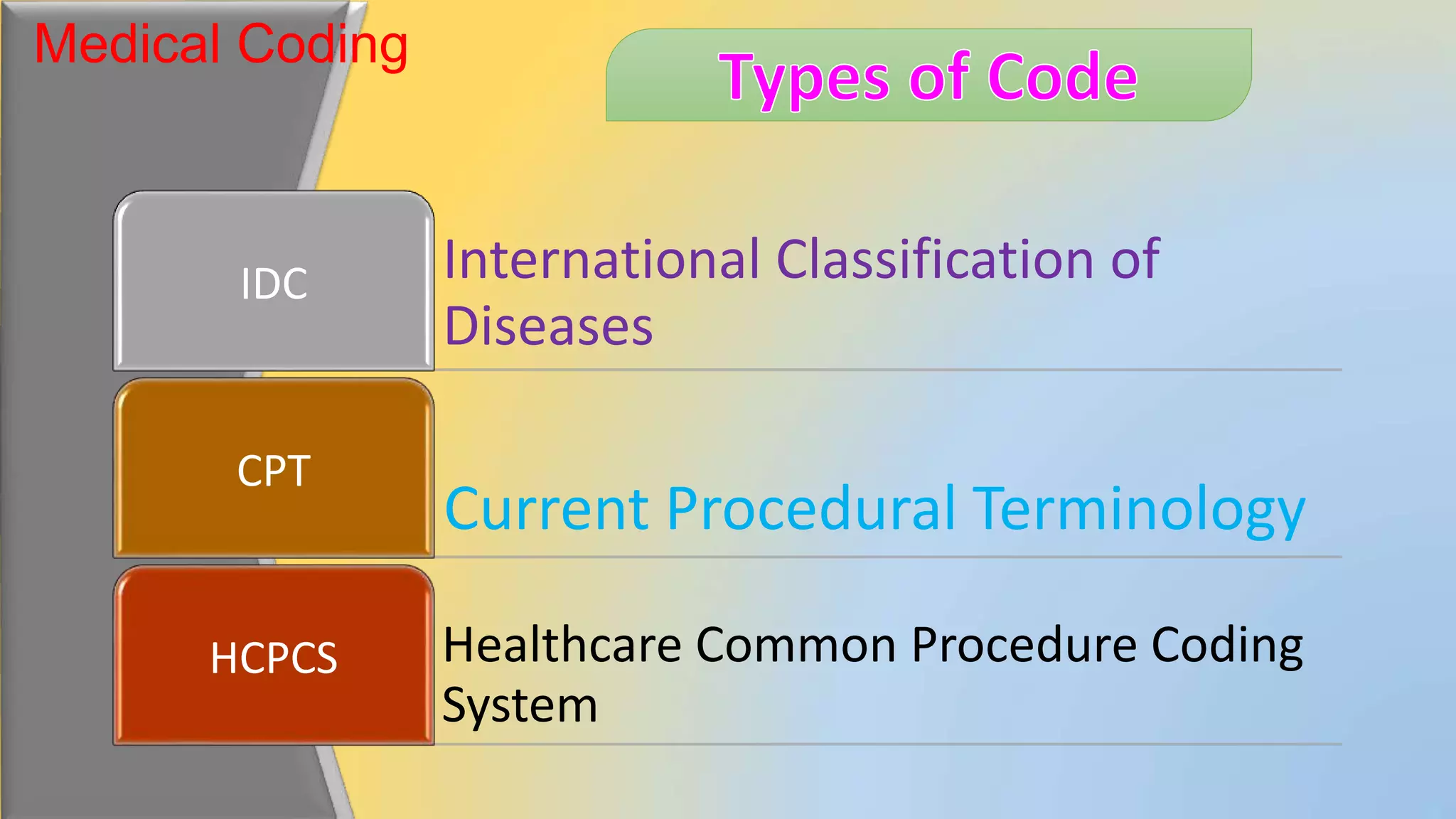
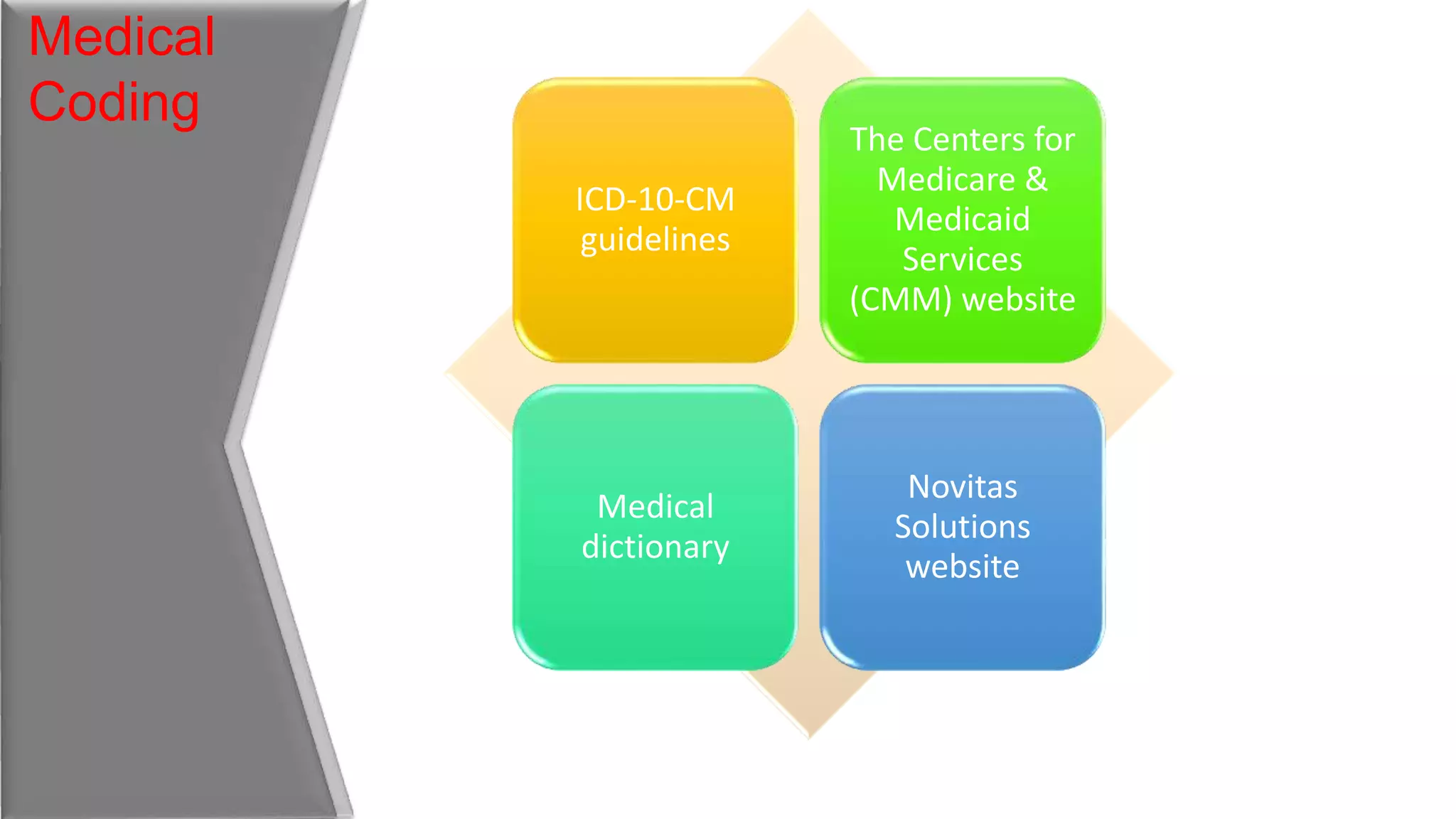
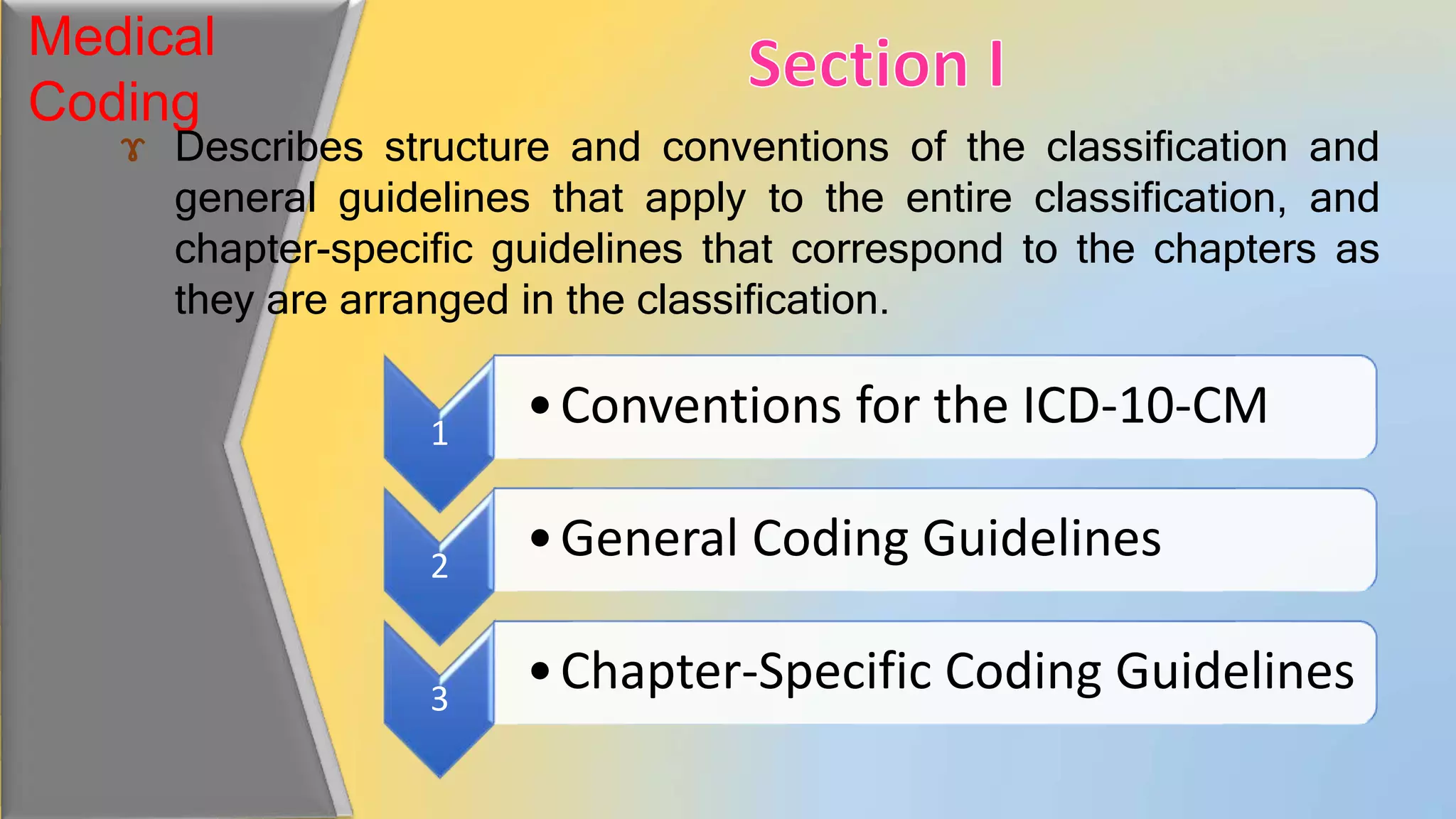
This document provides an overview of common medical coding systems used in the United States. It discusses the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes, and Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS). ICD codes are used for diagnoses. CPT codes document medical procedures and services performed by physicians. HCPCS codes include additional medical items and services not covered by ICD or CPT codes, such as durable medical equipment. The document provides details on the purpose and guidelines for each coding system.