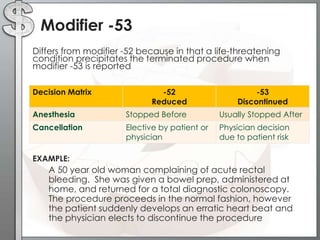
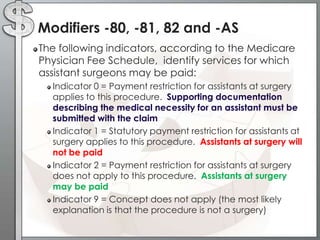
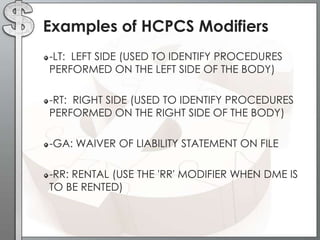
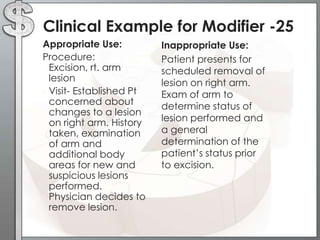
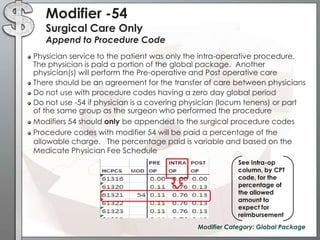
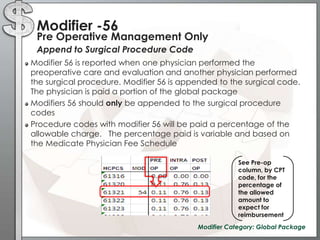
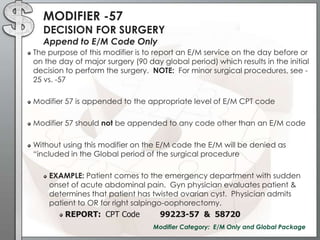
The document outlines the importance of modifiers in coding for medical procedures, explaining their definitions, categories, and appropriate usages to ensure proper reimbursement. Modifiers, which are two-digit codes appended to CPT codes, indicate alterations in service without changing the procedure's definition and help avoid claim denials. Various examples illustrate the correct application of modifiers in specific clinical scenarios, emphasizing the necessity for accurate coding in healthcare billing practices.


















![Modifier -24Example: Patient came in for post-operative visit. He is 12 weeks s/p diskectomy. During the exam, pt c/o severe headaches with visual changes, preceded by an aura. The physician performs an expanded problem focused exam. His impression is migraine with medical decision making of low complexity. Report: CPT Code 99213 [24] Level 3, established patient office visit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theinsandoutsofcodingwithmods-111001135238-phpapp01/85/The-In-s-and-Out-s-of-Coding-with-Modifiers-21-320.jpg)











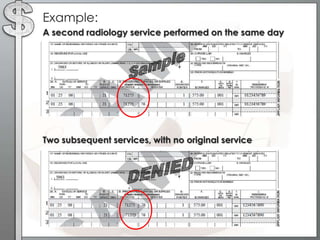

![Modifier -78Unplanned return to the operating/procedure room by the same physician following initial procedure for a related procedure during the postop period Append to Procedure CodeThe purpose of this modifier is to report a related procedure performed during the postoperative period of the initial procedure (unplanned procedure following initial procedure) and requires use of the operating/procedure room. Modifier 78 should not be used if a complication does not require use of the operating/procedure room. Modifier 78 may be used to report procedures performed on the same day (usually in emergency situations) Example: Pt. brought to recovery room S/P abdominal surgery. Dressings became saturated, vital signs were unstable. Pt. brought back to OR for exploration post-op hemorrhage. Report: CPT Codes 35840 [78]Modifier Category: Global Package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theinsandoutsofcodingwithmods-111001135238-phpapp01/85/The-In-s-and-Out-s-of-Coding-with-Modifiers-40-320.jpg)
![Modifier -79Unrelated Procedure/Service by same MD during the post-op periodAppend to Procedure CodeThe purpose of this modifier is to report services during the postoperative period that are unrelated to the original procedure. The procedure must be performed by the same physician, and modifier 79 is appended to the procedure codeClaim should be submitted with a different diagnosis and documentation should the different diagnosis and support medical necessity Example: A repair of femoral hernia [49550 (90 day global)] is performed on Jan. 5th. On Feb. 12th, the same physician performs an appendectomy. Report: CPT Code: 44950 [79]Modifier Category: Global Package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theinsandoutsofcodingwithmods-111001135238-phpapp01/85/The-In-s-and-Out-s-of-Coding-with-Modifiers-41-320.jpg)