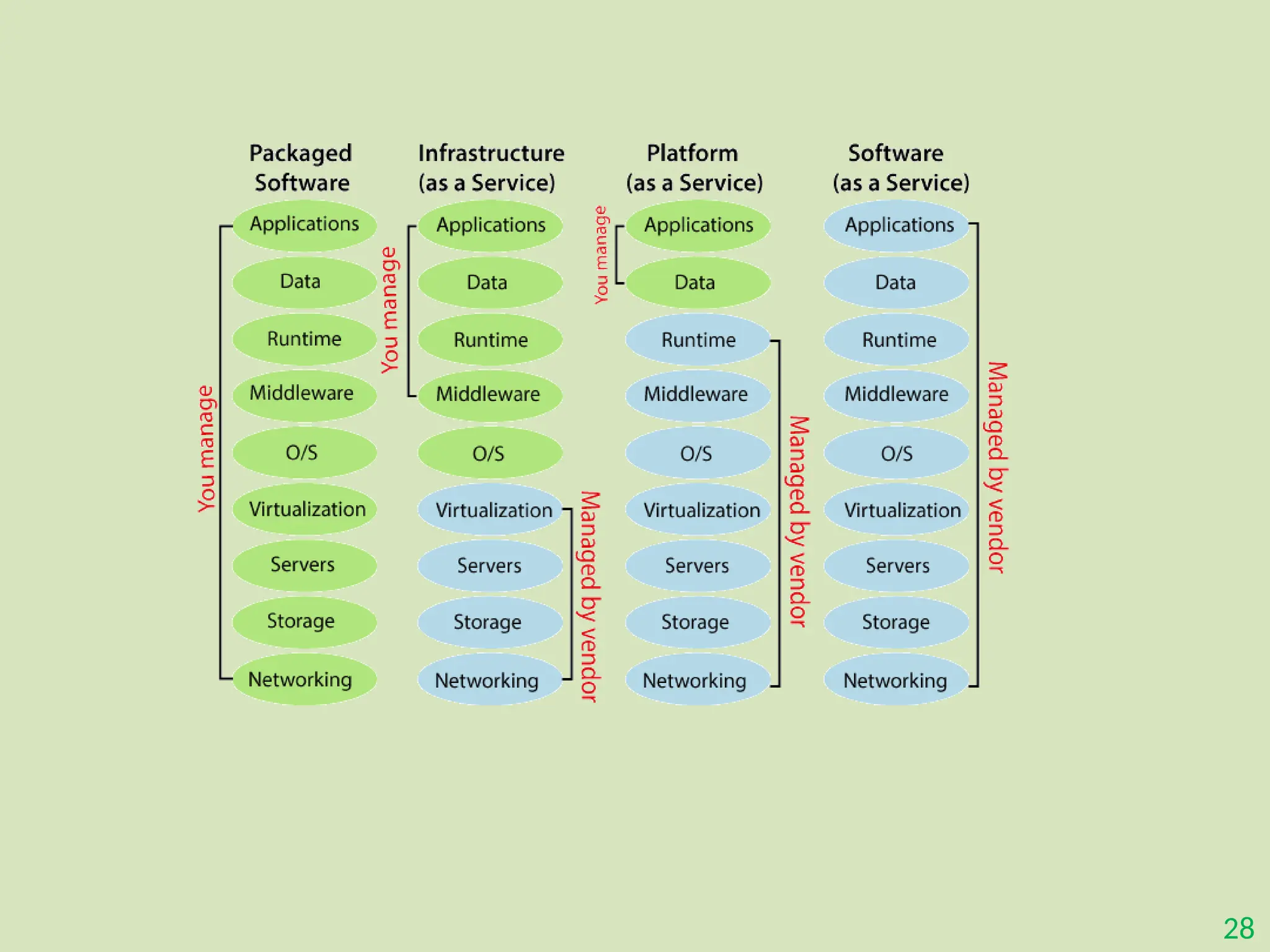
The document provides an overview of the Internet of Things (IoT), describing it as a network of interconnected devices that can collect and exchange data, thereby enhancing everyday life. It outlines the evolution of IoT, its architecture, fundamental components, applications in various sectors such as smart homes and healthcare, as well as the benefits and challenges of IoT technology. Additionally, it introduces cloud computing as a complementary technology that offers scalable resources and services for managing IoT systems.