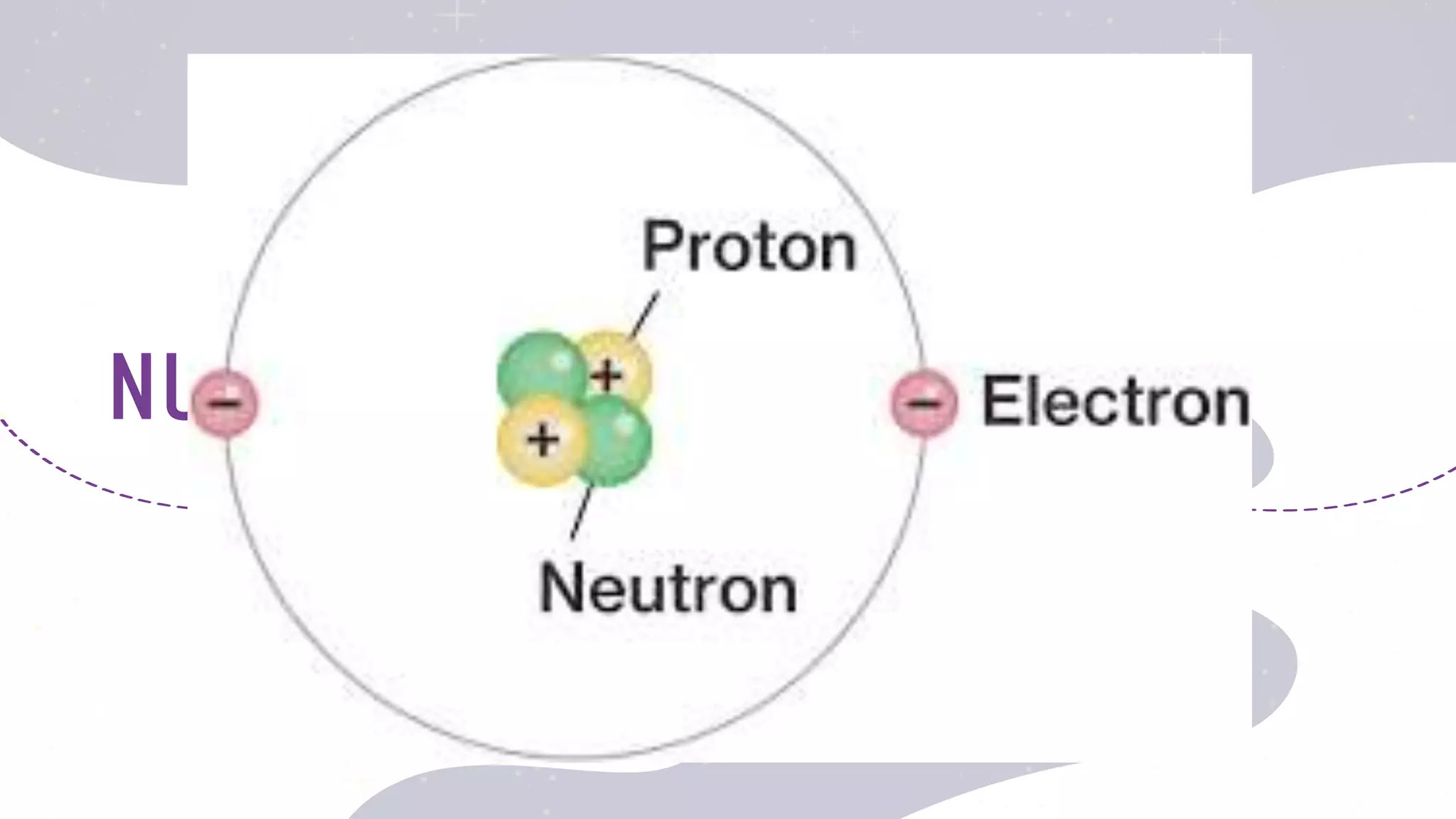
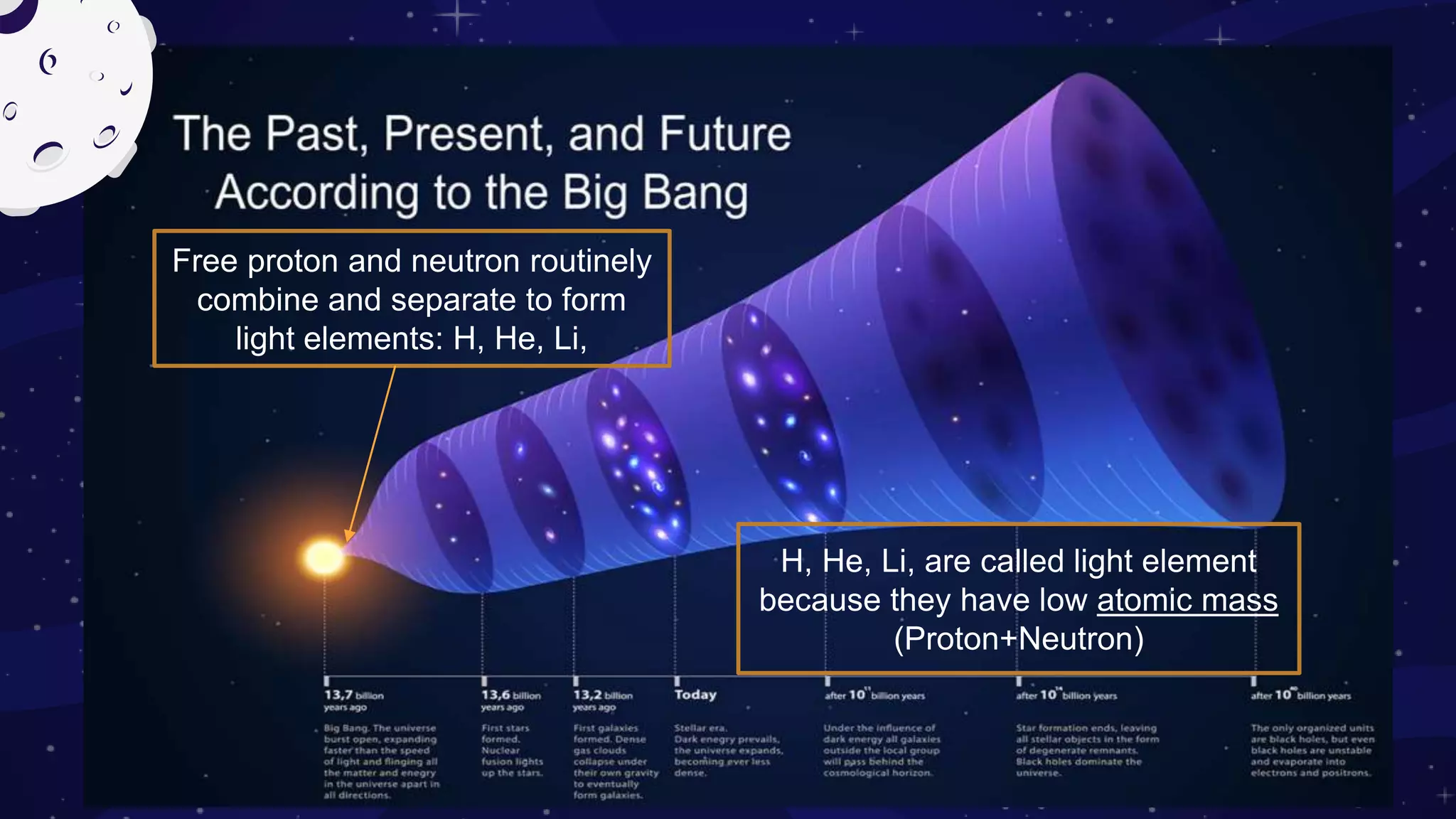
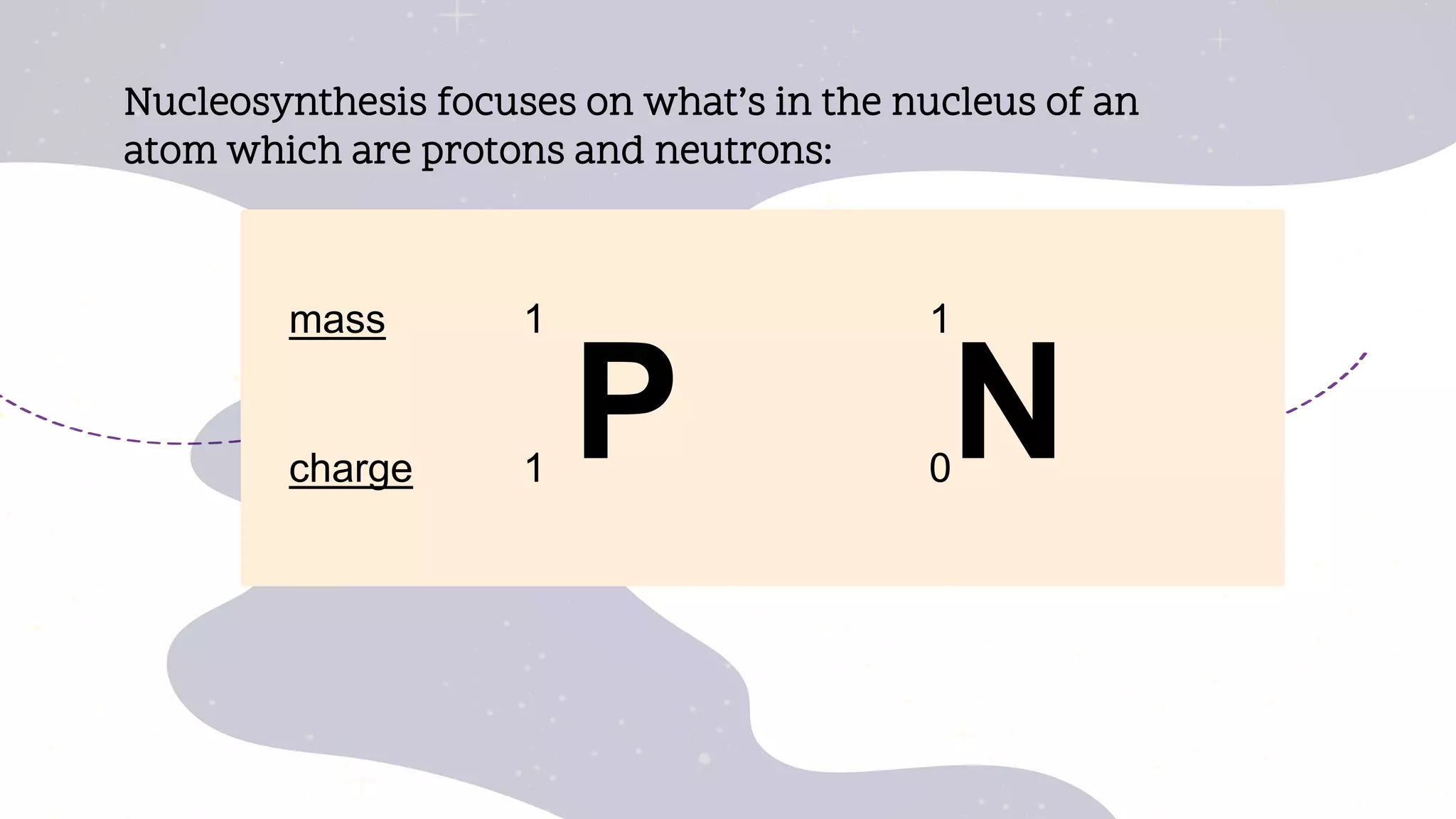
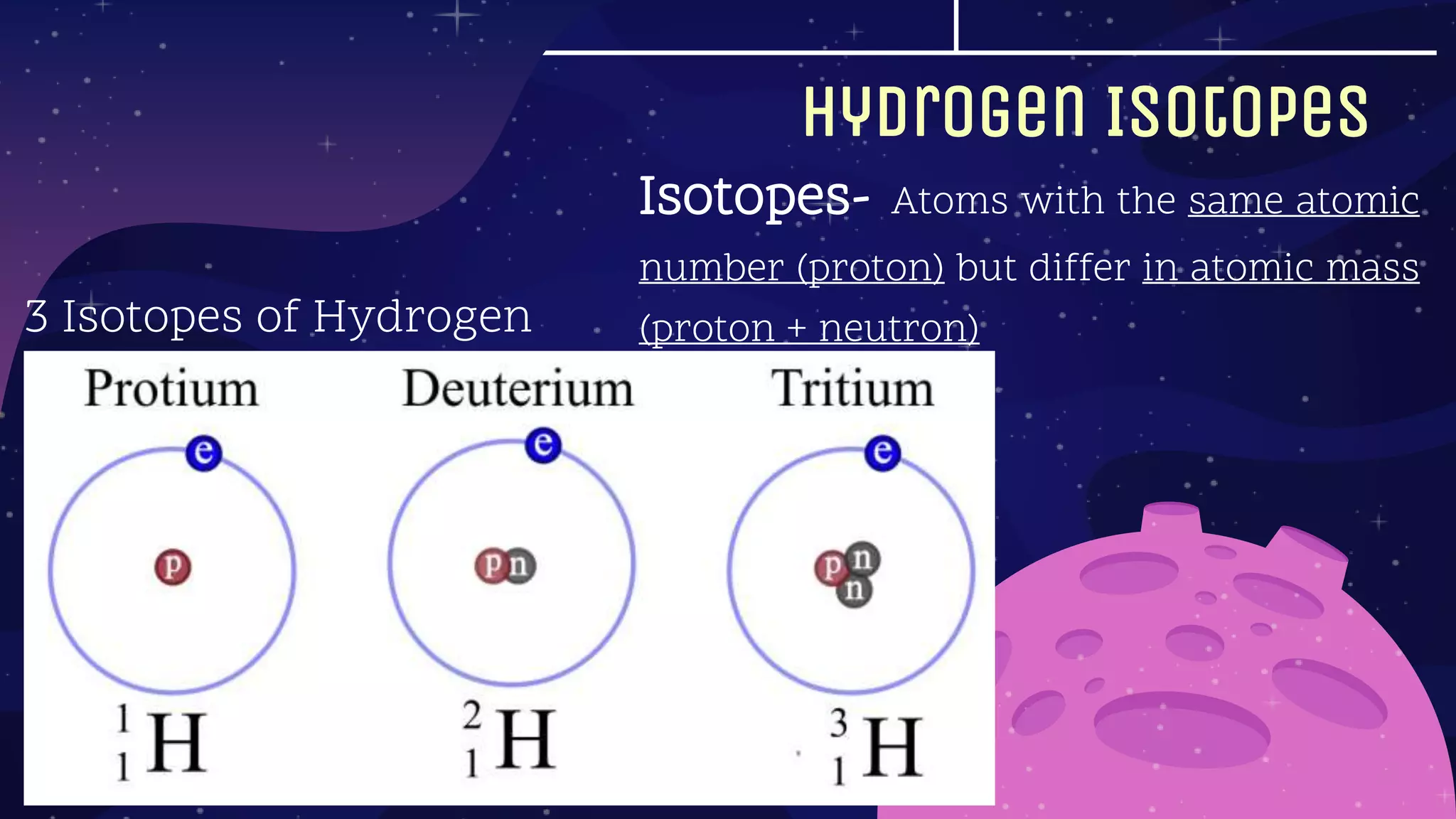
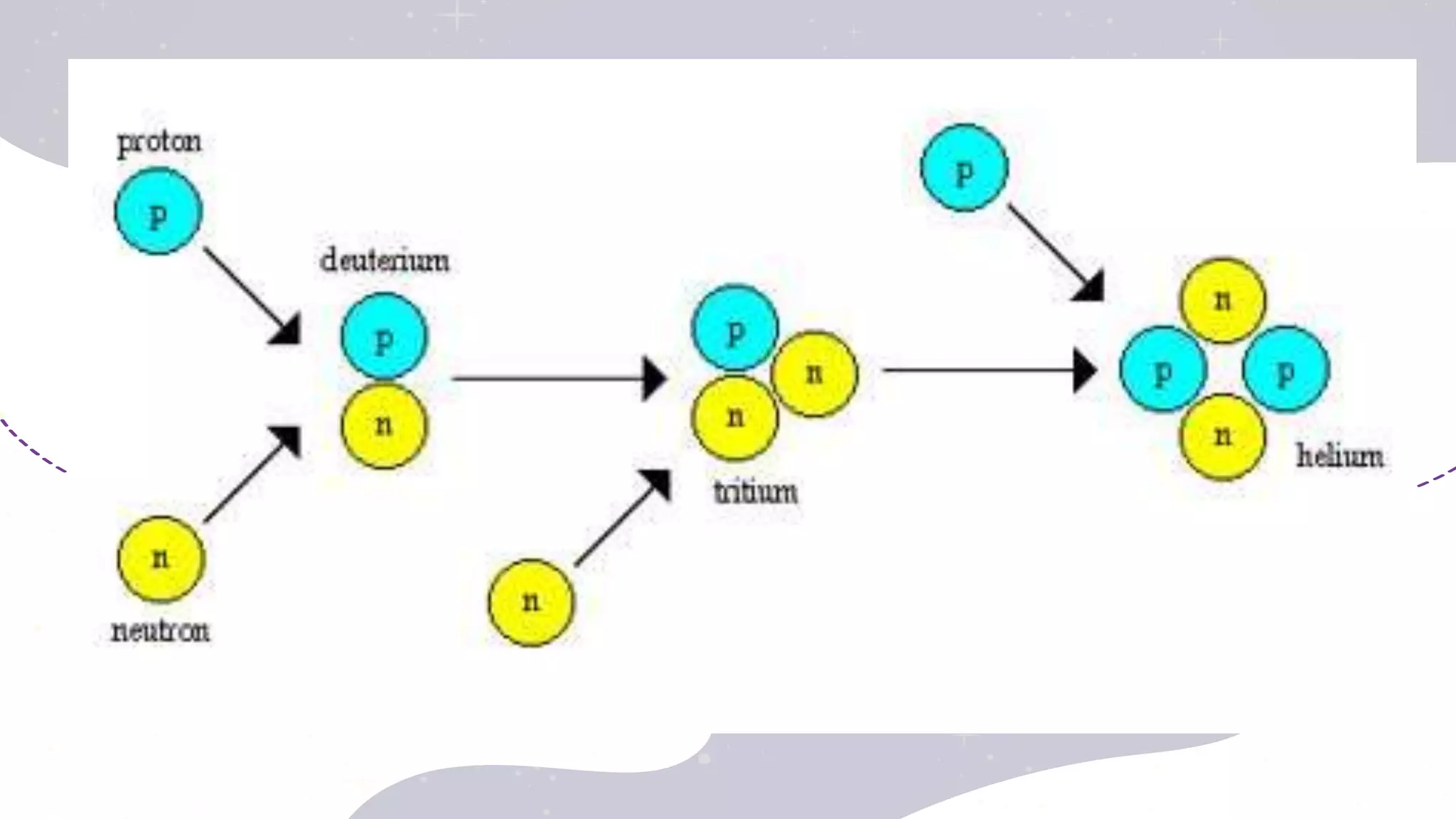
This document provides an overview of the topics to be covered in a physical science course in week 1, including: the formation of elements in the universe through nucleosynthesis; the evolution of ideas about atoms and the elements; how the properties of matter relate to chemical structure; chemistry's role in understanding household products; realizing the Earth is not the center of the universe; why physics laws are believed to be universal; and light acting as both a wave and particle. It further discusses the big bang theory of the universe's formation from an enormous amount of energy packed into a very small, hot, and dense space that then rapidly expanded.